JS面向对象高级特性
本篇是通过学习视频《一头扎进javascirpt高级篇》整理的一些相关知识,大致包括下面几个方面:
1 对象的创建方法
2 对象的对象属性、私有属性、类属性
3 对象的对象方法、私有方法、类方法
4 javascirpt的继承、封装、与多态
对象的创建方法:
对象的创建可以通过两种方式,第一种通过对象初始化的方法:
var person={
name:"xingoo",
age:26,
say:function(){
console.log("say something");
},
action:function(){
console.log("do something");
}
};
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.age);
person.say();
person.action();
第二种方式通过构造函数创建:
function student(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.say = function(){
console.log("say something");
}
this.action = function(){
console.log("do something");
}
}
var xingoo = new student("xingoo",27);
console.log(xingoo.name);
console.log(xingoo.age);
xingoo.say();
xingoo.action();
对象的属性
对象的属性分为对象属性、私有属性和类属性。
对象属性需要创建对象后才能使用;
私有属性在内部可以直接使用,在外部需要通过闭包才能使用。
类属性可以通过对象名称直接使用。
function func(){
this.objPro1 = "对象属性";
func.prototype.objPro2 = "对象属性";
var privatePro = "私有属性";
}
func.classPro = "类属性";
console.log(func.classPro);
var f = new func();
console.log(f.objPro1);
console.log(f.objPro2);
<!-- 私有属性可以通过闭包获取 -->
对象的方法
对象方法包括:对象方法,私有方法和类方法,使用类似前面的属性。
function demoFunc1(){
var privateFunc = function(){
console.log("this is privateFunc");
};
privateFunc();
this.objFunc1 = function(){
console.log("this is objFunc1");
};
demoFunc1.prototype.objFunc2 = function(){
console.log("this is objFunc2");
};
}
demoFunc1.classFunc = function(){
console.log("this is classFunc");
};
demoFunc1.classFunc();
var f = new demoFunc1();
f.objFunc1();
f.objFunc2();
继承、封装与多态
JS要想实现继承,需要通过apply方法或者prototype实现。
如果单纯的使用apply方法,子类的原型是子类;如果使用prototype,那么子类的原型也将继承父类。
例如下面的代码:
function Animal(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age =age;
this.say = function(){
console.log("animal say something");
}
}
function Cat(name,age){
Animal.apply(this,[name,age]);
}
<!-- Cat.prototype = new Animal();-->
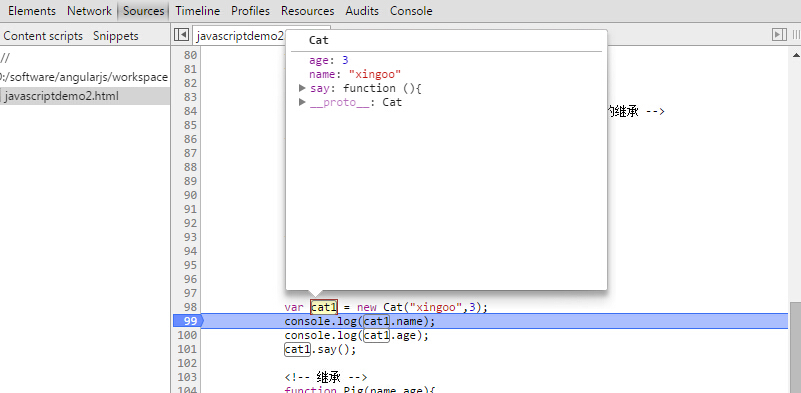
var cat1 = new Cat("xingoo",3);
console.log(cat1.name);
console.log(cat1.age);
cat1.say();
上面代码中,cat的原型是cat;
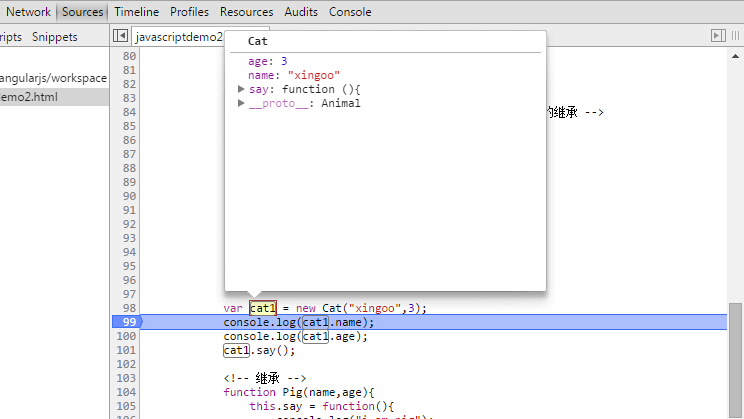
如果开启注释的部分,可以发现,cat类的原型也变成了Animal。
子类的方法会覆盖父类的方法,即表现出多态性:
function Pig(name,age){
this.say = function(){
console.log("i am pig");
}
}
Pig.prototype = new Animal();
function Dog(name,age){
this.say = function(){
console.log("i am dog");
}
}
Dog.prototype = new Animal();
function say(animal){
if(animal instanceof Animal){
animal.say();
}
}
var dog = new Dog();
var pig = new Pig();
say(dog);
say(pig);
使用到的全部代码:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
<!-- 对象初始化器方式 -->
var person={
name:"xingoo",
age:26,
say:function(){
console.log("say something");
},
action:function(){
console.log("do something");
}
}; console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.age);
person.say();
person.action(); <!-- 构造函数方式 -->
function student(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.say = function(){
console.log("say something");
}
this.action = function(){
console.log("do something");
}
}
var xingoo = new student("xingoo",27);
console.log(xingoo.name);
console.log(xingoo.age);
xingoo.say();
xingoo.action(); <!-- 对象属性 私有属性,对象属性,类属性 -->
function func(){
this.objPro1 = "对象属性";
func.prototype.objPro2 = "对象属性"; var privatePro = "私有属性";
}
func.classPro = "类属性"; console.log(func.classPro); var f = new func();
console.log(f.objPro1);
console.log(f.objPro2); <!-- 私有属性可以通过闭包获取 --> <!-- 私有方法,对象方法,类方法 -->
function demoFunc1(){
var privateFunc = function(){
console.log("this is privateFunc");
}; privateFunc(); this.objFunc1 = function(){
console.log("this is objFunc1");
};
demoFunc1.prototype.objFunc2 = function(){
console.log("this is objFunc2");
};
}
demoFunc1.classFunc = function(){
console.log("this is classFunc");
};
demoFunc1.classFunc(); var f = new demoFunc1();
f.objFunc1();
f.objFunc2(); <!-- 封装性,继承性,多态性 -->
<!-- apply()实现属性和方法的集成,prototype实现原型的继承 --> function Animal(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age =age;
this.say = function(){
console.log("animal say something");
}
}
function Cat(name,age){
Animal.apply(this,[name,age]);
}
<!-- Cat.prototype = new Animal();--> var cat1 = new Cat("xingoo",3);
console.log(cat1.name);
console.log(cat1.age);
cat1.say(); <!-- 继承 -->
function Pig(name,age){
this.say = function(){
console.log("i am pig");
}
}
Pig.prototype = new Animal();
function Dog(name,age){
this.say = function(){
console.log("i am dog");
}
}
Dog.prototype = new Animal(); function say(animal){
if(animal instanceof Animal){
animal.say();
}
}
var dog = new Dog();
var pig = new Pig();
say(dog);
say(pig);
</script>
</body>
</html>
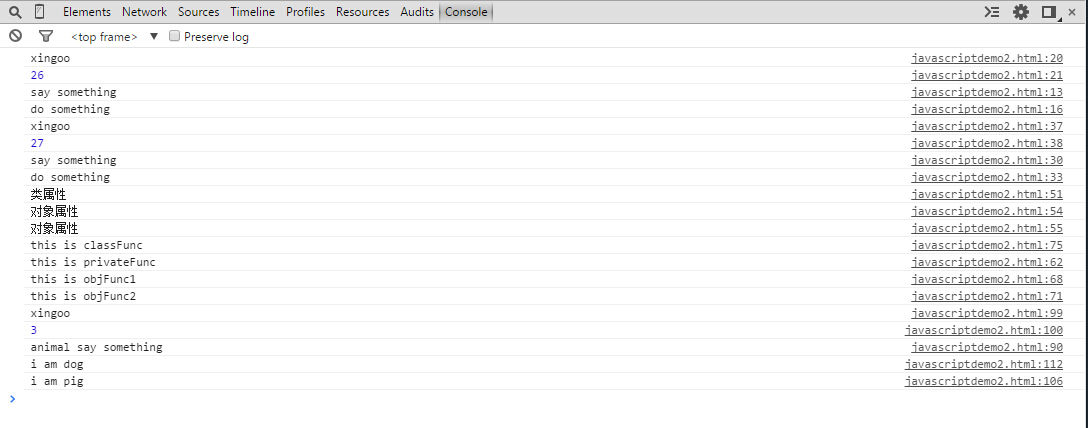
运行结果:
JS面向对象高级特性的更多相关文章
- Java第五次作业--面向对象高级特性(抽象类与接口)
Java第五次作业--面向对象高级特性(抽象类与接口) (一)学习总结 1.在上周完成的思维导图基础上,补充本周的学习内容,对Java面向对象编程的知识点做一个全面的总结. 2.汽车租赁公司,出租汽车 ...
- Java第四次作业——面向对象高级特性(继承和多态)
Java第四次作业--面向对象高级特性(继承和多态) (一)学习总结 1.学习使用思维导图对Java面向对象编程的知识点(封装.继承和多态)进行总结. 2.阅读下面程序,分析是否能编译通过?如果不能, ...
- Java第四次作业,面向对象高级特性(继承和多态)
Java第四次作业-面向对象高级特性(继承和多态) (一)学习总结 1.学习使用思维导图对Java面向对象编程的知识点(封装.继承和多态)进行总结. 2.阅读下面程序,分析是否能编译通过?如果不能,说 ...
- Java第四次作业—面向对象高级特性(继承和多态)
Java第四次作业-面向对象高级特性(继承和多态) (一)学习总结 1.学习使用思维导图对Java面向对象编程的知识点(封装.继承和多态)进行总结. 2.阅读下面程序,分析是否能编译通过?如果不能,说 ...
- js面向对象高级编程
面向对象的组成 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www ...
- Java第五次作业--面向对象高级特性(抽象类和接口)
一.学习要点 认真看书并查阅相关资料,掌握以下内容: 掌握抽象类的设计 掌握接口的设计 理解简单工厂设计模式 理解抽象类和接口的区别 掌握包装类的应用 掌握对象的比较方法和比较器的使用 学习使用日期操 ...
- Java第四次作业--面向对象高级特性(继承和多态)
一.学习要点 认真看书并查阅相关资料,掌握以下内容: 掌握类的继承概念和设计 掌握构造方法的继承原则 掌握方法重写 掌握super键字和final关键字 理解多态的概念,掌握通过方法重写和方法重载机制 ...
- 五. 面向对象高级特性6. Java 泛型
我们知道,使用变量之前要定义,定义一个变量时必须要指明它的数据类型,什么样的数据类型赋给什么样的值. 假如我们现在要定义一个类来表示坐标,要求坐标的数据类型可以是整数.小数和字符串,例如: x = 1 ...
- 五. 面向对象高级特性1. Java内部类及其实例化
在 Java 中,允许在一个类(或方法.语句块)的内部定义另一个类,称为内部类(Inner Class),有时也称为嵌套类(Nested Class). 内部类和外层封装它的类之间存在逻辑上的所属关系 ...
随机推荐
- scau 8633 回文划分
8633 回文划分 时间限制:1000MS 内存限制:1000K 题型: 编程题 语言: 无限制 Description 我们说一个字符串是回文串,那么意味着这个串从两边读起来的字母都是一样的. ...
- SQL Server with(nolock)详解
大家在写查询时,为了性能,往往会在表后面加一个nolock,或者是with(nolock),其目的就是查询是不锁定表,从而达到提高查询速度的目的. 什么是并发访问:同一时间有多个用户访问同一资源,并发 ...
- LAMP编译参数查看
Linux下查看Nginx.Napache.MySQL.PHP的编译参数的命令如下: 1.nginx编译参数:#/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -V2.apache编译参数:# ...
- Hive conf issue
Hive --hiveconf v1="test" --hiveconf v2 -e "select * from ${hiveconf:v1} where col1=' ...
- [转]Getting Start With Node.JS Tools For Visual Studio
本文转自:http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/g_arora/getting-started-with-node-js-tools-for-visual-s ...
- openfire+asmack搭建的安卓即时通讯(四) 15.4.10
之前的教程不知道你们成功了没,,,没成功可以问我啊=-= 第四篇博文是要实现发送消息的功能. 首先在我们登陆后的活动的layout里添加这样的两个控件,一个EditText和一个Button用于发送数 ...
- 【Android UI设计与开发】1.引导界面(一)ViewPager介绍和简单实现
1.ViewPager 实现效果图 2.ViewPager 实现功能 ViewPager类提供了多界面切换的新效果,新效果有如下特征: <1>当前显示一组界面中的其中一个界面: <2 ...
- 广搜+打表 POJ 1426 Find The Multiple
POJ 1426 Find The Multiple Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 25734 Ac ...
- Redis安全访问
限制IP(只能一个) # If you want you can bind a single interface, if the bind option is not # specified all ...
- Jenkins遇到问题二:Jenkins服务器磁盘空间管理策略
Jenkins在帮助我们自动化构建服务的同时也在消耗服务器的磁盘空间,试想如果构建的项目个数很多,而Jenkins 服务器磁盘空间又不是非常大的话,每隔一段时间磁盘空间就会爆满导致Jenkins出现磁 ...
