《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example4.11
代码:
b = [1, 0]; a = [1, -0.9]; % %% ----------------------------------------------
%% START a determine H(z) and sketch
%% ----------------------------------------------
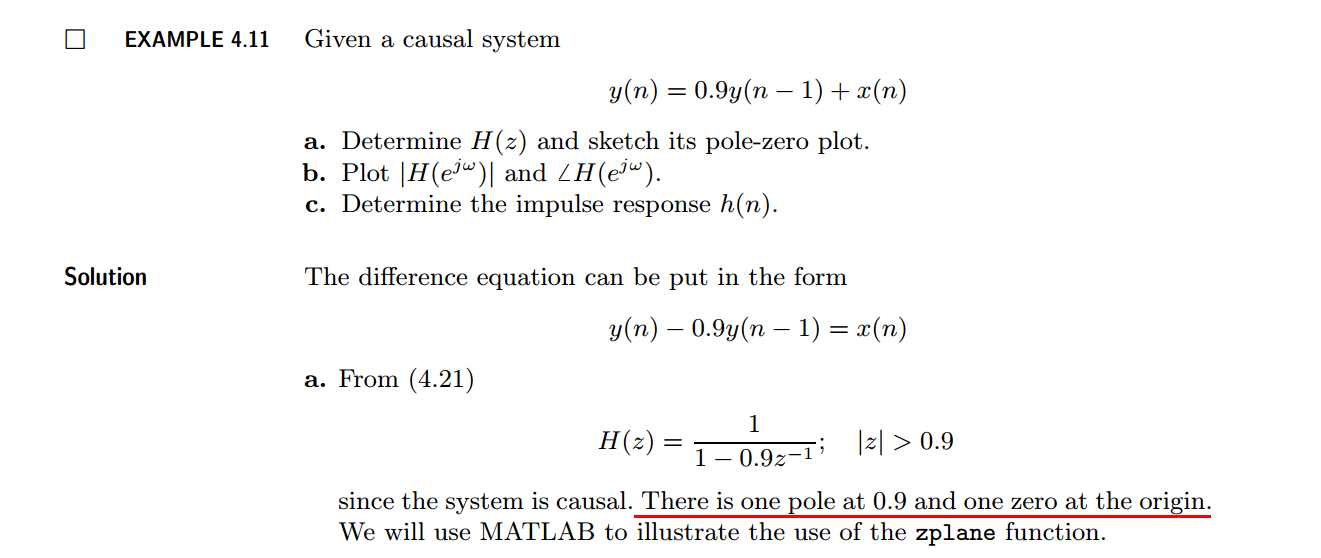
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.11a H(z) its pole-zero plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title('pole-zero plot'); grid on; %% ----------------------------------------------
%% END
%% ---------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 1st form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
[H,w] = freqz(b,a,100); % 1st form of freqz magH = abs(H); angH = angle(H); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.11b H its mag ang real imag');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% --------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 2nd form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
[H,w] = freqz(b,a,200,'whole'); % 2nd form of freqz magH = abs(H(1:101)); angH = angle(H(1:101)); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.11b using 2nd form freqz ');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% --------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 3rd form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
w = [0:1:100]*pi/100; H = freqz(b,a,w);
%[H,w] = freqz(b,a,200,'whole'); % 3rd form of freqz magH = abs(H); angH = angle(H); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
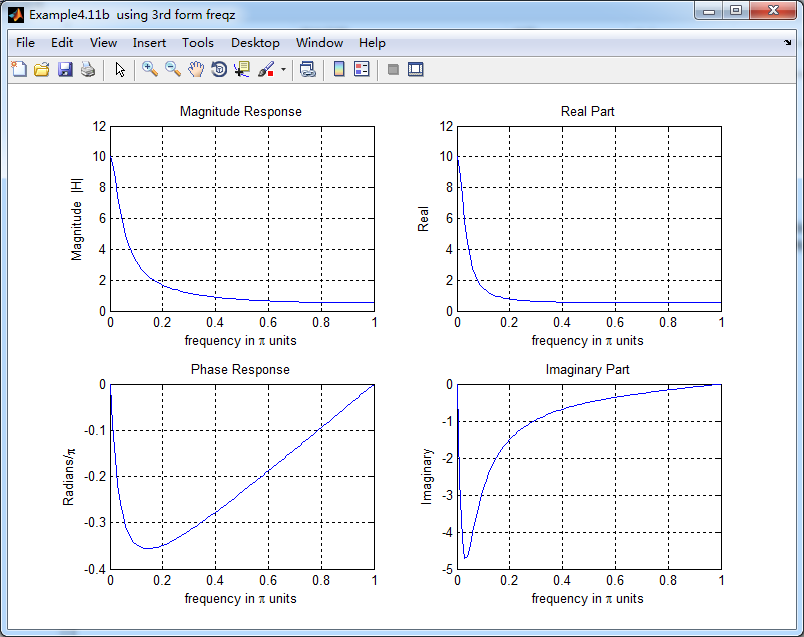
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.11b using 3rd form freqz ');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% ---------------------------------------------------------------
结果:

《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example4.11的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.11
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi an ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example2.11
上代码: b = [1]; a = [1, -1, 0.9]; n = [-20:120]; h = impz(b,a,n); set(gcf,'Color','white'); %subplot(2 ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.8
代码: x = rand(1,11); n = 0:10; k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. X = ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.7
上代码: x1 = rand(1,11); x2 = rand(1,11); n = 0:10; alpha = 2; beta = 3; k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [ ...
- DSP using MATlAB 示例Example2.10
上代码 % noise sequence 1 x = [3, 11, 7, 0, -1, 4, 2]; nx = [-3:3]; % given signal x(n) [y,ny] = sigshi ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
随机推荐
- 【leetcode】Remove Duplicates from Sorted List (easy)
Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appear only once. For examp ...
- DropDownList如何添加一个空白的选项
ddl_class.Items.Insert(0,new ListItem("",""));
- Java Collection、Map集合总结
1.Java中的Collection集合总结 Collection |---List(存储有序,可重复) |---ArrayList 底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢. 线程不安全.效率高 |--- ...
- ios的链式编程笔记
1.Masonry的语法为啥能连续的使用点语法? >> 底层使用的是:用block当函数的返回参数 > 链式编程思想 2. 使用block当函数的返回参数 // 之前开发中比较习惯 ...
- ios 上下拉刷新
UITableView:下拉刷新和上拉加载更多 - cDigger 时间 2013-11-24 02:00:00 博客园精华区 原文 http://www.cnblogs.com/lexingyu ...
- spring AOP 的几种实现方式(能测试)
我们经常会用到的有如下几种 1.基于代理的AOP 2.纯简单Java对象切面 3.@Aspect注解形式的 4.注入形式的Aspcet切面 一.需要的java文件 public class ChenL ...
- Lua程序设计入门
在Lua中,一切都是变量,除了关键字.TTMD强大了. 1.注释 -- 表示注释一行 --[[ ]]表示注释一段代码,相当于C语言的/*....*/ 注意:[[ ... ]]表示一段字符串 2.lua ...
- 《Thinking in Java》十七章_容器深入研究_练习14(Page486)
练习14 Properties的继承树如下:
- Android缓存学习入门(二)
本文主要包括以下内容 内存缓存策略 文件缓存策略 内存缓存策略 当有一个图片要去从网络下载的时候,我们并不会直接去从网络下载,因为在这个时代,用户的流量是宝贵的,耗流量的应用是不会得到用户的青睐的.那 ...
- codevs 1702素数判定2
Miller-Rabin算法实现,但是一直被判题程序搞,输入9999999999得到的结果分明是正确的但是一直说我错 #include <cstdio> #include <cmat ...
