Classification week3: decision tree 笔记
华盛顿大学 machine learnign :classification week 3 笔记
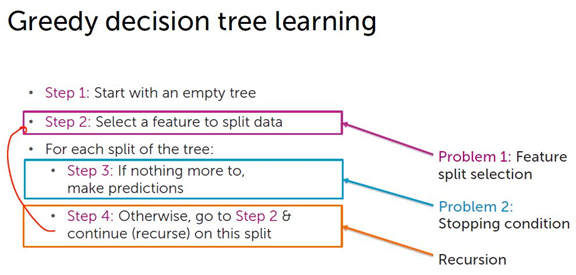
第二步:
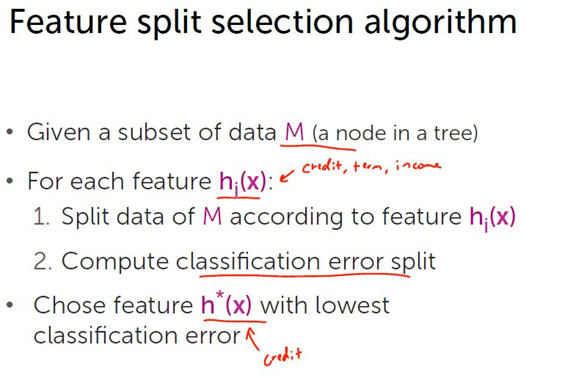
注:
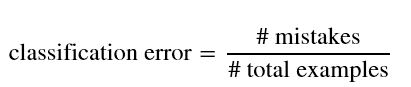
其中 ,mistake 的计算方法:
给定一个节点的数据集M,对每个特征hi(x),根据特征hi(x)将节点的数据集M分类。
统计哪个类别占多数,记为多数类。
所有不在多数类里的数据都作为误判mistakes
classification error = (left_mistakes + right_mistakes) / num_data_points
第三步:建树
考虑到防止过拟合:

1. early stopping:
停止条件:

建树过程:
def decision_tree_create(data, features, target, current_depth = 0,
max_depth = 10, min_node_size=1,
min_error_reduction=0.0): remaining_features = features[:]
target_values = data[target] # Stopping condition 1: All nodes are of the same type.
if intermediate_node_num_mistakes(target_values) == 0:
return create_leaf(target_values) # Stopping condition 2: No more features to split on.
if remaining_features == []:
return create_leaf(target_values) # Early stopping condition 1: Reached max depth limit.
if current_depth >= max_depth:
return create_leaf(target_values) # Early stopping condition 2: Reached the minimum node size.
if reached_minimum_node_size(data, min_node_size):
return create_leaf(target_values) # Find the best splitting feature and split on the best feature.
splitting_feature = best_splitting_feature(data, features, target)
left_split = data[data[splitting_feature] == 0]
right_split = data[data[splitting_feature] == 1] # calculate error
error_before_split = intermediate_node_num_mistakes(target_values) / float(len(data))
left_mistakes = intermediate_node_num_mistakes(left_split[target])
right_mistakes = intermediate_node_num_mistakes(right_split[target])
error_after_split = (left_mistakes + right_mistakes) / float(len(data)) # Early stopping condition 3: Minimum error reduction
if error_before_split - error_after_split < min_error_reduction:
return create_leaf(target_values) remaining_features.remove(splitting_feature) # Repeat (recurse) on left and right subtrees
left_tree = decision_tree_create(left_split, remaining_features, target,
current_depth + 1, max_depth, min_node_size, min_error_reduction)
right_tree = decision_tree_create(right_split, remaining_features, target,
current_depth + 1, max_depth, min_node_size, min_error_reduction) return create_node(splitting_feature, left_tree, right_tree)
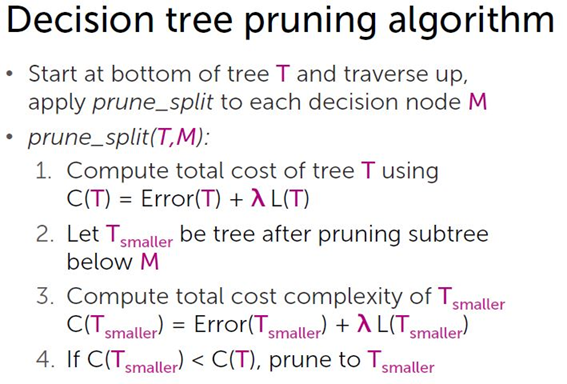
2. pruning
Total cost C(T) = Error(T) + λ L(T)
用建好的树预测数据:

def classify(tree, input):
# if the node is a leaf node.
if tree['is_leaf']:
return tree['prediction']
else:
# split on feature.
split_feature_value = input[tree['splitting_feature']]
if split_feature_value == 0:
return classify(tree['left'], input)
else:
return classify(tree['right'], input)
Classification week3: decision tree 笔记的更多相关文章
- OpenCV码源笔记——Decision Tree决策树
来自OpenCV2.3.1 sample/c/mushroom.cpp 1.首先读入agaricus-lepiota.data的训练样本. 样本中第一项是e或p代表有毒或无毒的标志位:其他是特征,可以 ...
- [ML学习笔记] 决策树与随机森林(Decision Tree&Random Forest)
[ML学习笔记] 决策树与随机森林(Decision Tree&Random Forest) 决策树 决策树算法以树状结构表示数据分类的结果.每个决策点实现一个具有离散输出的测试函数,记为分支 ...
- 【机器学习】决策树(Decision Tree) 学习笔记
[机器学习]决策树(decision tree) 学习笔记 标签(空格分隔): 机器学习 决策树简介 决策树(decision tree)是一个树结构(可以是二叉树或非二叉树).其每个非叶节点表示一个 ...
- 决策树学习笔记(Decision Tree)
什么是决策树? 决策树是一种基本的分类与回归方法.其主要有点事模型具有可得性,分类速度快.学习时,利用训练数据,根据损失函数最小化原则建立决策树模型:预测时,对新数据,利用决策树模型进行分类. 决策树 ...
- 机器学习技法笔记:09 Decision Tree
Roadmap Decision Tree Hypothesis Decision Tree Algorithm Decision Tree Heuristics in C&RT Decisi ...
- 机器学习技法笔记:11 Gradient Boosted Decision Tree
Roadmap Adaptive Boosted Decision Tree Optimization View of AdaBoost Gradient Boosting Summary of Ag ...
- Coursera台大机器学习技法课程笔记11-Gradient Boosted Decision Tree
将Adaboost和decision tree相结合,需要注意的地主是,训练时adaboost需要改变资料的权重,如何将有权重的资 料和decision tree相结合呢?方法很类似于前面讲过的bag ...
- [学习笔记] Uplift Decision Tree With KL Divergence
Uplift Decision Tree With KL Divergence Intro Uplift model 我没找到一个合适的翻译,这方法主要应用是,探究用户在给予一定激励之后的表现,也就是 ...
- 【3】Decision tree(决策树)
前言 Decision tree is one of the most popular classification tools 它用一个训练数据集学到一个映射,该映射以未知类别的新实例作为输入,输出 ...
随机推荐
- javascript快速入门7--ECMAScript语法基础
ECMAScript的基础概念 熟悉Java.C和Perl这些语言的开发者会发现ECMAScript的语法很容易掌握,因为它借用了这些语言的语法.Java和ECMAScript有一些关键语法特性相同, ...
- profiler
推荐C++ 的profiler 用于GPU CPU 综合测试 FramePro http://www.puredevsoftware.com/ 可以在进度条上拉时间 查看GPU CPU bound
- 集成方法:渐进梯度回归树GBRT(迭代决策树)
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/60776803 单决策树C4.5由于功能太简单.而且非常easy出现过拟合的现象.于是引申出了很多变种决 ...
- 让Qt Creator支持Windows Phone 8开发
让Qt Creator支持Windows Phone 8开发 近期QtCreator3.2出了.修复了一些Bug.比上一个版本号3.1.2要好了一些. 因为在上一个版本号(Qt for WinRT自带 ...
- C++ x86程序与x64程序中,各种内置类型的大小比较
代码: #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <list> #include <string> ...
- Linux学习笔记 (四)归档和压缩
一.zip压缩命令: 1.压缩文件: 格式:zip 压缩文件 源文件 例:zip abc.zip abc //将abc文件压缩到abc.zip文件内. 2.压缩目录: 格式:zip –r 压缩目录 ...
- Win10 系统变成黑白屏幕了怎么办?
快捷键"windows徽标键+Ctrl+C"可以切换屏幕黑白了 这是win自带的一个"应用颜色筛选器", 桌面右键,选择个性化 点到背景页面,下拉,点击&q ...
- select * from (select user())a 为什么是查询user()的意思?
步骤:1.先查询 select user() 这里面的语句,将这里面查询出来的数据作为一个结果集 取名为 a2.然后 再 select * from a 查询a ,将 结果集a 全部查询出来
- 用尽洪荒之力整理的Mysql数据库32条军规(转)
今天上午吐血整理了Oracle SQL性能优化的40条军规,其中很多规则也是适用于Mysql的,结果今晚发现这一篇文章——用尽洪荒之力整理的Mysql数据库32条军规,和我的竟有异曲同工之妙,当然不同 ...
- python 排序函数
1.sorted()函数:内建函数,适用于所有类型,返回排序后的对象,原对象不改变,sorted(a,key=,reversed=True) >>> sorted((3,1,4,2) ...
