7. The Singular Value Decomposition(SVD)
7.1 Singular values and Singular vectors
The SVD separates any matrix into simple pieces.
A is any m by n matrix, square or rectangular, Its rank is r.
Choices from the SVD
A^TAv_i = \sigma_i^{2}v_i \\
Av_i = \sigma_i u_i
\]
\(u_i\)— the left singular vectors (unit eigenvectors of \(AA^T\))
\(v_i\)— the right singular vectors (unit eigenvectors of \(A^TA\))
\(\sigma_i\)— singular values (square roots of the equal eigenvalues of \(AA^T\) and \(A^TA\))
The rank of A is equal to numbers of \(\sigma _i\)
example:
\Downarrow \\
AA^T =
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&0 \\ 1&1 \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&1 \\ 0&1 \end{matrix}\right]
=\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&1 \\ 1&2 \end{matrix}\right]
\\
A^TA =
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&1 \\ 0&1 \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&0 \\ 1&1 \end{matrix}\right]
=\left [ \begin{matrix} 2&1 \\ 1&1 \end{matrix}\right]
\\
\Downarrow \\
det(AA^T - I) = 0 \ \quad \ det(A^TA - I) = 0 \\
\lambda_1 = \frac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2} , \sigma_1=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2},
u_1= \frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\sigma_1^2}}\left [ \begin{matrix} 1 \\ \sigma_1 \end{matrix}\right],
v_1= \frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\sigma_1^2}}\left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1 \\ 1 \end{matrix}\right]
\\
\lambda_2 = \frac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2} , \sigma_1=\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2},
u_2= \frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\sigma_2^2}}\left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1 \\ -1 \end{matrix}\right],
v_2= \frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\sigma_2^2}}\left [ \begin{matrix} 1 \\ -\sigma_1 \end{matrix}\right]\\
\Downarrow \\
A =
\left [ \begin{matrix} u_1&u_2 \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1&\\&\sigma_2 \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} v_1^T\\v_2^T \end{matrix}\right]
\\
A\left [ \begin{matrix} v_1&v_2 \end{matrix}\right] =
\left [ \begin{matrix} u_1&u_2 \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1&\\&\sigma_2 \end{matrix}\right]
\]
7.2 Bases and Matrices in the SVD
Keys:
The SVD produces orthonormal basis of \(u's\) and $ v's$ for the four fundamental subspaces.
- \(u_1,u_2,...,u_r\) is an orthonormal basis of the column space. (\(R^m\))
- \(u_{r+1},...,u_{m}\) is an orthonormal basis of the left nullspace. (\(R^m\))
- \(v_1,v_2,...,v_r\) is an orthonormal basis of the row space. (\(R^n\))
- \(v_{r+1},...,u_{n}\) is an orthonormal basis of the nullspace.(\(R^n\))
Using those basis, A can be diagonalized :
Reduced SVD: only with bases for the row space and column space.
\[A = U_r \Sigma_r V_r^T \\
U = \left [ \begin{matrix} u_1&\cdots&u_r\\ \end{matrix}\right] ,
\Sigma_r = \left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1&&\\&\ddots&\\&&\sigma_r \end{matrix}\right],
V_r^T=\left [ \begin{matrix} v_1\\ \vdots \\ v_r \end{matrix}\right] \\
\Downarrow \\
A = \left [ \begin{matrix} u_1&\cdots&u_r\\ \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1&&\\&\ddots&\\&&\sigma_r \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} v_1\\ \vdots \\ v_r \end{matrix}\right] \\
= u_1\sigma_1v_{1}^T + u_2\sigma_2v_{2}^T + \cdots + u_r\sigma_rv_r^T
\]Full SVD: include four subspaces.
\[A = U \Sigma V^T \\
U = \left [ \begin{matrix} u_1&\cdots&u_r&\cdots&u_n\\ \end{matrix}\right] ,
\Sigma_r = \left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1&&\\&\ddots&\\&&\sigma_r \\ &&&\ddots \\ &&&&\sigma_n \end{matrix}\right],
V^T=\left [ \begin{matrix} v_1\\ \vdots \\ v_r \\ \vdots \\ v_m \end{matrix}\right] \\
\Downarrow \\
A = \left [ \begin{matrix} u_1&\cdots&u_r&\cdots&u_n\\ \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1&&\\&\ddots&\\&&\sigma_r \\ &&&\ddots \\ &&&&\sigma_n \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} v_1\\ \vdots \\ v_r \\ \vdots \\ v_m \end{matrix}\right] \\
= u_1\sigma_1v_{1}^T + u_2\sigma_2v_{2}^T + \cdots + u_r\sigma_rv_r^T\cdots + u_n\sigma_n v_n^{T} + \cdots + u_m\sigma_mv_m^T
\]example: \(A=\left [ \begin{matrix} 3&0 \\ 4&5 \end{matrix}\right]\), r=2
\[A^TA =\left [ \begin{matrix} 25&20 \\ 20&25 \end{matrix}\right],
AA^T =\left [ \begin{matrix} 9&12 \\ 12&41 \end{matrix}\right] \\
\lambda_1 = 45, \sigma_1 = \sqrt{45},
v_1 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1 \\ 1 \end{matrix}\right],
u_1 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1 \\ 3 \end{matrix}\right]\\
\lambda_2 = 5, \sigma_2 = \sqrt{5} ,
v_2 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}
\left [ \begin{matrix} -1 \\ 1 \end{matrix}\right],
u_2 = \frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}
\left [ \begin{matrix} -3 \\ 1 \end{matrix}\right]\\
\Downarrow \\
U = \frac{1}{\sqrt{10}}
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&-3 \\ 3&1 \end{matrix}\right],
\Sigma = \left [ \begin{matrix} \sqrt{45}& \\ &\sqrt{5} \end{matrix}\right],
V = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&-1 \\ 1&1 \end{matrix}\right]
\]
7.3 The geometry of the SVD
- \(A = U\Sigma V^T\) factors into (rotation)(stretching)(rotation), the geometry shows how A transforms vectors x on a circle to vectors Ax on an ellipse.
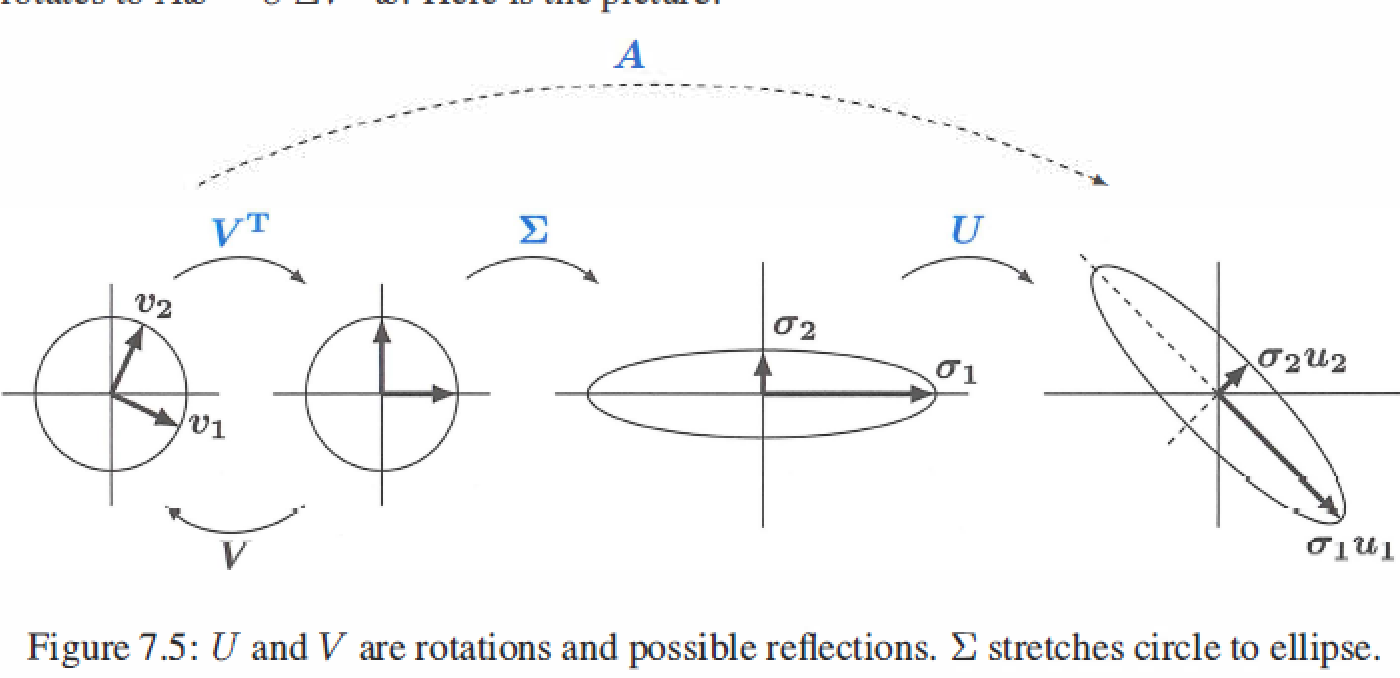
Polar decomposition factors A into QS : rotation \(Q=UV^T\) times streching \(S=V \Sigma V^T\).
\[V^TV = I \\
A = U\Sigma V^T = (UV^T)(V\Sigma V^T) = (Q)(S)
\]Q is orthogonal and inclues both rotations U and \(V^T\), S is symmetric positive semidefinite and gives the stretching directions.
If A is invertible, S is positive definite.
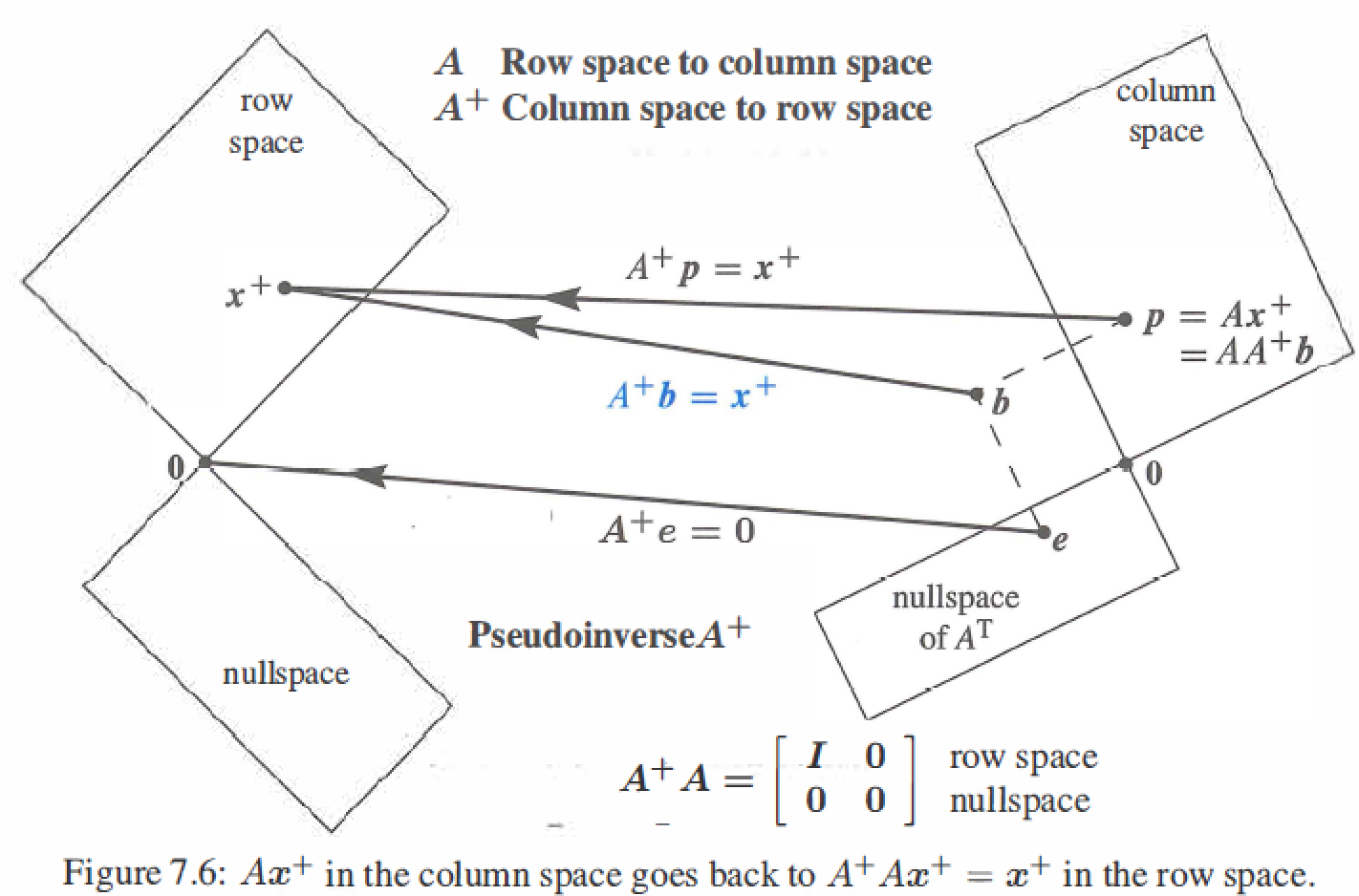
The Pseudoinverse \(A^{+}: AA^{+}=I\)
\(Av_i=\sigma_iu_i\) : A multiplies \(v_i\) in the row space of A to give \(\sigma_i u_i\) in the column space of A.
If \(A^{-1}\) exists, \(A^{-1}u_i=\frac{v_i}{\sigma}\) : \(A^{-1}\) multiplies \(u_i\) in the row space of \(A^{-1}\) to give \(\sigma_i u_i\) in the column space of \(A^{-1}\), \(1/\sigma_i\) is singular values of \(A^{-1}\).
Pseudoinverse of A: if \(A^{-1}\) exists, then \(A^{+}\) is the same as \(A^{-1}\)
\[A^{+} = V \Sigma^{+}U^{T} = \left [ \begin{matrix} v_1&\cdots&v_r&\cdots&v_n\\ \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} \sigma_1^{-1}&&\\&\ddots&\\&&\sigma_r^{-1} \\ &&&\ddots \\ &&&&\sigma_n^{-1} \end{matrix}\right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} u_1\\ \vdots \\ u_r \\ \vdots \\ u_m \end{matrix}\right] \\
\]
7.4 Principal Component Analysis ( PCA by the SVD)
PCA gives a way to understand a data plot in dimension m, applications mostly are human genetics \ face recognition\ finance \ model order reduction (computation) .
The sample covariance matrix \(S=AA^T/(n-1)\)
The crucial connection to linear algebra is in the singular values and singular vectors of A, which comes from the eigenvalues \(\lambda=\sigma^2\) and the eigenvectors u of the sample covariance matrix \(S=AA^T/(n-1)\)
The total variance in the data is the sum of all eigenvalues and of sample variances \(s^2\) :
\[T = \sigma_1^2 + \cdots + \sigma_m^2 = s_1^2 + \cdots + s_m^2 = trace(diagonal \ \ sum)
\]The first eigenvector \(u_1\) of S points in the most significant direction of the data.That direction accounts for a fraction \(\sigma_1^2/T\) of the total variance.
The next eigenvectors \(u_2\) (orthogonal to \(u_1\)) accounts for a small fraction \(\sigma_2^2/T\).
Stop when those fractions are small. You have the R directions that explain most of the data.The n data points are very near an R-dimensional subspace with basis \(u_1, \cdots, u_R\), which are the principal components.
R is the "effective rank" of A. The true rank r is probably m or n : full rank matrix.
example: \(A = \left[ \begin{matrix} 3&-4&7&-1&-4&-3 \\ 7&-6&8&-1&-1&-7 \end{matrix} \right]\) has sample covariance \(S=AA^T/5 = \left [ \begin{matrix} 20&25 \\ 25&40 \end{matrix}\right]\)
The eigenvalues of S are 57 and 3,so the first rank one piece \(\sqrt{57}u_1v_1^T\) is much larger than the second piece \(\sqrt{3}u_2v_2^T\).
The leading eigenvector \(u_1 = (0.6,0.8)\) shows the direction that you see in the scatter graph.
The SVD of A (centered data) shows the dominant direction in the scatter plot.
The second eigenvector \(u_2\) is perpendicular to \(u_1\). The second singular value \(\sigma_2=\sqrt{3}\) measures the spread across the dominant line.

7. The Singular Value Decomposition(SVD)的更多相关文章
- [Math Review] Linear Algebra for Singular Value Decomposition (SVD)
Matrix and Determinant Let C be an M × N matrix with real-valued entries, i.e. C={cij}mxn Determinan ...
- SVD singular value decomposition
SVD singular value decomposition https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Singular_value_decomposition 奇异值分解在统计 ...
- 奇异值分解(We Recommend a Singular Value Decomposition)
奇异值分解(We Recommend a Singular Value Decomposition) 原文作者:David Austin原文链接: http://www.ams.org/samplin ...
- We Recommend a Singular Value Decomposition
We Recommend a Singular Value Decomposition Introduction The topic of this article, the singular val ...
- 【转】奇异值分解(We Recommend a Singular Value Decomposition)
文章转自:奇异值分解(We Recommend a Singular Value Decomposition) 文章写的浅显易懂,很有意思.但是没找到转载方式,所以复制了过来.一个是备忘,一个是分享给 ...
- [转]奇异值分解(We Recommend a Singular Value Decomposition)
原文作者:David Austin原文链接: http://www.ams.org/samplings/feature-column/fcarc-svd译者:richardsun(孙振龙) 在这篇文章 ...
- [转载]We Recommend a Singular Value Decomposition
原文:http://www.ams.org/samplings/feature-column/fcarc-svd Introduction The topic of this article, the ...
- Singular value decomposition
SVD is a factorization of a real or complex matrix. It has many useful applications in signal proces ...
- 关于SVD(Singular Value Decomposition)的那些事儿
SVD简介 SVD不仅是一个数学问题,在机器学习领域,有相当多的应用与奇异值都可以扯上关系,比如做feature reduction的PCA,做数据压缩(以图像压缩为代表)的算法,还有做搜索引擎语义层 ...
- 从矩阵(matrix)角度讨论PCA(Principal Component Analysis 主成分分析)、SVD(Singular Value Decomposition 奇异值分解)相关原理
0. 引言 本文主要的目的在于讨论PAC降维和SVD特征提取原理,围绕这一主题,在文章的开头从涉及的相关矩阵原理切入,逐步深入讨论,希望能够学习这一领域问题的读者朋友有帮助. 这里推荐Mit的Gilb ...
随机推荐
- SUB-LVDS 与LVDS 互联
SUB-LVDS 与 LVDS介绍 电气规范 今天有同学问SUB-LVDS输出是否能接到LVDS输入上,以前没用过SUB-LVDS,一起学习一下. Sub-LVDS is a differential ...
- 从零开始学Spring Boot系列-返回json数据
欢迎来到从零开始学Spring Boot的旅程!在Spring Boot中,返回JSON数据是很常见的需求,特别是当我们构建RESTful API时.我们对上一篇的Hello World进行简单的修改 ...
- mongo重启、远程连接
1.查看当前mongo启动进程 ps -ef | grep mongo 2.修改mongo启动远程连接配制文件 vi /etc/mongod.conf 将 bind_ip=127.0.0.1 这一行注 ...
- 【Azure 存储服务】.NET7.0 示例代码之上传大文件到Azure Storage Blob (二)
问题描述 在上一篇博文([Azure 存储服务].NET7.0 示例代码之上传大文件到Azure Storage Blob (一):https://www.cnblogs.com/lulight/p/ ...
- linux服务器文件实时同步
linux服务器文件实时同步 1 背景说明 在做系统集群部署时,涉及到两个或多个服务器之间文件同步.在软件层面linux服务环境找到以下两种同步方式 利用linux NFS功能将网络共享文件挂载成本地 ...
- Glide源码解析四(解码和转码)
本文基于Glide 4.11.0 Glide加载过程有一个解码过程,比如将url加载为inputStream后,要将inputStream解码为Bitmap. 从Glide源码解析一我们大致知道了Gl ...
- 将Abp移植进.NET MAUI项目(二):配置与基类编写
因为我们要做一个数据持久化型的小应用,所以在完成Abp功能的集成后,我们需要做数据库相关的配置工作 配置数据库 在MauiBoilerplate.Core项目中,添加两个实体类: 我们简单的写一个 ...
- Zabbix Agent item监控项讲解
前言 agent与snmp是Zabbix两种重要的监控方式,这一期主要介绍Zabbix Agent item监控项..Zabbix agent分为主动代理.被动代理,配置item类型时,可以选择需要的 ...
- 关于vue.js:iview-Bug-5114在iview的Poptip气泡提示内调用DatePicker出现遮挡或同时关闭窗口等冲突问题[转]
转自:https://lequ7.com/guan-yu-vuejsiviewbug5114-zai-iview-de-poptip-qi-pao-ti-shi-nei-diao-yong-datep ...
- ulimit.conf中soft和hard区别及常用配置
在Linux中,ulimit命令用于限制用户对shell资源的访问,包括进程数.文件打开数等.这些限制可以分为软限制(soft limit)和硬限制(hard limit). 软限制(soft lim ...
