源码分析(5)-ArrayList、Vector和LinkedList(JDK1.8)
一、概述
1、线程安全:ArrayList和LinkedList非线程安全的、Vector线程安全的。
2、底层数据结构:ArrayList和Vector底层数据结构是数组;LinkedList双向链表。
3、时间复杂度是否受插入和删除元素位置影响:ArrayList和Vector受影响,add(E e)方法时间复杂度O(1)和add(int index, E element)方法时间复杂度O(n-index);LinkedList受影响,add(E e)方法时间复杂度O(1)和add(int index, E element)方法时间复杂度O(n)。
4、是否支持随机访问:ArrayList和Vector支持;LinkedList不支持。
5、内存空间占用:ArrayList和Vector空间浪费主要体现在在list列表的结尾会预留一定的容量空间;LinkedList空间花费则体现在每一个元素都需要消耗更多的空间(因为要存放直接后继和直接前驱以及数据)。
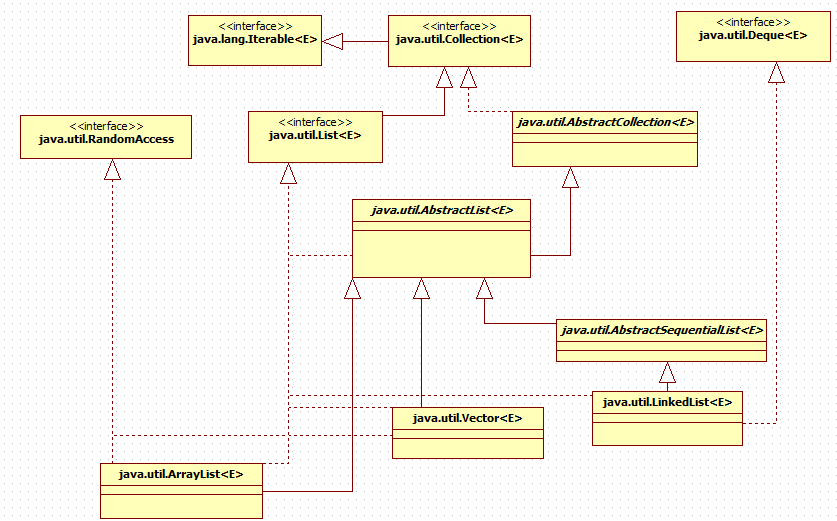
二、集合UML类图
ArrayList和LinkedList继承和实现相同,LinkedList实现java.util.Deque<E>接口和继承java.util.AbstractSequentialList<E>抽象类。
三、ArrayList源码分析
1、重要成员变量
//数组,存储数据
transient Object[] elementData;
//数组长度
private int size;
//数组结构变更次数
protected transient int modCount = 0;
2、插入
//添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);//确认容量足够
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
} private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
//计算容量
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);//初始化容量10,返回初始容量和需要最小容量选择最大值
}
return minCapacity;
}
//
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)//最小需要容量大于数组长度,进行扩容
grow(minCapacity);
}
//扩容
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);扩容1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)//扩容后容量和需要的最小容量
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);//设置最大容量
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//复制数组
}
//指定位置添加数组
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index);//复制插入数组
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
3、删除
//删除元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);数组复制,index位置以后的元素前移1个位置
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
四、Vector源码分析
成员方法和ArrayList相似,不同之处在于方法都是synchronized同步锁修饰。
1、重要成员变量
//数组,存储数据和ArrayList相同
protected Object[] elementData;
//数组长度,等同于ArrayList的size
protected int elementCount;
//扩容量
protected int capacityIncrement;
2、插入
//添加元素
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);//确保容量
elementData[elementCount++] = e;//尾部添加元素
return true;
}
//
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);//扩容
}
//
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);//默认扩容2倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//复制数组
}
五、LinkedList源码分析
1、重要成员变量
//双向链表节点长度
transient int size = 0;
//头结点
transient Node<E> first;
//尾结点
transient Node<E> last;
2、数据结构
private static class Node<E> {
E item;//数据
Node<E> next;//下一个节点
Node<E> prev;//前一个节点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
3、插入
//插入到头部
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;//头结点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)//头结点为空
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;//原头结点的前一个节点指向新节点
size++;
modCount++;
}
//尾部添加节点
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
//
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;//尾结点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)//尾结点为空,此时头尾节点都是空
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;//尾结点执行新节点
size++;
modCount++;
}
//插入节点默认在尾部添加
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//指定位置添加节点
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size)
linkLast(element);//尾部添加节点
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
//
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) {//插入位置小于0.5*size,正向遍历
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)//查询待插入位置节点
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)//逆向遍历
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
4、删除
//删除指定位置元素
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));//遍历查询index位置元素
}
//
E unlink(Node<E> x) {//删除数据
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
} if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
} x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
其他方法不再讲解。
源码分析(5)-ArrayList、Vector和LinkedList(JDK1.8)的更多相关文章
- 集合源码分析[3]-ArrayList 源码分析
历史文章: Collection 源码分析 AbstractList 源码分析 介绍 ArrayList是一个数组队列,相当于动态数组,与Java的数组对比,他的容量可以动态改变. 继承关系 Arra ...
- java读源码 之 list源码分析(ArrayList)---JDK1.8
java基础 之 list源码分析(ArrayList) ArrayList: 继承关系分析: public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之ArrayList详解(一)
[集合框架]JDK1.8源码分析之ArrayList详解(一) 一. 从ArrayList字表面推测 ArrayList类的命名是由Array和List单词组合而成,Array的中文意思是数组,Lis ...
- 源码分析(2)-LinkedHashMap(JDK1.8)
1.概述 LinkedHashMap继承自HashMap:在HashMap基础上,通过维护一条双向链表,解决了HashMap键值对遍历顺序和插入顺序一致的问题. 想了解LinkedHashMap源码, ...
- 【集合框架】JDK1.8源码分析之ArrayList(六)
一.前言 分析了Map中主要的类之后,下面我们来分析Collection下面几种常见的类,如ArrayList.LinkedList.HashSet.TreeSet等.下面通过JDK源码来一起分析Ar ...
- Java集合源码分析之ArrayList
ArrayList简介 从上图可以看到,ArrayList是集合框架中List接口的一个实现类,它继承了AbstractList类,实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, ...
- JDK源码学习笔记——ArrayList/Vector
一.类定义 public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, Random ...
- 源码分析(4)-ConcurrentHashMap(JDK1.8)
一.UML类图 ConcurrentHashMap键值不能为null:底层数据结构是数组+链表/红黑二叉树:采用CAS(比较并交换)和synchronized来保证并发安全. CAS文章:https: ...
- 源码分析(1)-HashMap(JDK1.8)
UML类图 java.util.Map<K, V>接口,有4个实现类:HashMap.Hashtable.LinkedHashMap和TreeMap. 1.说明 (1)HashMap除允许 ...
- 源码分析二(ArrayList与LinkedList的区别)
一:首先看一下ArrayList类的结构体系: public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements Lis ...
随机推荐
- Postman学习之Authorization
前言:本章将学习Postman当中的授权——Authorization 一.简介 Authorization顾名思义就是授权的意思,那是给谁授权呢?又有多少种授权的方式呢?Authorization是 ...
- 网鼎杯2020青龙组writeup-web
本文首发于Leon的Blog,如需转载请注明原创地址并联系作者 AreUSerialz 开题即送源码: <?php include("flag.php"); highligh ...
- C#/VB.NET 将SVG图片添加到PDF、转换为PDF
以下内容介绍在C# 程序中如何将SVG图片添加到PDF文档.以及如何将SVG图片转换为PDF文档. 一.环境准备 先下载PDF类库工具,Spire.PDF for .NET hotfix 6.5.6及 ...
- node的buffer模块
Buffer这块很早前就想留一篇笔记.前端JS处理buffer的场景其实并不多,虽然后来基于webGL与显卡通信的需求增加了二进制数组,但毕竟相对小众. Buffer的含义是,在数据传输时用内存中的一 ...
- mvc 页面上循环datatable
@using System.Data; @{ Layout = null; } @{ DataTable DataServiceStaff = ViewBag.ServiceStaff as Data ...
- iozone测试报错:Error writing block 12634, fd= 3 write: No space left on device
问题:使用iozone测试GFS的读写性能的时候,一直报错Error writing block 12634, fd= 3 write: No space left on device,百思不得其解: ...
- CF838A
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/838/problem/A 知识点: (void) 题目大意: 给一个 \(n \times m\) 的 01 矩阵,对于矩阵在 ...
- 【Spring】Spring AOP详解(转载)
一.前言 在以前的项目中,很少去关注spring aop的具体实现与理论,只是简单了解了一下什么是aop具体怎么用,看到了一篇博文写得还不错,就转载来学习一下,博文地址:http://www.cnbl ...
- 1417. 重新格式化字符串--来源:力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述: 给你一个混合了数字和字母的字符串 s,其中的字母均为小写英文字母. 请你将该字符串重新格式化,使得任意两个相邻字符的类型都不同.也就是说,字母后面应该跟着数字,而数字后面应该跟着字母. 请 ...
- zookeeper启动报错:Error contacting service. It is probably not running
Error contacting service. It is probably not running. 今天启动zookeeper集群时,正常启动,但是查看状态时发现,Error contacti ...
