hdu 1885
Key Task
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 990 Accepted Submission(s):
378
already know that it celebrates 300 years of its existence in 2007. Some of the
university buildings are old as well. And the navigation in old buildings can
sometimes be a little bit tricky, because of strange long corridors that fork
and join at absolutely unexpected places.
The result is that some
first-graders have often di?culties finding the right way to their classes.
Therefore, the Student Union has developed a computer game to help the students
to practice their orientation skills. The goal of the game is to find the way
out of a labyrinth. Your task is to write a verification software that solves
this game.
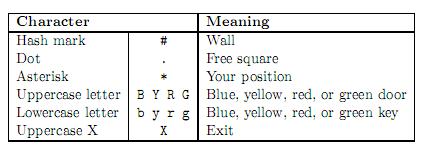
The labyrinth is a 2-dimensional grid of squares, each square
is either free or filled with a wall. Some of the free squares may contain doors
or keys. There are four di?erent types of keys and doors: blue, yellow, red, and
green. Each key can open only doors of the same color.
You can move
between adjacent free squares vertically or horizontally, diagonal movement is
not allowed. You may not go across walls and you cannot leave the labyrinth
area. If a square contains a door, you may go there only if you have stepped on
a square with an appropriate key before.
with a line containing two integer numbers R and C (1 ≤ R, C ≤ 100) specifying
the map size. Then there are R lines each containing C characters. Each
character is one of the following:
Note
that it is allowed to have
- more than one exit,
- no exit at all,
- more doors and/or keys of the same color, and
- keys without corresponding doors and vice versa.
You may assume that
the marker of your position (“*”) will appear exactly once in every map.There is one blank line after each map. The input is terminated by two
zeros in place of the map size.
“Escape possible in S steps.”, where S is the smallest possible number of step
to reach any of the exits. If no exit can be reached, output the string “The
poor student is trapped!” instead.
One step is defined as a movement
between two adjacent cells. Grabbing a key or unlocking a door does not count as
a step.
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<queue>
using namespace std; int n,m;
char a[][];
bool dp[][][(<<)+];
int map1[][]={{,},{,},{,-},{-,}};
struct node
{
int x,y;
int state;
int time;
};
queue<node>Q; int get(char cc)
{
if(cc=='B' || cc=='b')return ;
else if(cc=='Y' || cc=='y')return ;
else if(cc=='R' || cc=='r')return ;
else return ;
}
int bfs(int x,int y)
{
int i,x1,y1,state;
struct node t,cur; t.x=x;
t.y=y;
t.time=;
t.state=;
dp[x][y][]=true;
Q.push(t);
while(!Q.empty())
{
t=Q.front();
Q.pop();
for(i=;i<;i++)
{
x1=t.x+map1[i][];
y1=t.y+map1[i][];
if(x1>=&&x1<n && y1>=&&y1<m && a[x1][y1]!='#')
{
if(a[x1][y1]=='X')
{
printf("Escape possible in %d steps.\n",t.time+);
return ;
}
if(a[x1][y1]>='A'&&a[x1][y1]<='Z')
{
state=(<<get(a[x1][y1]));
if( (t.state&state)==state && dp[x1][y1][t.state]==false)
{
dp[x1][y1][t.state]=true;
cur=t;
cur.time++;
cur.x=x1;
cur.y=y1;
Q.push(cur);
}
}
else if(a[x1][y1]>='a'&&a[x1][y1]<='z')
{
state=(<<get(a[x1][y1]));
cur=t;
cur.state=(cur.state|state);
if(dp[x1][y1][cur.state]==false)
{
dp[x1][y1][cur.state]=true;
cur.x=x1;
cur.y=y1;
cur.time++;
Q.push(cur);
}
}
else if(dp[x1][y1][t.state]==false)
{
dp[x1][y1][t.state]=true;
cur.x=x1;
cur.y=y1;
cur.state=t.state;
cur.time=t.time+;
Q.push(cur);
}
}
}
}
return -;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,x,y,k;
bool cur;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)>)
{
if(n==&&m==)break;
memset(dp,false,sizeof(dp));
while(!Q.empty())
{
Q.pop();
}
for(i=;i<n;i++)
scanf("%s",a[i]);
cur=false;
for(i=;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=;j<m;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]=='*')
{
x=i;
y=j;
}
if(a[i][j]=='X')
cur=true;
}
}
if(cur==false) printf("The poor student is trapped!\n");
else
{
k=bfs(x,y);
if(k==-)printf("The poor student is trapped!\n");
}
}
return ;
}
hdu 1885的更多相关文章
- HDU 1885 Key Task(三维BFS)
题目链接 题意 : 出口不止一个,一共有四种颜色不同的门由大写字母表示,而钥匙则是对应的小写字母,当你走到门前边的位置时,如果你已经走过相应的钥匙的位置这个门就可以走,只要获得一把钥匙就可以开所有同颜 ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885 Key Task Description The Czech Technical Univers ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task(bfs)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885 再贴一个链接http://blog.csdn.net/u013081425/article/details ...
- HDU 1885 Key Task (带门和钥匙的迷宫搜索 bfs+二进制压缩)
传送门: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885 Key Task Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task(bfs+位运算)
题意:矩阵中'#'表示墙,'.'表示通路,要求从起点'*'到达终点'X',途中可能遇到一些门(大写字母),要想经过,必须有对应的钥匙(小写字母).问能否完成,若能,花费的时间是多少. 分析:同hdu ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task (三维bfs)
题目 之前比赛的一个题, 当时是崔老师做的,今天我自己做了一下.... 还要注意用bfs的时候 有时候并不是最先到达的就是答案,比如HDU 3442 这道题是要求最小的消耗血量伤害,但是并不是最先到 ...
- HDU 1885 Key Task (BFS + 状态压缩)
题意:给定一个n*m的矩阵,里面有门,有钥匙,有出口,问你逃出去的最短路径是多少. 析:这很明显是一个BFS,但是,里面又有其他的东西,所以我们考虑状态压缩,定义三维BFS,最后一维表示拿到钥匙的状态 ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task(bfs+状态压缩)
Problem Description The Czech Technical University years of its existence . Some of the university b ...
- HDU 1885 Key Task 国家压缩+搜索
点击打开链接 Key Task Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
随机推荐
- JQuery Mobile - 如何让listview不显示向右的箭头?
先看一下有向右箭头的截图吧 这个listview第二个项目,就有向右的箭头,如果单纯显示具体数据,没有扩展显示的内容,那么这个向右的箭头就是多余的,在这种情况下,最好是去掉这个向右箭头,程序中已经在第 ...
- python salt 实现windows账户自动化
import random import string import json import logging import time import os import sys def usage(): ...
- 压缩VBox虚拟机空间的方法
虚拟机使用久了就会发现虚拟文件越来越大,删除虚拟机中的文件之后物理主机的磁盘空间并不会相应减少,所以实际占用的空间并没有虚拟文件大小那么大,因此我们很有必要进行压缩.不过VirtualBox貌似没 ...
- 基于mongoose 的增删改查操作
无论是基于robomongo 的可视化工具,亦或是基于 mongoose 的函数工具,只要是对 mongodb 的操作,第一步都是开启数据库. 开启mongodb 数据库 进入mongod所在目录 执 ...
- python 爬虫之 正则的一些小例子
什么是正则表达式 正则表达式是对字符串操作的一种逻辑公式,就是 事先定义好的一些特定字符.及这些特定字符的组合,组成一个“规则字符”,这个“规则字符” 来表达对字符的一种过滤逻辑. 正则并不是pyth ...
- Python小白学习之路(十七)—【内置函数二】
序列操作类函数 all() 功能:判断可迭代对象的每个元素是否都为True值注意:If the iterable is empty, return True.(举例3) 回顾:None '' ...
- 【xsy1378】 水题7号 贪心
题目大意:有$m$组约束关系$(x_i,y_i)$,你要构造一个排列,满足数$x_i$出现在数$y_i$前面,请使得这个排列字典序最小,请输出这个排列.无解请输出-1. 数据范围:$n,m≤10^5$ ...
- Supporting Right-to-Left Languages
For the most part iOS supports Right-to-Left (RTL) languages such as Arabic with minimal developer e ...
- ThreadLocal的实现机制
TLS(Thread Local Storage)通过分配更多内存来解决多线程对临界资源访问的互斥问题,即每个线程均自己的临界资源对象, 这样也就不会发生访问冲突,也不需要锁机制控制,比较典型的以空间 ...
- Storm原理及安装
http://my.oschina.net/leejun2005/blog/147607 http://www.storm-geek.com/forum.php http://www.zhangjih ...