压缩感知重构算法之CoSaMP算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之OMP算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之CoSaMP算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之SP算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之IHT算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之OLS算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之IRLS算法python实现
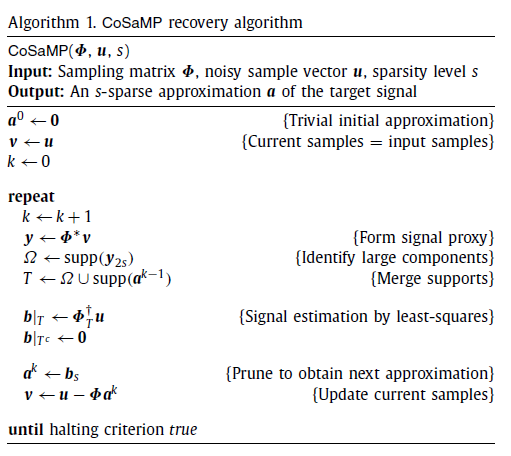
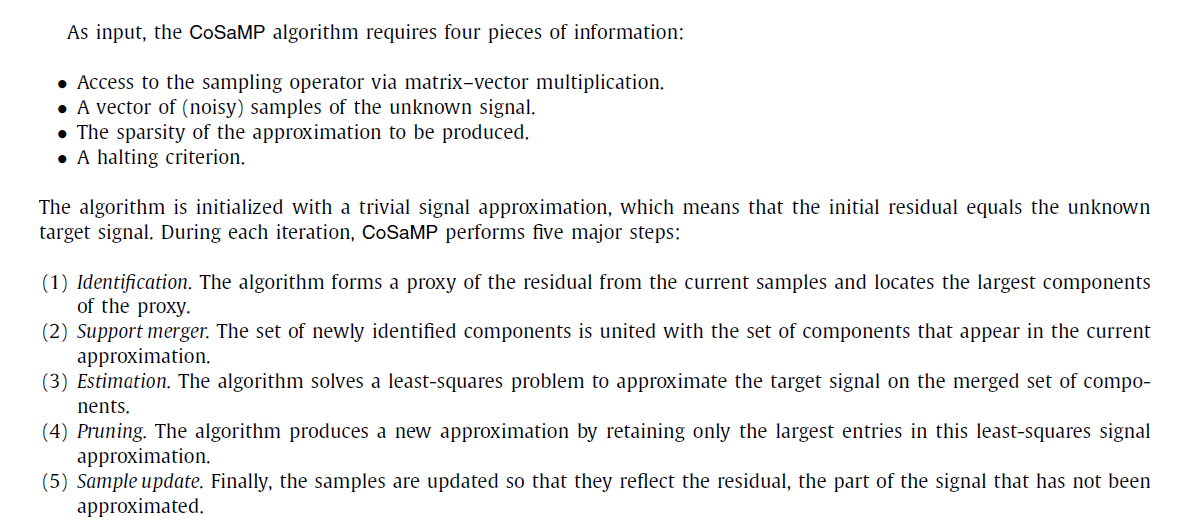
算法流程
算法分析
python代码
要利用python实现,电脑必须安装以下程序
- python (本文用的python版本为3.5.1)
- numpy python包(本文用的版本为1.10.4)
- scipy python包(本文用的版本为0.17.0)
- pillow python包(本文用的版本为3.1.1)
#coding:utf-8
#%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
# DCT基作为稀疏基,重建算法为CoSaMP算法,图像按列进行处理
# 参考文献: D. Deedell andJ. Tropp, “COSAMP: Iterative Signal Recovery from
#Incomplete and Inaccurate Samples,” 2008.
#%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
#导入集成库
import math
# 导入所需的第三方库文件
import numpy as np #对应numpy包
from PIL import Image #对应pillow包
#读取图像,并变成numpy类型的 array
im = np.array(Image.open('lena.bmp'))#图片大小256*256
#生成高斯随机测量矩阵
sampleRate=0.5 #采样率
Phi=np.random.randn(256*sampleRate,256)
# Phi=np.random.randn(256,256)
# u, s, vh = np.linalg.svd(Phi)
# Phi = u[:256*sampleRate,] #将测量矩阵正交化
#生成稀疏基DCT矩阵
mat_dct_1d=np.zeros((256,256))
v=range(256)
for k in range(0,256):
dct_1d=np.cos(np.dot(v,k*math.pi/256))
if k>0:
dct_1d=dct_1d-np.mean(dct_1d)
mat_dct_1d[:,k]=dct_1d/np.linalg.norm(dct_1d)
#随机测量
img_cs_1d=np.dot(Phi,im)
#CoSaMP算法函数
def cs_CoSaMP(y,D):
S=math.floor(y.shape[0]/4) #稀疏度
residual=y #初始化残差
pos_last=np.array([],dtype=np.int64)
result=np.zeros((256))
for j in range(S): #迭代次数
product=np.fabs(np.dot(D.T,residual))
pos_temp=np.argsort(product)
pos_temp=pos_temp[::-1]#反向,得到前面L个大的位置
pos_temp=pos_temp[0:2*S]#对应步骤3
pos=np.union1d(pos_temp,pos_last)
result_temp=np.zeros((256))
result_temp[pos]=np.dot(np.linalg.pinv(D[:,pos]),y)
pos_temp=np.argsort(np.fabs(result_temp))
pos_temp=pos_temp[::-1]#反向,得到前面L个大的位置
result[pos_temp[:S]]=result_temp[pos_temp[:S]]
pos_last=pos_temp
residual=y-np.dot(D,result)
return result
#重建
sparse_rec_1d=np.zeros((256,256)) # 初始化稀疏系数矩阵
Theta_1d=np.dot(Phi,mat_dct_1d) #测量矩阵乘上基矩阵
for i in range(256):
print('正在重建第',i,'列。。。')
column_rec=cs_CoSaMP(img_cs_1d[:,i],Theta_1d) #利用CoSaMP算法计算稀疏系数
sparse_rec_1d[:,i]=column_rec;
img_rec=np.dot(mat_dct_1d,sparse_rec_1d) #稀疏系数乘上基矩阵
#显示重建后的图片
image2=Image.fromarray(img_rec)
image2.show()
matlab代码
function Demo_CS_CoSaMP()
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% the DCT basis is selected as the sparse representation dictionary
% instead of seting the whole image as a vector, I process the image in the
% fashion of column-by-column, so as to reduce the complexity.
% Author: Chengfu Huo, roy@mail.ustc.edu.cn, http://home.ustc.edu.cn/~roy
% Reference: D. Deedell andJ. Tropp, “COSAMP: Iterative Signal Recovery from
% Incomplete and Inaccurate Samples,” 2008.
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%------------ read in the image --------------
img=imread('lena.bmp'); % testing image
img=double(img);
[height,width]=size(img);
%------------ form the measurement matrix and base matrix ---------------
Phi=randn(floor(height/2),width); % only keep one third of the original data
Phi = Phi./repmat(sqrt(sum(Phi.^2,1)),[floor(height/2),1]); % normalize each column
mat_dct_1d=zeros(256,256); % building the DCT basis (corresponding to each column)
for k=0:1:255
dct_1d=cos([0:1:255]'*k*pi/256);
if k>0
dct_1d=dct_1d-mean(dct_1d);
end;
mat_dct_1d(:,k+1)=dct_1d/norm(dct_1d);
end
%--------- projection ---------
img_cs_1d=Phi*img; % treat each column as a independent signal
%-------- recover using omp ------------
sparse_rec_1d=zeros(height,width);
Theta_1d=Phi*mat_dct_1d;
for i=1:width
column_rec=cs_cosamp(img_cs_1d(:,i),Theta_1d,height);
sparse_rec_1d(:,i)=column_rec'; % sparse representation
end
img_rec_1d=mat_dct_1d*sparse_rec_1d; % inverse transform
%------------ show the results --------------------
figure(1)
subplot(2,2,1),imagesc(img),title('original image')
subplot(2,2,2),imagesc(Phi),title('measurement mat')
subplot(2,2,3),imagesc(mat_dct_1d),title('1d dct mat')
psnr = 20*log10(255/sqrt(mean((img(:)-img_rec_1d(:)).^2)));
subplot(2,2,4),imshow(uint8(img_rec_1d));
title(strcat('PSNR=',num2str(psnr),'dB'));
disp('over')
%************************************************************************%
function hat_x=cs_cosamp(y,T_Mat,m)
% y=T_Mat*x, T_Mat is n-by-m
% y - measurements
% T_Mat - combination of random matrix and sparse representation basis
% m - size of the original signal
% the sparsity is length(y)/4
n=length(y); % length of measurements
s=floor(n/4); % sparsity
r_n=y; % initial residuals
sig_pos_lt=[]; % significant pos for last time iteration
for times=1:s % number of iterations
product=abs(T_Mat'*r_n);
[val,pos]=sort(product,'descend');
sig_pos_cr=pos(1:2*s); % significant pos for curretn iteration
sig_pos=union(sig_pos_cr,sig_pos_lt);
Aug_t=T_Mat(:,sig_pos); % current selected entries of T_Mat
aug_x_cr=zeros(m,1);
aug_x_cr(sig_pos)=(Aug_t'*Aug_t)^(-1)*Aug_t'*y; % temp recovered x (sparse)
[val,pos]=sort(abs(aug_x_cr),'descend');
hat_x=zeros(1,m);
hat_x(pos(1:s))=aug_x_cr(pos(1:s));% recovered x with s sparsity
sig_pos_lt=pos(1:s); % refresh the significant positions
r_n=y-T_Mat*hat_x';
end
参考文献
1、D. Deedell andJ. Tropp, “COSAMP: Iterative Signal Recovery from Incomplete and Inaccurate Samples,” 2008.
欢迎python爱好者加入:学习交流群 667279387
压缩感知重构算法之CoSaMP算法python实现的更多相关文章
- 压缩感知重构算法之IRLS算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之OMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之CoSaMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之SP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之IHT算法python实现 压缩感知重构 ...
- 压缩感知重构算法之OLS算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之OMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之CoSaMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之SP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之IHT算法python实现 压缩感知重构 ...
- 压缩感知重构算法之IHT算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之OMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之CoSaMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之SP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之IHT算法python实现 压缩感知重构 ...
- 压缩感知重构算法之SP算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之OMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之CoSaMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之SP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之IHT算法python实现 压缩感知重构 ...
- 压缩感知重构算法之OMP算法python实现
压缩感知重构算法之OMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之CoSaMP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之SP算法python实现 压缩感知重构算法之IHT算法python实现 压缩感知重构 ...
- 压缩感知重构算法之压缩采样匹配追踪(CoSaMP)
压缩采样匹配追踪(CompressiveSampling MP)是D. Needell继ROMP之后提出的又一个具有较大影响力的重构算法.CoSaMP也是对OMP的一种改进,每次迭代选择多个原子,除了 ...
- 浅谈压缩感知(二十三):压缩感知重构算法之压缩采样匹配追踪(CoSaMP)
主要内容: CoSaMP的算法流程 CoSaMP的MATLAB实现 一维信号的实验与结果 测量数M与重构成功概率关系的实验与结果 一.CoSaMP的算法流程 压缩采样匹配追踪(CompressiveS ...
- 浅谈压缩感知(二十八):压缩感知重构算法之广义正交匹配追踪(gOMP)
主要内容: gOMP的算法流程 gOMP的MATLAB实现 一维信号的实验与结果 稀疏度K与重构成功概率关系的实验与结果 一.gOMP的算法流程 广义正交匹配追踪(Generalized OMP, g ...
- 浅谈压缩感知(二十五):压缩感知重构算法之分段正交匹配追踪(StOMP)
主要内容: StOMP的算法流程 StOMP的MATLAB实现 一维信号的实验与结果 门限参数Ts.测量数M与重构成功概率关系的实验与结果 一.StOMP的算法流程 分段正交匹配追踪(Stagewis ...
随机推荐
- egret常用功能
egret常用功能<pre>//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// ...
- (转)白话数字签名(2)——软件&设备
然而它太慢了 非对称加密算法有一个重大缺点——加密速度慢,或者说得更拽一些,编码率比较低.例如在上一篇里我给Clark传的那个1GB的小电影,进行非对称加密足足用了66小时.那个借条小一些吧,也用了将 ...
- 【原创】使用批处理脚本生成包并自动上传到nuget
Hello 大家好,我是TANZAME,我们又见面了. NuGet 是什么这里就不再重复啰嗦,园子里一搜一大把.今天要跟大家分享的是,在日常开发过程中如何统一管理我们的包,如何通过批处理脚本生成包并自 ...
- 【原创】使用批处理脚本自动生成并上传NuGet包
Hello 大家好,我是TANZAME,我们又见面了. NuGet 是什么这里就不再重复啰嗦,园子里一搜一大把.今天要跟大家分享的是,在日常开发过程中如何统一管理我们的包,如何通过批处理脚本生成包并自 ...
- 大学生活这样过,校招 offer 飞来找
01.开门见山 由于我比较喜欢分享的原因,认识了不少大学生.其中有不少佼佼者,比如说一年读 50 本书的璐璐,校招斩获一线大厂 Offer 的晓峰,通过运营公众号实现经济独立的帅土. 当然也有一些不知 ...
- 微擎JS资源请求 403
微擎JS资源请求 403 1.确认JS是否指定 type ==> text/javascript 2.确认src的路径是否正确,{MODULE_URL}项目的根目录带反斜杠 3.实例:(PS:t ...
- opencv之常用还是忘,那咋办嘛
相机标定:https://blog.csdn.net/y2c58s43d69g8h7G_g/article/details/97239418 畸变参数个数要是镜头太凸的话,就像鱼眼相机和哨兵150视角 ...
- 【并发编程】Java对并发编程的支持历史
本博客系列是学习并发编程过程中的记录总结.由于文章比较多,写的时间也比较散,所以我整理了个目录贴(传送门),方便查阅. 并发编程系列博客传送门 本文转载,原文请点击链接 本章主要对Java并发(Con ...
- ASP.NET Core gRPC 使用 Consul 服务注册发现
一. 前言 gRPC 在当前最常见的应用就是在微服务场景中,所以不可避免的会有服务注册与发现问题,我们使用gRPC实现的服务可以使用 Consul 或者 etcd 作为服务注册与发现中心,本文主要介绍 ...
- Win 使用终端创建mysql数据库及使用(5)
删除你创建过的数据库newsql里面的所有表 这里必须安装了mysql,并且知道用户名密码IP地址.因为我用的window,所以只介绍Win使用cmd创建的方式 首先windown+R 出现窗口输入c ...