Codeforces 85D Sum of Medians
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
In one well-known algorithm of finding the k-th order statistics we should divide all elements into groups of five consecutive elements and find the median of each five. A median is called the middle element of a sorted array (it's the third largest element for a group of five). To increase the algorithm's performance speed on a modern video card, you should be able to find a sum of medians in each five of the array.
A sum of medians of a sorted k-element set S = {a1, a2, ..., ak}, where a1 < a2 < a3 < ... < ak, will be understood by as
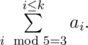
The 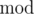 operator stands for taking the remainder, that is
operator stands for taking the remainder, that is 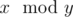 stands for the remainder of dividing x by y.
stands for the remainder of dividing x by y.
To organize exercise testing quickly calculating the sum of medians for a changing set was needed.
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), the number of operations performed.
Then each of n lines contains the description of one of the three operations:
- add x — add the element x to the set;
- del x — delete the element x from the set;
- sum — find the sum of medians of the set.
For any add x operation it is true that the element x is not included in the set directly before the operation.
For any del x operation it is true that the element x is included in the set directly before the operation.
All the numbers in the input are positive integers, not exceeding 109.
For each operation sum print on the single line the sum of medians of the current set. If the set is empty, print 0.
Please, do not use the %lld specificator to read or write 64-bit integers in C++. It is preferred to use the cin, cout streams (also you may use the %I64d specificator).
6
add 4
add 5
add 1
add 2
add 3
sum
3
14
add 1
add 7
add 2
add 5
sum
add 6
add 8
add 9
add 3
add 4
add 10
sum
del 1
sum
5
11
13
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAX_N=1e5+;
#define X first
#define Y second
//BIT
int bit[MAX_N], rb;
int sum(int i){
int s=;
while(i){
s+=bit[i];
i-=i&-i;
}
return s;
}
void add(int i, int x){
while(i<=rb){
bit[i]+=x;
i+=i&-i;
}
} typedef pair<int, int> P;
P q[MAX_N];
int val[MAX_N];
char type[MAX_N][];
int lisan(int N){
int v;
for(int i=; i<N; i++){
scanf("%s", type[i]);
switch(*type[i]){
case 'a':
case 'd':
scanf("%d", &v);
q[i]=P(v, i);
break;
case 's':
q[i]=P(, i); //TLE在这里
break;
}
}
sort(q, q+N);
int ord=;
for(int i=; i<N; ord++){
val[ord]=q[i].X;
do{
q[i].X=ord;
i++;
}while(i<N&&q[i].X==val[ord]);
}
return ord;
}
bool cmp(const P &a, const P &b){
return a.Y<b.Y;
}
//ST
struct node{
int l, r, tag;
ll sum[];
int mid(){return (l+r)>>;}
}T[MAX_N<<];
void shift(int id, int cnt){
cnt%=;
if(!cnt) return;
ll tmp[];
memcpy(tmp, T[id].sum, sizeof(tmp));
for(int i=; i<; i++){
int nt=(i+cnt+)%;
T[id].sum[nt]=tmp[i];
}
}
void pushdown(int id){
node &now=T[id], &lch=T[id<<], &rch=T[id<<|];
lch.tag+=now.tag, rch.tag+=now.tag;
shift(id<<, now.tag);
shift(id<<|, now.tag);
now.tag=; //error prone
}
void unite(int id){
node &now=T[id], &lch=T[id<<], &rch=T[id<<|];
for(int i=; i<; i++)
now.sum[i]=lch.sum[i]+rch.sum[i];
}
void build(int id, int l, int r){
node &now=T[id];
T[id].l=l, T[id].r=r, T[id].tag=;
memset(T[id].sum, , sizeof(T[id].sum));
if(l==r) return;
int mid=(l+r)>>;
build(id<<, l, mid);
build(id<<|, mid+, r);
}
void insert(int id, int pos, int ord, int v){
node &now=T[id];
if(now.l==now.r){
now.sum[ord%]+=v;
}
else{
pushdown(id);
if(pos<=now.mid())
insert(id<<, pos, ord, v);
else
insert(id<<|, pos, ord, v);
unite(id);
}
}
void shift(int id, int lb, int cnt){
if(lb>rb) return;
node &now=T[id];
if(now.l>=lb){
shift(id, cnt);
now.tag+=cnt;
}
else{
pushdown(id);
if(lb<=now.mid())
shift(id<<, lb, cnt);
shift(id<<|, lb, cnt);
unite(id);
}
} int main(){
//freopen("in", "r", stdin);
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
rb=lisan(N);
build(, , rb);
sort(q, q+N, cmp);
for(int i=; i<N; i++){
if(*type[i]=='a'){
int ord=sum(q[i].X)+;
add(q[i].X, );
shift(, q[i].X+, );
insert(, q[i].X, ord, val[q[i].X]);
}
else if(*type[i]=='d'){
int ord=sum(q[i].X);
add(q[i].X, -);
shift(, q[i].X+, -);
insert(, q[i].X, ord, -val[q[i].X]);
}
else{
printf("%I64d\n", T[].sum[]);
}
}
return ;
}
其实我已经考虑到这种无sum询问的输入,但没注意到它会导致我的代码TLE
AC version
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAX_N=1e5+;
#define X first
#define Y second
//BIT
int bit[MAX_N], rb;
int sum(int i){
int s=;
while(i){
s+=bit[i];
i-=i&-i;
}
return s;
}
void add(int i, int x){
while(i<=rb){
bit[i]+=x;
i+=i&-i;
}
} typedef pair<int, int> P;
P q[MAX_N];
int val[MAX_N];
char type[MAX_N][];
int lisan(int N){
int v;
for(int i=; i<N; i++){
scanf("%s", type[i]);
switch(*type[i]){
case 'a':
case 'd':
scanf("%d", &v);
q[i]=P(v, i);
break;
case 's':
q[i]=P(INT_MAX, i); //注意这里的改动
break;
}
}
sort(q, q+N);
int ord=;
for(int i=; i<N;){
++ord;
val[ord]=q[i].X;
do{
q[i].X=ord;
i++;
}while(i<N&&q[i].X==val[ord]);
}
return ord;
}
bool cmp(const P &a, const P &b){
return a.Y<b.Y;
}
//ST
struct node{
int l, r, tag;
ll sum[];
int mid(){return (l+r)>>;}
}T[MAX_N<<];
void shift(int id, int cnt){
cnt%=;
if(!cnt) return;
ll tmp[];
memcpy(tmp, T[id].sum, sizeof(tmp));
for(int i=; i<; i++){
int nt=(i+cnt+)%;
T[id].sum[nt]=tmp[i];
}
}
void pushdown(int id){
node &now=T[id], &lch=T[id<<], &rch=T[id<<|];
lch.tag+=now.tag, rch.tag+=now.tag;
shift(id<<, now.tag);
shift(id<<|, now.tag);
now.tag=; //error prone
}
void unite(int id){
node &now=T[id], &lch=T[id<<], &rch=T[id<<|];
for(int i=; i<; i++)
now.sum[i]=lch.sum[i]+rch.sum[i];
}
void build(int id, int l, int r){
node &now=T[id];
T[id].l=l, T[id].r=r, T[id].tag=;
memset(T[id].sum, , sizeof(T[id].sum));
if(l==r) return;
int mid=(l+r)>>;
build(id<<, l, mid);
build(id<<|, mid+, r);
}
void insert(int id, int pos, int ord, int v){
node &now=T[id];
if(now.l==now.r){
now.sum[ord%]+=v;
}
else{
pushdown(id);
if(pos<=now.mid())
insert(id<<, pos, ord, v);
else
insert(id<<|, pos, ord, v);
unite(id);
}
}
void shift(int id, int lb, int cnt){
if(lb>rb) return;
node &now=T[id];
if(now.l>=lb){
shift(id, cnt);
now.tag+=cnt;
}
else{
pushdown(id);
if(lb<=now.mid())
shift(id<<, lb, cnt);
shift(id<<|, lb, cnt);
unite(id);
}
} int main(){
//freopen("in", "r", stdin);
int N;
scanf("%d", &N);
rb=lisan(N);
build(, , rb);
sort(q, q+N, cmp);
for(int i=; i<N; i++){
if(*type[i]=='a'){
int ord=sum(q[i].X)+;
add(q[i].X, );
shift(, q[i].X+, );
insert(, q[i].X, ord, val[q[i].X]);
}
else if(*type[i]=='d'){
int ord=sum(q[i].X);
add(q[i].X, -);
shift(, q[i].X+, -);
insert(, q[i].X, ord, -val[q[i].X]);
}
else{
printf("%I64d\n", T[].sum[]);
}
}
return ;
}
Codeforces 85D Sum of Medians的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 85D Sum of Medians(线段树)
题目链接:Codeforces 85D - Sum of Medians 题目大意:N个操作,add x:向集合中加入x:del x:删除集合中的x:sum:将集合排序后,将集合中全部下标i % 5 ...
- 数据结构(线段树):CodeForces 85D Sum of Medians
D. Sum of Medians time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- CodeForces 85D Sum of Medians Splay | 线段树
Sum of Medians 题解: 对于这个题目,先想到是建立5棵Splay,然后每次更新把后面一段区间的树切下来,然后再转圈圈把切下来的树和别的树合并. 但是感觉写起来太麻烦就放弃了. 建立5棵线 ...
- 85D Sum of Medians
传送门 题目 In one well-known algorithm of finding the k-th order statistics we should divide all element ...
- CF 85D Sum of Medians (五颗线段树)
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/85/D 题意: 给你N(0<N<1e5)次操作,每次操作有3种方式, 1.向集合里加一个数a(0< ...
- codeforces 85D D. Sum of Medians Vector的妙用
D. Sum of Medians Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/problemset/prob ...
- codeforces 85D D. Sum of Medians 线段树
D. Sum of Medians time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
- Yandex.Algorithm 2011 Round 1 D. Sum of Medians 线段树
题目链接: Sum of Medians Time Limit:3000MSMemory Limit:262144KB 问题描述 In one well-known algorithm of find ...
- Coderforces 85 D. Sum of Medians(线段树单点修改)
D. Sum of Medians time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard i ...
随机推荐
- Spring AOP 针对注解的AOP
我也忘记是从哪里扒来的代码,不过有了这个思路,以后可以自己针对 Controller 还有 Service层的任意 方法进行代理了 package pw.jonwinters.aop; import ...
- .Net 内存溢出(System.OutOfMemoryException)的常见情况和处理方式总结
.Net 内存溢出(System.OutOfMemoryException)的常见情况和处理方式总结 在什么情况下会出现OutOfMemonryException呢? 在我们试图新建一个对象时,而垃圾 ...
- 在Linux用libcurl.a在链接的时候出错
其实出错是因为curl链接的时候需要别的库.我用如下方法解决 1.http://curl.haxx.se/download/curl-7.45.0.tar.gz官网下载源码 2../configure ...
- 求时间差的sql语句。 比如如下数据
msisdn createtime closetime138 2011-5-17 15:30:00:000 2011-5-17 15:30:00:530138 2011-5-17 15:40:00:0 ...
- 解决SaveChanges会Hold住之前的错误的问题
问题描述: 在一次新增操作中,由于有一个必填字段忘记写了,然后直接点击提交,运行到savechanges的地方,程序报错,提示***字段为必填字段. 然后关掉页面,重新填写一次,这次什么都填写上了,一 ...
- Python解析器源码加密系列之(二):一次使用标准c的FILE*访问内存块的尝试
摘要:由于近期打算修改Python解释器以实现pyc文件的加密/解密,出于保密的要求,解密之后的数据只能放在内存中,不能写入到文件中.但是后续的解析pyc文件的代码又只能接受FILE*作为入参,所以就 ...
- 《图解tcp/ip》读书笔记(二)
<图解tcp/ip>读书笔记(二) 本周主要阅读的是本书的第三章--数据链路. 当然了,从某些角度讲,我认为这一章就是计算机网络的最基本的内容之一.整章讲述了数据链路层的作用和相关技术,主 ...
- 足球运动训练心得及经验分析-c语言学习调查
在准备预备作业02之前,我参考娄老师的提示,阅读了<[做中学(Learning By Doing)]之乒乓球刻意训练一年总结>一文. 在文章描述的字里行间,给予我的印象是系统.负责,娄老师 ...
- 学习Java第一卷--态度的转变
你对自己的未来有什么规划?做了哪些准备? 认真学习,修身养性,做自己感兴趣的,在大学一定学好Java,将自己的专业学好学精. 我觉得未来十几年或几十年是自己无法完全控制的,只有自己朝着自己心中的目标努 ...
- javascript模块化详解
模块化:每个模块只完成一个独立的功能,然后提供该功能的接口.模块间通过接口访问.模块中的(过程和数据)对于其它模块来说是私有的(不能访问修改) 原始人写法: function m1(){ //... ...
