吴裕雄 python 机器学习-Logistic(1)
import numpy as np def loadDataSet():
dataMat = []
labelMat = []
fr = open('D:\\LearningResource\\machinelearninginaction\\Ch05\\testSet.txt')
for line in fr.readlines():
lineArr = line.strip().split()
dataMat.append([1.0, float(lineArr[0]), float(lineArr[1])])
labelMat.append(int(lineArr[2]))
return dataMat,labelMat dataMat,labelMat = loadDataSet()
print(dataMat)
print(labelMat)

def sigmoid(z):
sigmoid = 1.0/(1+np.exp(-z))
return sigmoid def gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels):
dataMatrix = np.mat(dataMatIn)
labelMat = np.mat(classLabels).transpose()
m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix)
alpha = 0.001
maxCycles = 500
weights = np.ones((n,1))
for k in range(maxCycles):
h = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weights)
error = (labelMat - h)
weights = weights + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose()* error
return weights weights = gradAscent(dataMat,labelMat)
print(weights)

def stocGradAscent0(dataMatrix, classLabels):
m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix)
alpha = 0.01
weights = np.ones(n)
for i in range(m):
h = sigmoid(sum(np.array(dataMatrix[i])*weights))
error = classLabels[i] - h
weights = weights + alpha * error * np.array(dataMatrix[i])
return weights weights = stocGradAscent0(dataMat,labelMat)
print(weights)
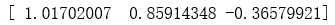
def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrix, classLabels, numIter=150):
m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix)
weights = np.ones(n)
for j in range(numIter):
dataIndex = list(range(m))
for i in range(m):
alpha = 4/(1.0+j+i)+0.0001
randIndex = int(np.random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))
h = sigmoid(sum(np.array(dataMatrix[randIndex])*weights))
error = classLabels[randIndex] - h
weights = weights + alpha * error * np.array(dataMatrix[randIndex])
del(dataIndex[randIndex])
return weights weights = stocGradAscent1(dataMat,labelMat)
print(weights)
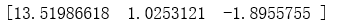
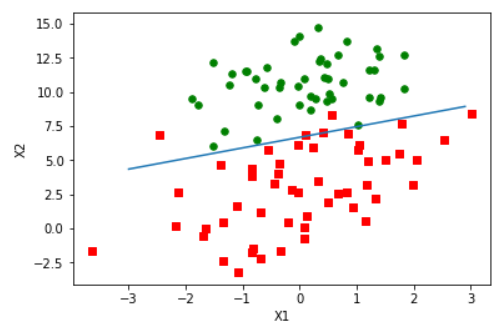
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def plotBestFit():
dataMat,labelMat=loadDataSet()
weights = gradAscent(dataMat,labelMat)
dataArr = np.array(dataMat)
n = np.shape(dataArr)[0]
xcord1 = []
ycord1 = []
xcord2 = []
ycord2 = []
for i in range(n):
if(int(labelMat[i])== 1):
xcord1.append(dataArr[i,1])
ycord1.append(dataArr[i,2])
else:
xcord2.append(dataArr[i,1])
ycord2.append(dataArr[i,2])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s=30, c='red', marker='s')
ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s=30, c='green')
x = np.arange(-3.0, 3.0, 0.1)
y = (-weights[0]-weights[1]*x)/weights[2]
y = np.array(y).reshape(len(x))
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('X1')
plt.ylabel('X2');
plt.show() plotBestFit()
def classifyVector(z, weights):
prob = sigmoid(sum(z*weights))
if(prob > 0.5):
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0 def colicTest():
frTrain = open('D:\\LearningResource\\machinelearninginaction\\Ch05\\horseColicTraining.txt')
frTest = open('D:\\LearningResource\\machinelearninginaction\\Ch05\\horseColicTest.txt')
trainingSet = []
trainingLabels = []
for line in frTrain.readlines():
currLine = line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr =[]
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
trainingSet.append(lineArr)
trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21]))
trainWeights = stocGradAscent1(np.array(trainingSet), trainingLabels, 1000)
errorCount = 0
numTestVec = 0.0
for line in frTest.readlines():
numTestVec += 1.0
currLine = line.strip().split('\t')
lineArr =[]
for i in range(21):
lineArr.append(float(currLine[i]))
if(int(classifyVector(np.array(lineArr), trainWeights))!= int(currLine[21])):
errorCount += 1
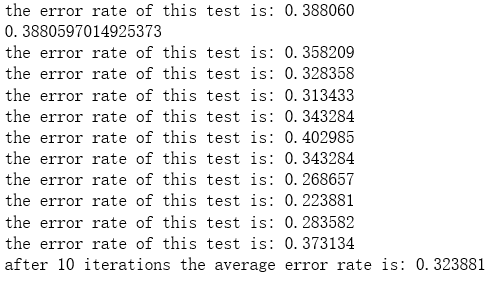
errorRate = (float(errorCount)/numTestVec)
print("the error rate of this test is: %f" % errorRate)
return errorRate errorRate = colicTest()
print(errorRate) def multiTest():
numTests = 10
errorSum=0.0
for k in range(numTests):
errorSum += colicTest()
print("after %d iterations the average error rate is: %f" % (numTests, errorSum/float(numTests))) multiTest()
吴裕雄 python 机器学习-Logistic(1)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——人工神经网络感知机学习算法的应用
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from sklearn import neighbors, datasets from ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——分类决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——回归决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——线性判断分析LinearDiscriminantAnalysis
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm from mpl_toolkits.mplot ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——逻辑回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm from mpl_toolkits.mplot ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——ElasticNet回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import cm from mpl_toolkits.mplot ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——Lasso回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model from s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——岭回归
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model from s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——线性回归模型
import numpy as np from sklearn import datasets,linear_model from sklearn.model_selection import tra ...
随机推荐
- Windows Server 2016 启用完整版任务管理器
众所周知 Windows Server 2012以上的任务管理器是被阉割过的 那么如何启用呢?首先把你的任务管理器复制一份出来位置:系统盘\Windows\System32\Taskmgr.exe和系 ...
- 使用路由和远程访问服务为Hyper-V中虚拟机实现NAT上网
众所周知,在微软的Hyper-V环境中的网络环境中没有VMware Workstation中的NAT功能,所以Hyper-V环境中虚拟机上网一般情况下需要通过设置为外部网络方可访问网络,当然也可设置为 ...
- css(层叠样式表)属性
CSS属性相关 宽和高 width属性可以为元素设置宽度. height属性可以为元素设置高度. 块级标签才能设置宽度,内联标签的宽度由内容来决定. 字体属性 文字字体 font-family可以把多 ...
- python 中logging模块
logging的作用:python中,logging模块主要是处理日志的.所谓日志,可理解为在软件运行过程中,所记录的的一些运行情况信息,软件开发人员可以根据自己的需求添加日志,日志可以帮助软件开发人 ...
- WPF Stake
WPF中的StackPanel.WrapPanel.DockPanel 转:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6c81891701017a34.html StackPane ...
- git 使用教程(二)
MyEclipse下使用GitHub方法(Eclipse同理) 原创 2016年01月04日 20:30:25 标签: myeclipse / 软件 / git / github / eclipse ...
- 自写UiAutomator 调试类
package sms_test; import java.lang.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; impor ...
- 28.纯 CSS 绘制一个世界上不存在的彭罗斯三角形
原文地址:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000014946883 感想:三个平面图形旋转 HTML代码: <!-- penrose: 彭罗斯 --> < ...
- Cannot invoke Tomcat manager: socket write error
一开始, 参照 http://www.cnblogs.com/yezhenhan/archive/2012/07/17/2594684.html mvn tomcat:redeploy 出现: Can ...
- Flex4学习笔记2--代码保存在单独的文件中
1 <!--调用外部as文件--> <fx:Script> <![CDATA[ import mx.controls.Alert; import a.Test3; ]]& ...
