tensorFlow(三)逻辑回归
tensorFlow 基础见前博客
逻辑回归广泛应用在各类分类,回归任务中。本实验介绍逻辑回归在 TensorFlow 上的实现
理论知识回顾
激活函数(activation function):
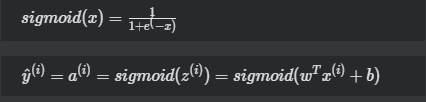
损失函数(cost function):

其中
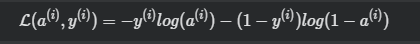
损失函数求偏导(derivative cost function):
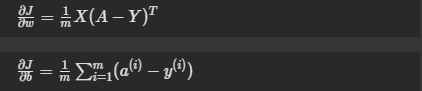
训练模型
- 数据准备首先我们需要先下载MNIST的数据集。使用以下的命令进行下载:
wget https://devlab-1251520893.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
wget https://devlab-1251520893.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
wget https://devlab-1251520893.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
wget https://devlab-1251520893.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
创建代码
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import time
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data MNIST = input_data.read_data_sets("./", one_hot=True) learning_rate = 0.01
batch_size = 128
n_epochs = 25 X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 784])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 10]) w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[784,10], stddev=0.01), name="weights")
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 10]), name="bias") logits = tf.matmul(X, w) + b entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=Y, logits=logits)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(entropy) optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(loss) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
n_batches = int(MNIST.train.num_examples/batch_size)
for i in range(n_epochs):
for j in range(n_batches):
X_batch, Y_batch = MNIST.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, loss_ = sess.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict={ X: X_batch, Y: Y_batch})
print "Loss of epochs[{0}] batch[{1}]: {2}".format(i, j, loss_)
执行结果
Loss of epochs[0] batch[0]: 2.28968191147
Loss of epochs[0] batch[1]: 2.30224704742
Loss of epochs[0] batch[2]: 2.26435565948
Loss of epochs[0] batch[3]: 2.26956915855
Loss of epochs[0] batch[4]: 2.25983452797
Loss of epochs[0] batch[5]: 2.2572259903
......
Loss of epochs[24] batch[420]: 0.393310219049
Loss of epochs[24] batch[421]: 0.309725940228
Loss of epochs[24] batch[422]: 0.378903746605
Loss of epochs[24] batch[423]: 0.472946226597
Loss of epochs[24] batch[424]: 0.259472459555
Loss of epochs[24] batch[425]: 0.290799200535
Loss of epochs[24] batch[426]: 0.256865829229
Loss of epochs[24] batch[427]: 0.250789999962
Loss of epochs[24] batch[428]: 0.328135550022
测试模型
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import time
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data MNIST = input_data.read_data_sets("./", one_hot=True) learning_rate = 0.01
batch_size = 128
n_epochs = 25 X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 784])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [batch_size, 10]) w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[784,10], stddev=0.01), name="weights")
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, 10]), name="bias") logits = tf.matmul(X, w) + b entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=Y, logits=logits)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(entropy) optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(loss) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init) n_batches = int(MNIST.train.num_examples/batch_size)
for i in range(n_epochs):
for j in range(n_batches):
X_batch, Y_batch = MNIST.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, loss_ = sess.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict={ X: X_batch, Y: Y_batch})
print "Loss of epochs[{0}] batch[{1}]: {2}".format(i, j, loss_) n_batches = int(MNIST.test.num_examples/batch_size)
total_correct_preds = 0
for i in range(n_batches):
X_batch, Y_batch = MNIST.test.next_batch(batch_size)
preds = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(X_batch, w) + b)
correct_preds = tf.equal(tf.argmax(preds, 1), tf.argmax(Y_batch, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct_preds, tf.float32)) total_correct_preds += sess.run(accuracy) print "Accuracy {0}".format(total_correct_preds/MNIST.test.num_examples)
执行结果
Accuracy 0.9108
tensorFlow(三)逻辑回归的更多相关文章
- 机器学习 (三) 逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
文章内容均来自斯坦福大学的Andrew Ng教授讲解的Machine Learning课程,本文是针对该课程的个人学习笔记,如有疏漏,请以原课程所讲述内容为准.感谢博主Rachel Zhang 的个人 ...
- 利用Tensorflow实现逻辑回归模型
官方mnist代码: #下载Mnist数据集 import tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist.input_data mnist = input_data.read ...
- tensorflow之逻辑回归模型实现
前面一篇介绍了用tensorflow实现线性回归模型预测sklearn内置的波士顿房价,现在这一篇就记一下用逻辑回归分类sklearn提供的乳腺癌数据集,该数据集有569个样本,每个样本有30维,为二 ...
- tensorflow 实现逻辑回归——原以为TensorFlow不擅长做线性回归或者逻辑回归,原来是这么简单哇!
实现的是预测 低 出生 体重 的 概率.尼克·麦克卢尔(Nick McClure). TensorFlow机器学习实战指南 (智能系统与技术丛书) (Kindle 位置 1060-1061). Kin ...
- 深度学习原理与框架-Tensorflow基本操作-mnist数据集的逻辑回归 1.tf.matmul(点乘操作) 2.tf.equal(对应位置是否相等) 3.tf.cast(将布尔类型转换为数值类型) 4.tf.argmax(返回最大值的索引) 5.tf.nn.softmax(计算softmax概率值) 6.tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(损失值梯度下降器)
1. tf.matmul(X, w) # 进行点乘操作 参数说明:X,w都表示输入的数据, 2.tf.equal(x, y) # 比较两个数据对应位置的数是否相等,返回值为True,或者False 参 ...
- Stanford大学机器学习公开课(三):局部加权回归、最小二乘的概率解释、逻辑回归、感知器算法
(一)局部加权回归 通常情况下的线性拟合不能很好地预测所有的值,因为它容易导致欠拟合(under fitting).如下图的左图.而多项式拟合能拟合所有数据,但是在预测新样本的时候又会变得很糟糕,因为 ...
- 10分钟搞懂Tensorflow 逻辑回归实现手写识别
1. Tensorflow 逻辑回归实现手写识别 1.1. 逻辑回归原理 1.1.1. 逻辑回归 1.1.2. 损失函数 1.2. 实例:手写识别系统 1.1. 逻辑回归原理 1.1.1. 逻辑回归 ...
- 逻辑回归,附tensorflow实现
本文旨在通过二元分类问题.多元分类问题介绍逻辑回归算法,并实现一个简单的数字分类程序 在生活中,我们经常会碰到这样的问题: 根据苹果表皮颜色判断是青苹果还是红苹果 根据体温判断是否发烧 这种答案只有两 ...
- 利用TensorFlow实现多元逻辑回归
利用TensorFlow实现多元逻辑回归,代码如下: import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model impo ...
随机推荐
- svn更新项目之后,项目报错一大堆并且tomcat部署项目时找不到项目
原因是:svn更新项目以后jdk路劲不对,需要使用自己安装的jdk,即可.具体步骤如下 第一步:右击项目-->Build path-->Configure Build path... 第二 ...
- Docker 基础 (一)
为什么要使用 Docker? 作为一种新兴的虚拟化方式,Docker 跟传统的虚拟化方式相比具有众多的优势.首先,Docker 容器的启动可以在秒级实现,这相比传统的虚拟机方式要快得多. 其次,Doc ...
- Matlab的用法总结
1. 对序列进行洗牌 randperm() randperm()产生随机的序列 %if filepaths 是一个5*1的结构体,then cshuffle = randperm(length(fil ...
- vue项目中postcss-pxtorem的使用及webpack中的配置 css中单位px和em,rem的区别
移动手机版要求我们在制作嵌入h5的时候去适配不同的手机.适配有多重模式,有flex.百分比等.字体大小的控制也有px.百分比.rem等单位,webpack中 px转rem. vue项目中postcss ...
- 【winform】listbox 列表
一.Item 一个ListBox是由一个个的Item项组成的 1.向下添加Item lstResult.Items.Add("***" + PostWebRequest(cbxUr ...
- 判断(if)语句
目标 开发中的应用场景 if语句体验 if语句进阶 综合应用 一 开发中的应用场景 转换成代码 判断的定义 如果 条件满足,才能做某件事 如果 条件不满足,就做另外一件事,或者什么也不做 判断语句 又 ...
- Redis学习-常用命令
keys * 返回满足的所有键 exists key 是否存在指定的key,存在返回1,不存在返回0 expire key time 设置指定key的过期时间,可以使用ttl key查看剩余时间 pe ...
- 如何将数据库中的数据导入到Solr中
要使用solr实现网站中商品搜索,需要将mysql数据库中数据在solr中创建索引. 1.需要在solr的schema.xml文件定义要存储的商品Field. 商品表中的字段为: 配置内容是: < ...
- Consul 常用指令
Consul 常用指令 # 通告地址 -advertise # 集群节点之间通信地址 -bind # 设置服务器为bootstrap模式.在一个dc中只有一个server处于bootstrap模式.一 ...
- VMware安装步骤既常见问题
一.vmware出问题? 可以使用vmvare的修复功能. 二.创建虚拟机 1)第一步:选择自定义下一步,典型里是都设定好了的. 2)第二步:选择12默认下一步 3)第三步:可以从光驱中安装,可以从文 ...
