Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(六)
在上一篇《Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(五)》中实现了眨眼睛的恐龙,这一篇主要研究恐龙的跳跃。
恐龙的跳跃
游戏通过敲击键盘的Spacebar或者Up来实现恐龙的跳跃。先用一张图来表示整个跳跃的过程:
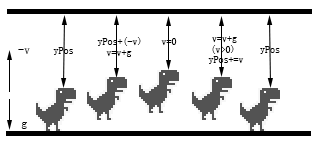
- 首先规定向下为正方向,即重力加速度(g)为正,起跳的速度(v)为负,恐龙距离画布上方的距离为yPos;
- 每一帧动画中,速度都会与重力加速度相加得到新的速度,再用新的速度与yPos相加得到新的yPos,改变恐龙的位置为新的yPos,表现出来为yPos不断减小;
- 当恐龙升至最高点,此时速度为0,并且仍具有向下的重力加速度。
- 速度仍与重力加速度相加得到新的速度,此时速度方向向下,为正值,表现为yPos逐渐增加;
- 落地,并使yPos不超过地面的高度,将速度重置为0,更新状态jumping为false。
下面通过代码来实现。首先注册键盘事件:
document.addEventListener('keydown',onKeyDown);
document.addEventListener('keyup',onKeyUp);
function onKeyDown(e) {
if(keycode.JUMP[e.keyCode]) {
if(!trex.jumping) {
trex.startJump(6);
}
}
}
按下跳跃键后,执行startJump方法:
startJump: function(speed) {
if (!this.jumping) {
//切换到jump状态
this.update(0, Trex.status.JUMPING);
//设置跳跃速度
this.jumpVelocity = this.config.INIITAL_JUMP_VELOCITY - (speed / 10);
this.jumping = true;
this.reachedMinHeight = false;
}
}
之后在每次GameLoop中更新状态:
if (trex.jumping) {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, 600, 150);
trex.updateJump(deltaTime);
}
updateJump: function(deltaTime) {
//帧切换速率
var msPerFrame = Trex.animFrames[this.status].msPerFrame;
//经过的帧数
var framesElapsed = deltaTime / msPerFrame;
//更新y轴坐标
this.yPos += Math.round(this.jumpVelocity * framesElapsed);
//由于速度受重力影响,需要对速度进行修正
this.jumpVelocity += this.config.GRAVITY * framesElapsed;
//达到最小跳跃高度
if (this.yPos < this.minJumpHeight) {
this.reachedMinHeight = true;
}
//达到最大高度后停止跳跃
if (this.yPos < this.config.MAX_JUMP_HEIGHT) {
this.endJump();
}
if (this.yPos > this.groundYPos) {
this.reset();
this.jumpCount++;
}
this.update(deltaTime);
},
update: function(deltaTime, opt_status) {
this.timer += deltaTime;
if (opt_status) {
this.status = opt_status;
this.currentFrame = 0;
//得到对应状态的帧率 e.g. WAITING 1000ms / 3fps = 333ms/fps
this.msPerFrame = Trex.animFrames[opt_status].msPerFrame;
//对应状态的动画帧 e.g. WAITING [44,0]
this.currentAnimFrames = Trex.animFrames[opt_status].frames;
if (opt_status === Trex.status.WAITING) {
//开始计时
this.animStartTime = getTimeStamp();
//设置延时
this.setBlinkDelay();
}
}
//计时器超过一帧的运行时间,切换到下一帧
if (this.timer >= this.msPerFrame) {
this.currentFrame = this.currentFrame === this.currentAnimFrames.length - 1 ? 0 : this.currentFrame + 1;
this.timer = 0;
}
//待机状态
if (this.status === Trex.status.WAITING) {
//执行眨眼动作
this.blink(getTimeStamp());
} else {
this.draw(this.currentAnimFrames[this.currentFrame], 0);
}
}
这样就实现了跳跃的过程。
轻跳
如果持续按住Spacebar或者Up不放,跳跃总是能达到最大高度的,但很多情况下我们只是轻轻敲击一下键盘然后就放手了,这时的游戏表现为恐龙只跳起一个很低的高度,然后开始下落,一般称之为“轻跳”、“小跳”。这看起来是根据按键时长来决定跳跃高度,实现起来有一定的难度,但实际情况却比较简单,只监听键盘的onkeyup事件即可。
function onKeyUp(e) {
if (keycode.JUMP[e.keyCode]) {
trex.endJump();
}
}
当键盘抬起时,执行endJump方法,而endJump方法也十分简单:
endJump: function() {
if (this.reachedMinHeight && this.jumpVelocity < this.config.DROP_VELOCITY) {
this.jumpVelocity = this.config.DROP_VELOCITY;
}
}
首先要判断是否达到了最小跳跃高度,this.reachedMinHeight这个变量非常有用,它避免了游戏角色只跳起数像素然后落地这样的无意义跳跃。此时如果向上的速度仍比较大的话,则强制减小为this.config.DROP_VELOCITY以便能够更快地下落。
下图分别是“大跳”和“小跳”的区别:
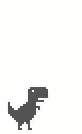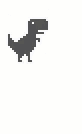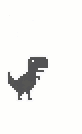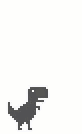

快速落地
在跳跃过程中如果按下了Down键,恐龙会加速下降。
function onKeyDown(e) {
//......
if(keycode.DUCK[e.keyCode]) {//Down
if(trex.jumping) {
trex.setSpeedDrop(); //加速下降
}
}
}
松开键位时取消加速:
function onKeyUp(e) {
//......
if (keycode.DUCK[e.keyCode]) {
trex.speedDrop = false;
}
}
在构造函数中添加setSpeedDrop方法:
setSpeedDrop: function() {
this.speedDrop = true;
this.jumpVelocity = 1; //将速度设置为1,正方向(向下为正方向)
}
还需要对updateJump方法做一些更新:
updateJump:function (deltaTime) {
//......
//更新y轴坐标
if (this.speedDrop) {
//SPEED_DROP_COEFFICIENT为加速倍数,初始设定为3
this.yPos += Math.round(this.jumpVelocity * this.config.SPEED_DROP_COEFFICIENT * framesElapsed);
} else {
this.yPos += Math.round(this.jumpVelocity * framesElapsed);
}
//达到最小跳跃高度
//speedDrop也能触发reachedMinHeight
if (this.yPos < this.minJumpHeight || this.speedDrop) {
this.reachedMinHeight = true;
}
//达到最大高度后停止跳跃
//speedDrop也能触发endJump
if (this.yPos < this.config.MAX_JUMP_HEIGHT || this.speedDrop) {
this.endJump();
}
//......
}
效果如下图所示,在跳跃过程中按住Down,可以发现下落速度比平时快:
闪避
在地面上按住Down键,恐龙会进入闪避状态。首先还是从keydown方法入手:
if (keycode.DUCK[e.keyCode]) {
e.preventDefault();
if (trex.jumping) {
trex.setSpeedDrop();
} else if (!trex.jumping && !trex.ducking) {
trex.setDuck(true); //闪避
}
}
keyup方法取消闪避:
function onKeyUp(e) {
if (keycode.JUMP[e.keyCode]) {
trex.endJump();
}
if (keycode.DUCK[e.keyCode]) {
trex.speedDrop = false;
trex.setDuck(false); //取消闪避
}
}
setDuck方法:
setDuck: function(isDucking) {
if (isDucking && this.status !== Trex.status.DUCKING) {
this.update(0, Trex.status.DUCKING);
this.ducking = true;
} else if (this.status === Trex.status.DUCKING) {
this.update(0, Trex.status.RUNNING);
this.ducking = false;
}
}
最终效果如下(Spacebar或Up跳跃;Down快速下降/闪避):
// this.bumpThreshold ? this.dimensions.WIDTH : 0;
},
draw:function() {
this.ctx.drawImage(imgSprite,
this.sourceXPos[0], this.spritePos.y,
this.dimensions.WIDTH, this.dimensions.HEIGHT,
this.xPos[0],this.yPos,
this.dimensions.WIDTH,this.dimensions.HEIGHT);
this.ctx.drawImage(imgSprite,
this.sourceXPos[1], this.spritePos.y,
this.dimensions.WIDTH, this.dimensions.HEIGHT,
this.xPos[1],this.yPos,
this.dimensions.WIDTH,this.dimensions.HEIGHT);
},
updateXPos:function(pos,increment) {
var line1 = pos,
line2 = pos === 0 ? 1 : 0;
this.xPos[line1] -= increment;
this.xPos[line2] = this.xPos[line1] + this.dimensions.WIDTH;
if(this.xPos[line1] = this.msPerFrame) {
this.currentFrame = this.currentFrame === this.currentAnimFrames.length - 1 ?
0 : this.currentFrame + 1;
this.timer = 0;
}
if (this.speedDrop && this.yPos === this.groundYPos) {
this.speedDrop = false;
this.setDuck(true);
}
},
//开始跳跃
startJump:function (speed) {
if(!this.jumping) {
//切换到jump状态
this.update(0,Trex.status.JUMPING);
//设置跳跃速度
this.jumpVelocity = this.config.INIITAL_JUMP_VELOCITY - (speed / 10);
this.jumping = true;
this.reachedMinHeight = false;
this.speedDrop = false;
}
},
updateJump:function (deltaTime, speed) {
//帧切换速率
var msPerFrame = Trex.animFrames[this.status].msPerFrame;
//经过的帧数
var framesElapsed = deltaTime / msPerFrame;
//更新y轴坐标
if(this.speedDrop) {
this.yPos += Math.round(this.jumpVelocity *
this.config.SPEED_DROP_COEFFICIENT * framesElapsed);
} else {
this.yPos += Math.round(this.jumpVelocity * framesElapsed);
}
//由于速度受重力影响,需要对速度进行修正
this.jumpVelocity += this.config.GRAVITY * framesElapsed;
//达到最小跳跃高度
if (this.yPos this.groundYPos) {
this.reset();
this.jumpCount++;
}
this.update(deltaTime);
},
endJump: function() {
if (this.reachedMinHeight && this.jumpVelocity = this.blinkDelay) {
this.draw(this.currentAnimFrames[this.currentFrame],0);
if (this.currentFrame === 1) {//0闭眼 1开眼
//设置新的眨眼间隔时间
this.setBlinkDelay();
this.animStartTime = time;
}
}
},
draw:function (x,y) {
var sourceX = x;
var sourceY = y;
var sourceWidth = this.ducking && this.status != Trex.status.CRASHED ?
this.config.WIDTH_DUCK : this.config.WIDTH;
var sourceHeight = this.config.HEIGHT;
sourceX += this.spritePos.x;
sourceY += this.spritePos.y;
this.ctx.drawImage(imgSprite,
sourceX, sourceY,
sourceWidth, sourceHeight,
this.xPos, this.yPos,
this.ducking ? this.config.WIDTH_DUCK : this.config.WIDTH, this.config.HEIGHT);
}
};
window.onload = function () {
var h = new HorizonLine(c,spriteDefinition.HORIZON);
trex = new Trex(c,spriteDefinition.TREX);
var startTime = 0;
var deltaTime;
var speed = 3;
(function draw(time) {
gameFrame++;
time = time || 0;
deltaTime = time - startTime;
if(trex.jumping) {
ctx.clearRect(0,0,600,150);
trex.updateJump(deltaTime);
h.update(deltaTime,speed);
} else {
ctx.clearRect(0,0,600,150);
h.update(deltaTime,speed);
trex.update(deltaTime);
}
startTime = time;
requestAnimationFrame(draw,c);
})();
};
// ]]>
Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(六)的更多相关文章
- Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(七)
在上一篇<Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(六)>中研究了恐龙的跳跃过程,这一篇研究恐龙与障碍物之间的碰撞检测. 碰撞盒子 游戏中采用的是矩形(非旋转矩形)碰撞.这类碰撞优点是计算比较 ...
- Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(一)
目录 Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(一)——绘制地面 Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(二)——绘制云朵 Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(三)——昼夜交替 Chrome自带恐龙小游戏 ...
- Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(完)
在上一篇<Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(七)>中研究了恐龙与障碍物的碰撞检测,这一篇主要研究组成游戏的其它要素. 游戏分数记录 如图所示,分数及最高分记录显示在游戏界面的右上角,每 ...
- Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(五)
在上一篇<Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(四)>中实现了障碍物的绘制及移动,从这一篇开始主要研究恐龙的绘制及一系列键盘动作的实现. 会眨眼睛的恐龙 在游戏开始前的待机界面,如果仔细观 ...
- Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(四)
在上一篇<Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(三)>中实现了让游戏昼夜交替,这一篇主要研究如何绘制障碍物. 障碍物有两种:仙人掌和翼龙.仙人掌有大小两种类型,可以同时并列多个:翼龙按高. ...
- Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(三)
在上一篇<Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(二)>中实现了云朵的绘制和移动,这一篇主要研究如何让游戏实现昼夜交替. 昼夜交替的效果主要是通过样式来完成,但改变样式的时机则由脚本控制. ...
- Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(二)
在上一篇<Chrome自带恐龙小游戏的源码研究(一)>中实现了地面的绘制和运动,这一篇主要研究云朵的绘制. 云朵的绘制通过Cloud构造函数完成.Cloud实现代码如下: Cloud.co ...
- WinFom中经典小游戏(含源码)
最近整理了若干经典的小游戏,无聊时可以打发时间.程序本身不大,练手非常不错,主要是GDI编程,主界面地址如下图所示 源码下载方式 1,关注微信公众号:小特工作室(也可直接扫描签名处二维码) 2,发送: ...
- github下载下来的C#控制台小游戏[含源码]
早就听说了github是世界最大的源码库,但自己却不是很懂,今天去研究了下,注册了一个帐号,然后在上面搜索了一下C# game,然后发现有许多的游戏. 随意地选择了一个,感觉比较简单,于是就下载了下来 ...
随机推荐
- Connect(bzoj 1948)
Description 给定一个R*C大小的迷宫,其中R,C均为奇数 迷宫中坐标为两个奇数的点不能通过,称为障碍,迷宫中其他不能通过的点统称为墙壁 坐标为两个偶数的点可以通过,称为房间,迷宫中其他可通 ...
- 如何在win2003下安装sql2008[多次安装sql2008失败者必看]
原文发布时间为:2010-11-02 -- 来源于本人的百度文章 [由搬家工具导入] 如何在win2003下安装sql2008[多次安装sql2008失败者必看] 1. 安装win2003,升级全部补 ...
- repeater做成gridview【更新删除编辑等】
原文发布时间为:2009-06-14 -- 来源于本人的百度文章 [由搬家工具导入] 不多说,不会说。。看我做的范例。。。 http://download.csdn.net/source/138556 ...
- 在android app中使用STL库(转)
1.在jni目录下新建Application.mk; 加入 APP_STL := stlport_static右边的值还可以换成下面几个: system - 使用默认最小的C++运行库,这样生成的应用 ...
- C结构体struct用法小结
结构体和int,float等类型一样是一种常用的类型,它是由各种基本数据类型构成,通常包含有struct关键字,结构体名,结构体成员,结构体变量. 一.结构体定义 通常有3种定义方式,以例子方式表示: ...
- python 代码格式
python 代码格式 Python对代码的缩进要求非常严格,如果不采用合理的代码缩进,将抛出SyntaxError异常 Python语句中一般以新行作为为语句的结束符.但是我们可以使用斜杠( )将一 ...
- AC日记——还是01串 51nod 1396
还是01串 思路: 前缀和: 来,上代码: #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #in ...
- mysql5.6新补充
输入:cd C:\Program Files(x86)\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.6\bin 回车 然后输入:mysqld -install再回车 然后出现 安装成功后,再输入net ...
- Ruby on rails初体验(三)
继体验一和体验二中的内容,此节将体验二中最开始的目标来实现,体验二中已经将部门添加的部分添加到了公司的show页面,剩下的部分是将部门列表也添加到公司的显示页面,整体思路和体验二中相同,但是还是会有点 ...
- 使用PreloadJS加载图片资源
一. 使用createjs里的LoadQueue函数实现异步加载图片,监听加载进度 1.实例对象LoadQueue加载队列对象 var queue = new createjs.LoadQueue(f ...
