DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.10

用到的性质

上代码:
n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)) + j * rand(1,length(n));
k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , [0,pi] axis divided into 101 points.
X = x * (exp(-j*pi/100)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of x % conjugation property
y = conj(x); % signal conjugation
Y = y * (exp(-j*pi/100)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of y magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X);
magY = abs(Y); angY = angle(Y); realY = real(Y); imagY = imag(Y); %verification
Y_check = conj(fliplr(X)); % conj(X(-w)) DTFT flip first, then conjugation
error = max(abs(Y-Y_check)); % Difference figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'x & y sequence')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); stem(n,real(x)); title('x sequence Real Part'); xlabel('n'); ylabel('Real x(n)'); grid on;
subplot(2,2,2); stem(n,imag(x)); title('x sequence Imaginary Part'); xlabel('n'); ylabel('Imaginary x(n))'); grid on;
subplot(2,2,3); stem(n,real(y)); title('y sequence Real Part'); xlabel('n'); ylabel('Real y(n)'); grid on;
subplot(2,2,4); stem(n,imag(y)); title('y sequence Imaginary Part'); xlabel('n'); ylabel('Imaginary y(n))'); grid on; %% ----------------------------------------------------------------
%% START Graphical verification
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'X Y compare theirs Magnitude and Angle');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
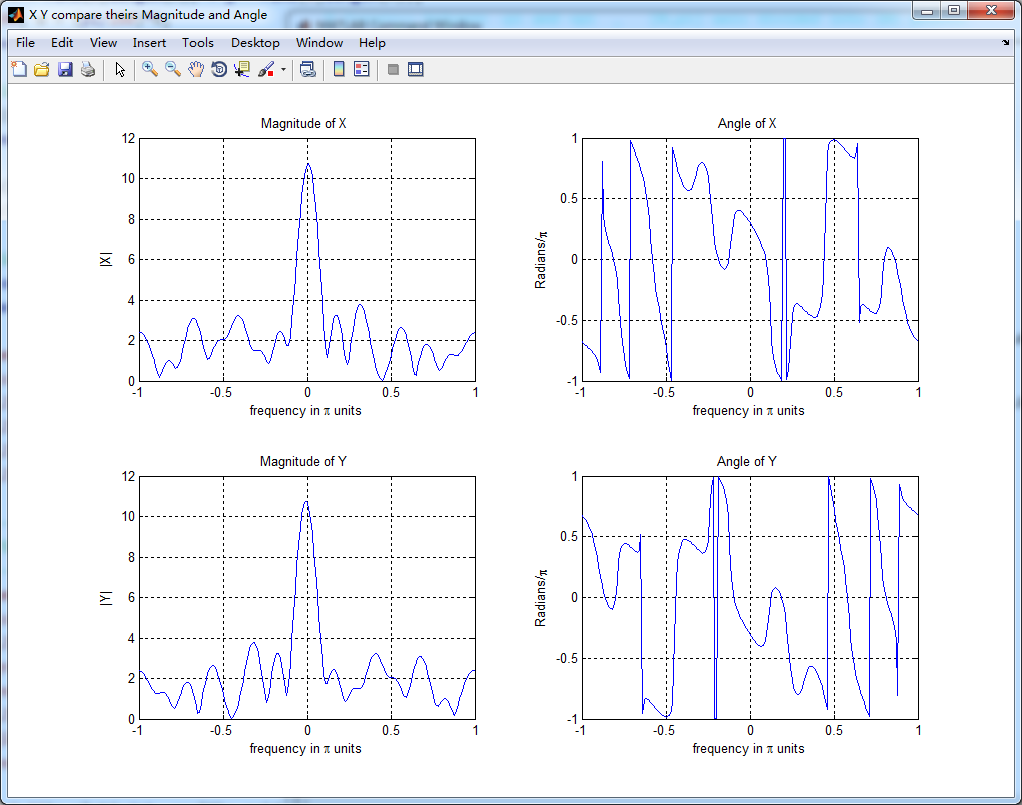
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX); grid on; axis([-1,1,0,12]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|X|'); title('Magnitude of X ');
subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi,angX/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); title('Angle of X '); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi,magY); grid on; axis([-1,1,0,12]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|Y|'); title('Magnitude of Y ');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi,angY/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); title('Angle of Y '); %% ----------------------------------------------------------------
%% END Graphical verification
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果:
DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.10的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
用到的性质 代码: n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.11
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi an ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.8
代码: x = rand(1,11); n = 0:10; k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. X = ...
随机推荐
- JSON数据格式
JSON 数据格式 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,这些特性使JSON成为理想的数据交换语言.易于人 ...
- jquery.dataTable分页
jsp页面,引入几个js <link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="/library/css/b ...
- LeetCode 191 Number of 1 Bits
Problem: Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has ( ...
- Jquery的鼠标移动上去显示div,鼠标离开的时候隐藏div效果
有时候我们需要这个效果:当鼠标放上去的时候显示一个div,当鼠标移走的时候就将div隐藏了.代码如下,记得引入Jquyer库.(当鼠标移动到id=menu的div上的时候,显示id=list的div, ...
- yii和wp做博客
第一步,安装yii和wp: 第二步,创建protected/components/ExceptionHandler.php文件 <?php class ExceptionHandler { pu ...
- 由浅入深剖析.htaccess
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/21aspnet/article/details/6908025 [-] htaccess文件使用前提 htaccess基本语法介绍 现学现用学习正则表 ...
- osg 纹理访问器
#include<osgViewer/Viewer> #include<osg/Node>#include<osg/Geode>#include<osg/Gr ...
- C#复制、粘贴文本信息到剪贴板
复制:private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) { // Takes the selected text from a ...
- 在程序中使用geos.dll
1 在项目->property->configuration properties->c/c++->general->additional include directo ...
- 最简单的Web服务器
//读取浏览器发过来的内容Socket serverSocket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, Protoco ...
