hdu 2196(方法1:经典树形DP+方法2:树的直径)
Computer
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 5194 Accepted Submission(s): 2620
school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer's id is
1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each
new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school
are anxious about slow functioning of the net and want to know the
maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e.
length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this
information.
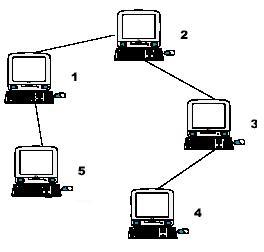
Hint:
the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph,
you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3.
Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is
the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N
(N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with
descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers -
number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected and length of
cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9.
Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
2
3
4
4
///题意:求树上每个点到离它最远的点的距离.
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#define N 10050
using namespace std; struct Edge{
int u,v,w,next;
}edge[*N];
int head[N];
int dp[N][]; ///dp[i][0]代表以i为根子树中的最长路,dp[i][1]代表子树中的次长路,dp[i][2]代表父亲树中的最长路 void addEdge(int u,int v,int w,int &k){
edge[k].u = u,edge[k].v = v,edge[k].w = w;
edge[k].next = head[u],head[u]=k++;
} void dfs(int u,int fa){ ///找子树中的最大值和次大值
for(int k = head[u];k!=-;k=edge[k].next){
int v = edge[k].v;
if(v==fa) continue;
//printf("%d\n",v);
dfs(v,u);
if(dp[u][]<dp[v][]+edge[k].w){
dp[u][] = dp[v][] + edge[k].w;
if(dp[u][]>dp[u][]){
swap(dp[u][],dp[u][]);
}
}
}
}
void dfs1(int u,int fa){///找从父亲延伸过去的最大值
for(int k = head[u];k!=-;k=edge[k].next){
int v = edge[k].v,w = edge[k].w;
if(v==fa) continue;
dp[v][] = max(dp[u][] , dp[v][]+edge[k].w==dp[u][]?dp[u][]:dp[u][]) + edge[k].w;
dfs1(v,u);
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
memset(dp,,sizeof(dp));
int tot=;
for(int u=;u<=n;u++){
int v,w;
scanf("%d%d",&v,&w);
addEdge(u,v,w,tot);
addEdge(v,u,w,tot);
}
dfs(,-);
dfs1(,-);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
printf("%d\n",max(dp[i][],dp[i][]));
}
}
return ;
}
方法二:先对任意一个点进行搜索的到离它最远的端点,这个点必定是树的直径(树的直径指树中的最长路)的其中一个端点,然后以这个端点开始又进行搜索,得到一个离他最远
的店,这个点是直径的另外一个端点,我们在找的时候分别更新所有点到两个端点的距离,对于每个点我们区大值就是结果。
///题意:求树上每个点到离它最远的点的距离.
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define N 10050
using namespace std; struct Edge{
int u,v,w,next;
}edge[*N];
int head[N]; void addEdge(int u,int v,int w,int &k){
edge[k].u = u,edge[k].v = v,edge[k].w = w;
edge[k].next = head[u],head[u]=k++;
}
int dis[N],dis1[N];
int vis[N];
void BFS(int x){
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
queue<int> q;
q.push(x);
vis[x]=;
while(!q.empty()){
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int k=head[t];k!=-;k=edge[k].next){
int v = edge[k].v,w=edge[k].w;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v]=;
q.push(v);
dis[v] =max(dis[v],dis[t]+w);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
memset(dis,,sizeof(dis));
memset(dis1,,sizeof(dis1));
int tot=;
for(int u=;u<=n;u++){
int v,w;
scanf("%d%d",&v,&w);
addEdge(u,v,w,tot);
addEdge(v,u,w,tot);
}
BFS();
int START=,END=;
int len = -;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) {
if(dis[i]>len) {len = dis[i],START = i;}
}
memset(dis,,sizeof(dis));
BFS(START);
len = -;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) {
dis1[i]=dis[i];
if(dis[i]>len) {len = dis[i],END = i;}
}
memset(dis,,sizeof(dis));
BFS(END);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
printf("%d\n",max(dis[i],dis1[i]));
} }
return ;
}
hdu 2196(方法1:经典树形DP+方法2:树的直径)的更多相关文章
- HDU 5293 Tree chain problem 树形dp+dfs序+树状数组+LCA
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5293 题意: 给你一些链,每条链都有自己的价值,求不相交不重合的链能够组成的最大价值. 题解: 树形 ...
- HDU 4616 Game(经典树形dp+最大权值和链)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4616 题意:给出一棵树,每个顶点有权值,还有存在陷阱,现在从任意一个顶点出发,并且每个顶点只能经过一次,如果经过 ...
- hdu 1054 Strategic Game 经典树形DP
Strategic Game Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- hdoj3534(树形dp,求树的直径的条数)
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/HDU-3534 题意:给出一棵树,求树上最长距离(直径),以及这样的距离的条数. 思路:如果只求直径,用两次dfs即可.但是现在要求最 ...
- hdu 4514 并查集+树形dp
湫湫系列故事——设计风景线 Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/32768 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
- HDU 5293 Annoying problem 树形dp dfs序 树状数组 lca
Annoying problem 题目连接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5293 Description Coco has a tree, w ...
- [HDU 5293]Tree chain problem(树形dp+树链剖分)
[HDU 5293]Tree chain problem(树形dp+树链剖分) 题面 在一棵树中,给出若干条链和链的权值,求选取不相交的链使得权值和最大. 分析 考虑树形dp,dp[x]表示以x为子树 ...
- HDU 1561 The more, The Better 经典树形DP
The more, The Better Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Oth ...
- HDU 3534 Tree (经典树形dp)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3534 题意: 给你一棵树,问你有多少对点的距离等于树的直径. 思路: dp[i][0]表示在i的子树中 ...
随机推荐
- Uva 294 Divisors(唯一分解定理)
题意:求区间内正约数最大的数. 原理:唯一分解定义(又称算术基本定理),定义如下: 任何一个大于1的自然数 ,都可以唯一分解成有限个质数的乘积 ,这里 均为质数,其诸指数 是正整数.这样的分解称 ...
- tar 加密压缩和解密解压
加密压缩 tar -czvf - file | openssl des3 -salt -k password -out /path/to/file.tar.gz 解密解压 openssl des3 - ...
- python的运算符及优先级与python的表达式
什么是运算符 >>在Python中,我们对一个或者是多个数字或字符串进行操作的符号 运算符有哪些 >>在Python中我们常见的运算符有:+.-.*./.**.<.> ...
- sqoop工具从oracle导入数据2
sqoop工具从oracle导入数据 sqoop工具是hadoop下连接关系型数据库和Hadoop的桥梁,支持关系型数据库和hive.hdfs,hbase之间数据的相互导入,可以使用全表导入和增量导入 ...
- [洛谷P3521][POI2011]ROT-Tree Rotations
题目大意:给一棵$n(n\leqslant2\times10^5)$个叶子的二叉树,可以交换每个点的左右子树,要求前序遍历叶子的逆序对最少.输出最少的逆序对个数 题解:线段树合并,对于每个节点求出交换 ...
- C++——内存使用
内存分配方式: (1)从静态存储区域分配.内存在程序编译的时候就已经分配好,这块内存在程序的整个运行期间都存在.例如全局变量,static变量. (2)在栈上创建.在执行函数时,函数内局部变量的存储单 ...
- SICAU-OJ: 三角关系
三角关系 题意: 给出两个数n和k,统计(a,b,c)三元组满足(a+b)%k=0,(b+c)%k=0,(a+c)%k=0且1<=a,b,c<=n的数量. 题解: 由(a+b)%k=0,( ...
- ActiveMQ(4) ActiveMQ JDBC 持久化 Mysql 数据库
ActiveMQ 消息持久化机制: ActiveMQ 消息的持久化机制有 JDBC.AMQ.KahaDB 和 LevelDB,其中本示例版本(5.15.2)默认机制为 KahaDB.无论哪种持久化机制 ...
- TypeScript+Vue初体验Demo
github: https://github.com/lanleilin/Typescript-Vue-Demo
- 转:增强学习(二)----- 马尔可夫决策过程MDP
1. 马尔可夫模型的几类子模型 大家应该还记得马尔科夫链(Markov Chain),了解机器学习的也都知道隐马尔可夫模型(Hidden Markov Model,HMM).它们具有的一个共同性质就是 ...
