Android Intent机制与常见的用法
Activity
Android于。Activity所有的程序都是必不可少,程都执行在Activity之中。Activity具有自己的生命周期(见http://www.cnblogs.com/feisky/archive/2010/01/01/1637427.html,由系统控制生命周期,程序无法改变。但能够用onSaveInstanceState保存其状态)。
对于Activity,关键是其生命周期的把握(例如以下图),其次就是状态的保存和恢复(onSaveInstanceState onRestoreInstanceState)。以及Activity之间的跳转和传输数据(intent)。
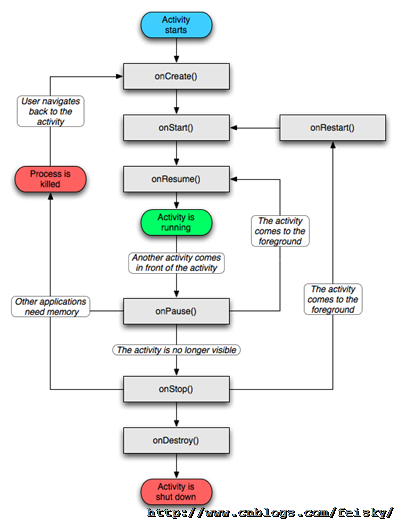
Activity中经常使用的函数有SetContentView() findViewById() finish() startActivity(),其生命周期涉及的函数有:
void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
void onStart()
void onRestart()
void onResume()
void onPause()
void onStop()
void onDestroy()
注意的是,Activity的使用须要在Manifest文件里加入对应的<Activity>。并设置其属性和intent-filter。
Intent
Android中提供了Intent机制来协助应用间的交互与通讯,Intent负责相应用中一次操作的动作、动作涉及数据、附加数据进行描写叙述,Android则依据此Intent的描写叙述。负责找到相应的组件,将 Intent传递给调用的组件,并完毕组件的调用。
Intent不仅可用于应用程序之间。也可用于应用程序内部的Activity/Service之间的交互。
因此。Intent在这里起着一个媒体中介的作用,专门提供组件互相调用的相关信息,实现调用者与被调用者之间的解耦。在SDK中给出了Intent作用的表现形式为:
- 通过
Context.startActivity()Activity.startActivityForResult()
启动一个Activity。 - 通过
Context.startService()Context.bindService()
和后台服务交互。 - 通过广播方法(比方
Context.sendBroadcast()Context.sendOrderedBroadcast()Context.sendStickyBroadcast()
发给broadcast receivers。
Intent属性的设置,包含下面几点:(下面为XML中定义,当然也能够通过Intent类的方法来获取和设置)
(1)Action,也就是要运行的动作
SDk中定义了一些标准的动作,包含
| onstant | Target component | Action |
|---|---|---|
ACTION_CALL |
activity | Initiate a phone call. |
ACTION_EDIT |
activity | Display data for the user to edit. |
ACTION_MAIN |
activity | Start up as the initial activity of a task, with no data input and no returned output. |
ACTION_SYNC |
activity | Synchronize data on a server with data on the mobile device. |
ACTION_BATTERY_LOW |
broadcast receiver | A warning that the battery is low. |
ACTION_HEADSET_PLUG |
broadcast receiver | A headset has been plugged into the device, or unplugged from it. |
ACTION_SCREEN_ON |
broadcast receiver | The screen has been turned on. |
ACTION_TIMEZONE_CHANGED |
broadcast receiver | The setting for the time zone has changed. |
当然,也能够自己定义动作(自己定义的动作在使用时,须要加上包名作为前缀,如"com.example.project.SHOW_COLOR”),并可定义对应的Activity来处理我们的自己定义动作。
(2)Data,也就是运行动作要操作的数据
Android中採用指向数据的一个URI来表示,如在联系人应用中。一个指向某联系人的URI可能为:content://contacts/1。对于不同的动作,其URI数据的类型是不同的(能够设置type属性指定特定类型数据),如ACTION_EDIT指定Data为文件URI。打电话为tel:URI,訪问网络为http:URI,而由content provider提供的数据则为content: URIs。
(3)type(数据类型)。显式指定Intent的数据类型(MIME)。
一般Intent的数据类型可以依据数据本身进行判定,可是通过设置这个属性,可以强制採用显式指定的类型而不再进行推导。
(4)category(类别),被运行动作的附加信息。
比如 LAUNCHER_CATEGORY 表示Intent 的接受者应该在Launcher中作为顶级应用出现;而ALTERNATIVE_CATEGORY表示当前的Intent是一系列的可选动作中的一个,这些动作能够在同一块数据上运行。还有其它的为
| Constant | Meaning |
|---|---|
CATEGORY_BROWSABLE |
The target activity can be safely invoked by the browser to display data referenced by a link — for example, an image or an e-mail message. |
CATEGORY_GADGET |
The activity can be embedded inside of another activity that hosts gadgets. |
CATEGORY_HOME |
The activity displays the home screen, the first screen the user sees when the device is turned on or when the HOME key is pressed. |
CATEGORY_LAUNCHER |
The activity can be the initial activity of a task and is listed in the top-level application launcher. |
CATEGORY_PREFERENCE |
The target activity is a preference panel. |
(5)component(组件)。指定Intent的的目标组件的类名称。通常 Android会依据Intent 中包括的其他属性的信息。比方action、data/type、category进行查找。终于找到一个与之匹配的目标组件。
可是,假设 component这个属性有指定的话,将直接使用它指定的组件,而不再运行上述查找过程。指定了这个属性以后。Intent的其他全部属性都是可选的。
(6)extras(附加信息),是其他全部附加信息的集合。
使用extras能够为组件提供扩展信息,比方。假设要运行“发送电子邮件”这个动作,能够将电子邮件的标题、正文等保存在extras里,传给电子邮件发送组件。
理解Intent的关键之中的一个是理解清楚Intent的两种基本使用方法:一种是显式的Intent,即在构造Intent对象时就指定接收者;还有一种是隐式的Intent。即Intent的发送者在构造Intent对象时,并不知道也不关心接收者是谁,有利于减少发送者和接收者之间的耦合。
对于显式Intent。Android不须要去做解析,由于目标组件已经非常明白,Android须要解析的是那些隐式Intent,通过解析,将 Intent映射给能够处理此Intent的Activity、IntentReceiver或Service。
Intent解析机制主要是通过查找已注冊在AndroidManifest.xml中的全部IntentFilter及当中定义的Intent,终于找到匹配的Intent。在这个解析过程中。Android是通过Intent的action、type、category这三个属性来进行推断的,推断方法例如以下:
- 假设Intent指明定了action,则目标组件的IntentFilter的action列表中就必须包括有这个action。否则不能匹配;
- 假设Intent没有提供type,系统将从data中得到数据类型。
和action一样。目标组件的数据类型列表中必须包括Intent的数据类型。否则不能匹配。
- 假设Intent中的数据不是content: 类型的URI。并且Intent也没有明白指定它的type,将依据Intent中数据的scheme (比方 http: 或者mailto:) 进行匹配。同上,Intent 的scheme必须出如今目标组件的scheme列表中。
- 假设Intent指定了一个或多个category,这些类别必须所有出如今组建的类别列表中。比方Intent中包括了两个类别:LAUNCHER_CATEGORY 和 ALTERNATIVE_CATEGORY。解析得到的目标组件必须至少包括这两个类别。
Intent-Filter的定义
一些属性设置的样例:
<action android:name="com.example.project.SHOW_CURRENT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:mimeType="video/mpeg" android:scheme="http" . . . />
<data android:mimeType="image/*" />
<data android:scheme="http" android:type="video/*" />
完整的实例
<activity android:name="NotesList" android:label="@string/title_notes_list">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.EDIT" />
<action android:name="android.intent.action.PICK" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.google.note" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.GET_CONTENT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Intent使用方法实例
1.无參数Activity跳转
Intent it = new Intent(Activity.Main.this, Activity2.class);
startActivity(it);
2.向下一个Activity传递数据(使用Bundle和Intent.putExtras)
Intent it = new Intent(Activity.Main.this, Activity2.class);
Bundle bundle=new Bundle();
bundle.putString("name", "This is from MainActivity!");
it.putExtras(bundle); // it.putExtra(“test”, "shuju”);
startActivity(it); // startActivityForResult(it,REQUEST_CODE);
对于数据的获取能够採用:
Bundle bundle=getIntent().getExtras();
String name=bundle.getString("name");
3.向上一个Activity返回结果(使用setResult,针对startActivityForResult(it,REQUEST_CODE)启动的Activity)
Intent intent=getIntent();
Bundle bundle2=new Bundle();
bundle2.putString("name", "This is from ShowMsg!");
intent.putExtras(bundle2);
setResult(RESULT_OK, intent);
4.回调上一个Activity的结果处理函数(onActivityResult)
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (requestCode==REQUEST_CODE){
if(resultCode==RESULT_CANCELED)
setTitle("cancle");
else if (resultCode==RESULT_OK) {
String temp=null;
Bundle bundle=data.getExtras();
if(bundle!=null) temp=bundle.getString("name");
setTitle(temp);
}
}
}
以下是转载来的其它的一些Intent使用方法实例(转自javaeye)
显示网页
1. Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://google.com");
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
3. startActivity(it);
显示地图
1. Uri uri = Uri.parse("geo:38.899533,-77.036476");
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
3. startActivity(it);
4. //其它 geo URI 範例
5. //geo:latitude,longitude
6. //geo:latitude,longitude?z=zoom
7. //geo:0,0?q=my+street+address
8. //geo:0,0?q=business+near+city
9. //google.streetview:cbll=lat,lng&cbp=1,yaw,,pitch,zoom&mz=mapZoom
路径规划
1. Uri uri = Uri.parse("http://maps.google.com/maps?f=d&saddr=startLat%20startLng&daddr=endLat%20endLng&hl=en");
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
3. startActivity(it);
4. //where startLat, startLng, endLat, endLng are a long with 6 decimals like: 50.123456
打电话
1. //叫出拨号程序
2. Uri uri = Uri.parse("tel:0800000123");
3. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DIAL, uri);
4. startActivity(it);
1. //直接打电话出去
2. Uri uri = Uri.parse("tel:0800000123");
3. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL, uri);
4. startActivity(it);
5. //用這個,要在 AndroidManifest.xml 中,加上
6. //<uses-permission id="android.permission.CALL_PHONE" />
传送SMS/MMS
1. //调用短信程序
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
3. it.putExtra("sms_body", "The SMS text");
4. it.setType("vnd.android-dir/mms-sms");
5. startActivity(it);
1. //传送消息
2. Uri uri = Uri.parse("smsto://0800000123");
3. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, uri);
4. it.putExtra("sms_body", "The SMS text");
5. startActivity(it);
1. //传送 MMS
2. Uri uri = Uri.parse("content://media/external/images/media/23");
3. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
4. it.putExtra("sms_body", "some text");
5. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_STREAM, uri);
6. it.setType("image/png");
7. startActivity(it);
传送 Email
1. Uri uri = Uri.parse("mailto:xxx@abc.com");
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO, uri);
3. startActivity(it);
1. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
2. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_EMAIL, "me@abc.com");
3. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, "The email body text");
4. it.setType("text/plain");
5. startActivity(Intent.createChooser(it, "Choose Email Client"));
1. Intent it=new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
2. String[] tos={"me@abc.com"};
3. String[] ccs={"you@abc.com"};
4. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_EMAIL, tos);
5. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CC, ccs);
6. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, "The email body text");
7. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT, "The email subject text");
8. it.setType("message/rfc822");
9. startActivity(Intent.createChooser(it, "Choose Email Client"));
1. //传送附件
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
3. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT, "The email subject text");
4. it.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_STREAM, "file:///sdcard/mysong.mp3");
5. sendIntent.setType("audio/mp3");
6. startActivity(Intent.createChooser(it, "Choose Email Client"));
播放多媒体
Uri uri = Uri.parse("file:///sdcard/song.mp3");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
it.setType("audio/mp3");
startActivity(it);
Uri uri = Uri.withAppendedPath(MediaStore.Audio.Media.INTERNAL_CONTENT_URI, "1");
Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(it);
Market 相关
1. //寻找某个应用
2. Uri uri = Uri.parse("market://search?q=pname:pkg_name");
3. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
4. startActivity(it);
5. //where pkg_name is the full package path for an application
1. //显示某个应用的相关信息
2. Uri uri = Uri.parse("market://details?
id=app_id");
3. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
4. startActivity(it);
5. //where app_id is the application ID, find the ID
6. //by clicking on your application on Market home
7. //page, and notice the ID from the address bar
Uninstall 应用程序
1. Uri uri = Uri.fromParts("package", strPackageName, null);
2. Intent it = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DELETE, uri);
3. startActivity(it);
版权声明:本文博主原创文章。博客,未经同意不得转载。
Android Intent机制与常见的用法的更多相关文章
- 最全面的Android Intent机制讲解
对于大型软件开发经验较少的程序员来说,这可能是一个不太容易理解的抽象概念,因为它与我们平常使用的简单函数调用,或者通过库调用接口的方式不太一样.在 Intent 的使用中你看不到直接的函数调用,相对函 ...
- [转]android Intent机制详解
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/t12x3456/article/details/7688154 1.什么是Intent Intent是一种运行时绑定(run-time binding ...
- android Intent机制详解
http://www.oschina.net/question/565065_67909 http://www.cnblogs.com/hummersofdie/archive/2011/02/12/ ...
- 【Android开发日记】之入门篇(十一)——Android的Intent机制
继续我们的Android之路吧.今天我要介绍的是Android的Intent. 对于基于组件的应用开发而言,不仅需要构造和寻找符合需求的组件,更重要的是要将组件有机的连接起来,互联互通交换信息,才能够 ...
- Android总结篇——Intent机制详解及示例总结
最近在进行android开发过程中,在将 Intent传递给调用的组件并完成组件的调用时遇到点困难,并且之前对Intent的学习也是一知半解,最近特意为此拿出一些时间,对Intent部分进行 ...
- Android Intent用法总结
Android中提供了Intent机制来协助应用间的交互与通讯,Intent负责对应用中一次操作的动作.动作涉及数据.附加数据进行描述,Android则根据此Intent的描述,负责找到对应的组件,将 ...
- 【转】Android Activity和Intent机制学习笔记----不错
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/feisky/archive/2010/01/16/1649081.html Activity Android中,Activity是所有程序的根 ...
- Android Activity和Intent机制学习笔记
转自 http://www.cnblogs.com/feisky: Activity Android中,Activity是所有程序的根本,所有程序的流程都运行在Activity之中,Activity具 ...
- Android Intent的几种用法全面总结
Android Intent的几种用法全面总结 Intent, 用法 Intent应该算是Android中特有的东西.你可以在Intent中指定程序要执行的动作(比如:view,edit,dial), ...
随机推荐
- php编码规范个人小结
1.原生态代码或者类的头上,注明作者,关键算法计算过程 例如 /** *@author zengmoumou *功能:根据列表ip,取得ip对应的运营商,省,市,县 */ 2.变量尽量用英文单词的组合 ...
- aspx向silverlight传值
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/lensso/archive/2010/07/27/1785844.html 方法1: 向嵌入aspx页面的silverlight对象添加imnit ...
- C语言中的函数指针
C语言中的函数指针 函数指针的概念: 函数指针是一个指向位于代码段的函数代码的指针. 函数指针的使用: #include<stdio.h> typedef struct (*fun_t ...
- HDU 4435 charge-station (并查集)
先说下题目的意思: 在一个二维坐标系中有N个点,某人要来个走遍所有点的旅行,但是他的车每次加油后只能走M个单位距离:所以要在这个N点中选一些建立加油站:问题来了:i^th 点 建加油站的花费是 2 ...
- Partition List -- LeetCode
原题链接: http://oj.leetcode.com/problems/partition-list/ 这是一道链表操作的题目,要求把小于x的元素按顺序放到链表前面.我们仍然是使用链表最经常使用 ...
- solr与.net课程(七)solr主从复制
既然solr是解决大量数据全文索引的方案,因为高并发的问题,我们就要考虑solr的负载均衡了,solr提供很easy的主从复制的配置方法,那么以下我们就来配置一下solr的主从复制 如果我们在192. ...
- 简单的虚拟摇杆控制移动(NGUI)
一.用NGUI创建虚拟摇杆贴图 先创建一个sprite作为背景叫做JoyStick 并添加一个BoxCollider,再创建一个sprite child作为虚拟摇杆中间的按钮,叫做button 二.通 ...
- .NET Framework 4.0 以上版本 下载地址
https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/5a4x27ek(v=vs.110).aspx
- 构建安全的Xml Web Service系列之wse之证书存储位置
原文:构建安全的Xml Web Service系列之wse之证书存储位置 我们在前几天对xml web service的安全性提出了一些建议,大家可以通过以下地址访问: 构建安全的Xml Web Se ...
- WWDC2014开源
A Cocoa OSX App to help you download WWDC2014 videos 地址:https://github.com/iosxtools/WWDC2014 版权声明:本 ...
