笔记7 AOP练习<有疑问>
场景描述:
核心业务:举行一场古典音乐会。
周边功能:观众入场,关闭手机、落座,觉得音乐好听时鼓掌,觉都不好听则退票。(切面)
1.编写切点(切点用于准确定位应该在什么地方应用切面的通 知)————即核心业务
首先定义一个Performance接口:
package concert;
public interface Performance {
public void perform();
}
2.定义切面,即编写Audience.java。
Audience类使用@Aspect注解进行了标注。该注解表明Audience不仅仅是一个POJO,还是一个切面。
@Pointcut注解能够在一 个切面内定义可重用的切点。
也可以在通知注解中直接使用切点表达式。
package concert; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect
@Component
public class Audience {
@Pointcut("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
public void perform() { } // @Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
@Before("perform()")
public void silenceCellPhones() {
System.out.println("Silencing cell phone");
} // @Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
@Before("perform()")
public void takeSeats() {
System.out.println("Taking seats");
} // @AfterReturning("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
@AfterReturning("perform()")
public void applause() {
System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP");
} // @AfterThrowing("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))")
@AfterThrowing("perform()")
public void demandRefund() {
System.out.println("Demanding a refund");
}
}
Audience有四个方法,定义了一个观众在观看演出时可能会做的事 情。在演出之前,观众要就坐(takeSeats())并将手机调至静音 状态(silenceCellPhones())。如果演出很精彩的话,观众应 该会鼓掌喝彩(applause())。不过,如果演出没有达到观众预期 的话,观众会要求退款(demandRefund())。 这些方法都使用了通知注解来表明它们应该在什么时候调用。

在这里也可以使用环绕通知,环绕通知是最为强大的通知类型。它能够让你所编写的逻辑将被通知 的目标方法完全包装起来。实际上就像在一个通知方法中同时编写前 置通知和后置通知,代码如下:
@Around("performs()") // 环绕通知方法
public void watchPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) {
try {
System.out.println("Silencing cell phone");
System.out.println("Taking seats");
jp.proceed();
System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("Demanding a refund");
}
}
在这里,@Around注解表明watchPerformance()方法会作 为performance()切点的环绕通知。ProceedingJoinPoint作为参数。这个对象是必须要有的,因为要在通知中通过它来调用被通知的方法。通知方法中可以做任何的 事情,当要将控制权交给被通知的方法时,它需要调 用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法。
<可以不调用proceed()方法,从而阻塞对被通知方 法的访问,与之类似,也可以在通知中对它进行多次调用。要这样 做的一个场景就是实现重试逻辑,也就是在被通知方法失败后,进行 重复尝试。>
3.定义Java配置文件ConcertConfig.java,使用Spring自动装配。在Java配置文件中启用AspectJ注解的自动代理。
AspectJ自动代理都会为使 用@Aspect注解的bean创建一个代理,这个代理会围绕着所有该切面 的切点所匹配的bean。
package concert; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; @Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 启用AspectJ自动代理
@ComponentScan
public class ConcertConfig { }
也可以定义XML配置文件
在Spring中要使用XML来装配bean的话,那么需要使用Spring aop命名空间中的<aop:aspectj-autoproxy>元素启用自动代理。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="concert"></context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> <!--启用自动代理-->
<!-- <bean class="concert.Audience"></bean>
<bean class="concert.Classcial"></bean> -->
</beans>
注:在使用XML进行装配的时候,如果在XML声明了bean后,一定要去掉两个bean原来的@Component注解,且不用使用自动代理;如果不在XML文件中声明bean,在Audience和Classcial中添加@Component注解,则可以启用自动代理。
4.编写测试文件ConcertTest.java
package concert; import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = concert.ConcertConfig.class)
public class ConcertTest {
@Autowired
private Performance perform; @Test
public void test() {
perform.perform();
}
}
疑问:在进行测试时,只能定义接口的对象来进行测试,定义接口的实现类对象时就会报错。
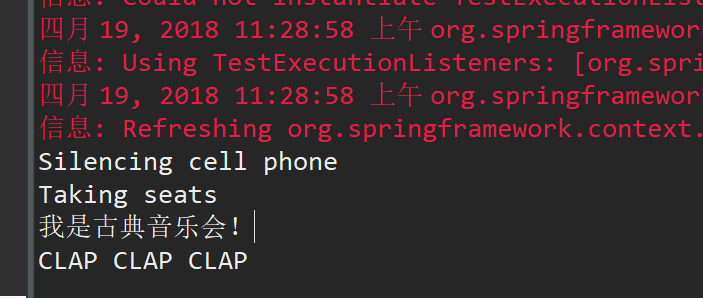
5.结果
两种配置方式结果一样
笔记7 AOP练习<有疑问>的更多相关文章
- Spring笔记:AOP基础
Spring笔记:AOP基础 AOP 引入AOP 面向对象的开发过程中,我们对软件开发进行抽象.分割成各个模块或对象.例如,我们对API抽象成三个模块,Controller.Service.Comma ...
- Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3)
Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3) 1.0 静态代理模式的缺点: 1.在该系统中有多少的dao就的写多少的proxy,麻烦 2.如果目标接口有方法的改动,则proxy也需要改动. Person ...
- 笔记13 AOP中After和AfterReturning的区别
AOP中 @Before @After @AfterThrowing@AfterReturning的执行顺序 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method met ...
- 笔记9 AOP练习3(通过注解引入新功能 )
切面可以为Spring bean添加新方法. 在Spring中,切面只是实现了它们所包装bean相同接口的 代理.如果除了实现这些接口,代理也能暴露新接口的话,会怎么样 呢?那样的话,切面所通知的be ...
- Spring笔记(三)AOP前篇之动态代理
AOP思想是将程序中的业务代码与服务代码进行分离,在运行时进行结合.比较强调程序的层次结构,是一种面向切面的编程.而在AOP实现的底层主要用到了动态代理,而动态代理又分为JDK动态代理和CGLIB动态 ...
- Spring学习笔记之AOP配置篇(一)
[TOC] 1. 创建并声明一个切面 首先,创建一个类,添加@Component注解使其添加到IoC容器 然后,添加@Aspect注解,使其成为一个切面 最后,在配置文件里面,使用<aop:as ...
- 笔记7 AOP
1. 通知(Advice) 切面的工作被称为通知.通知定义了切面是什么以及何时使用.除了描述切面要完成的工作, 通知还解决了何时执行这个工作的问题.它应该应用在某个方法被调 用之前?之后?之前和之 ...
- Spring学习笔记4——AOP
AOP 即 Aspect Oriented Program 面向切面编程 首先,在面向切面编程的思想里面,把功能分为核心业务功能,和周边功能. 所谓的核心业务,比如登陆,增加数据,删除数据都叫核心业务 ...
- [Spring学习笔记 4 ] AOP 概念原理以及java动态代理
一.Spring IoC容器补充(1) Spring IoC容器,DI(依赖注入): 注入的方式:设值方法注入setter(属性注入)/构造子注入(构造函数传入依赖的对象)/字段注入Field(注解) ...
随机推荐
- JS中的 map, filter, some, every, forEach, for...in, for...of 用法总结
1.map 有返回值,返回一个新的数组,每个元素为调用func的结果. let list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; let other = list.map((d, i) => { ...
- python django的ManyToMany简述
Django的多对多关系 在Django的关系中,有一对一,一对多,多对多的关系 我们这里谈的是多对多的关系 ==我们首先来设计一个用于示例的表结构== # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- ...
- 算法题丨Two Sum
描述 Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific ...
- Mybatis和Hibernate本质区别和应用场景
Hibernate:是一个标准ORM(对象关系映射)框架.入门门槛较高,不需要程序员写sql语句,sql语句自动生成,对sql语句优化.修改比较困难 应用场景:适用于需求变化不多的中小型项目,比如后台 ...
- kubernetes入门(09)kubernetes1.7集群安装(2017/11/13)
CentOS7.3利用kubeadm安装kubernetes1.7.3完整版(官方文档填坑篇) https://www.cnblogs.com/liangDream/p/7358847.html 一. ...
- SpringMvc采用 http+json 实现前后端交互
演示列表 报文表示 一.Json请求和Json响应 实现:Spring4.1.1.RELEASE + jackson2.4.4+JQuery1.10.2 1.pom.xml <propertie ...
- 日推20单词 Day03
1.occur v. 发生,发现 2.harvest n.收获,丰收 vt.收割,得到 3.crop n.庄稼,收成 4.yield n.产量 v.产出,屈服 5.field n.田野 6.featu ...
- 在Debian或Ubuntu中安装和使用'搜狗输入法for linux'
下载搜狗输入法 for linux点击 搜狗输入法 for linux 以下载安装包到本地 安装搜狗输入法 for linuxA.准备工作: (1) 连接网络.挂载系统安装盘 此安装过程需要网络连接, ...
- 简单搭建SpringMVC框架详解
在公司待了两年,用的一直是Spring+SpringMVC+Hibernate框架,都是公司自己搭建好的,自己从来没有主动搭建过,闲来无聊,自己搭建试试.一下即我搭建的过程以及搭建所遇到的问题,有部分 ...
- xpath的一般用法与特殊用法
# xpath的使用 安装lxml from lxml import etree Selector = etree.HTML(网页代码) Selector.xpath(一段神奇的代码) xpath的一 ...
