Flink学习(三)状态机制于容错机制,State与CheckPoint
摘自Apache官网
一、State的基本概念
什么叫State?搜了一把叫做状态机制。可以用作以下用途。为了保证 at least once, exactly once,Flink引入了State和Checkpoint
- 某个task/operator某时刻的中间结果
- 快照(snapshot)
- 程序一旦crash,恢复用的
- 机器学习模型的参数
二、Flink中包含的State
Keyed State和Opreator State
1、Keyed State基于KeyedStream的状态。这个状态是跟特定的key绑定的。对KeyedStream流上的每一个key,可能都对应一个state。
2、Operator State。于Keyed State不同。Operator State根一个特定的Operator绑定。整个Operator对应一个State。相比较而言一个State上有多个Keyed State。举例子来说,在Flink中的Kafka Connector就使用了Operator State。会在每个connector实例中,保存该实例中消费topic的所有(partition, offset)映射。
一些原子State
ValueState:即类型为T的单值状态。这个状态与对应的key绑定,是最简单的状态了。它可以通过update方法更新状态值,通过value()方法获取状态值。
ListState:即key上的状态值为一个列表。可以通过add方法往列表中附加值;也可以通过get()方法返回一个Iterable<T>来遍历状态值。
ReducingState:这种状态通过用户传入的reduceFunction,每次调用add方法添加值的时候,会调用reduceFunction,最后合并到一个单一的状态值。
MapState:即状态值为一个map。用户通过put或putAll方法添加元素。
上述的State仅仅与状态进行交互。而真正的状态值,有可能是存在内存,磁盘、或者其它分布式系统中。相当于只是我们持有了这个句柄。那么我们如何得到这个状态的句柄呢?Flink通过StateDescriptor来定义一个状态。这是一个抽象类,内部定义了状态名称、类型、序列化器等基础信息。与上面的状态对应、从StateDescriptor派生了ValueStateDescriptor,ListStateDescriptor等descriptor。
3、研究下Keyed State内部的结构
在StreamingRuntimeContext这个类中可以看到各个State的get方法
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.apache.flink.streaming.api.operators; import org.apache.flink.annotation.PublicEvolving;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.accumulators.Accumulator;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.BroadcastVariableInitializer;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.util.AbstractRuntimeUDFContext;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.AggregatingState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.AggregatingStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.FoldingState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.FoldingStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.KeyedStateStore;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ListState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ListStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.MapState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.MapStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ReducingState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ReducingStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.StateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueState;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.ValueStateDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.runtime.execution.Environment;
import org.apache.flink.runtime.jobgraph.tasks.InputSplitProvider;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.CheckpointingMode;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.graph.StreamConfig;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.ProcessingTimeService;
import org.apache.flink.util.Preconditions; import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; /**
* Implementation of the {@link org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RuntimeContext},
* for streaming operators.
*/
@PublicEvolving
public class StreamingRuntimeContext extends AbstractRuntimeUDFContext { /** The operator to which this function belongs. */
private final AbstractStreamOperator<?> operator; /** The task environment running the operator. */
private final Environment taskEnvironment; private final StreamConfig streamConfig; public StreamingRuntimeContext(AbstractStreamOperator<?> operator,
Environment env, Map<String, Accumulator<?, ?>> accumulators) {
super(env.getTaskInfo(),
env.getUserClassLoader(),
operator.getExecutionConfig(),
accumulators,
env.getDistributedCacheEntries(),
operator.getMetricGroup()); this.operator = operator;
this.taskEnvironment = env;
this.streamConfig = new StreamConfig(env.getTaskConfiguration());
} // ------------------------------------------------------------------------ /**
* Returns the input split provider associated with the operator.
*
* @return The input split provider.
*/
public InputSplitProvider getInputSplitProvider() {
return taskEnvironment.getInputSplitProvider();
} public ProcessingTimeService getProcessingTimeService() {
return operator.getProcessingTimeService();
} // ------------------------------------------------------------------------
// broadcast variables
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ @Override
public boolean hasBroadcastVariable(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Broadcast variables can only be used in DataSet programs");
} @Override
public <RT> List<RT> getBroadcastVariable(String name) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Broadcast variables can only be used in DataSet programs");
} @Override
public <T, C> C getBroadcastVariableWithInitializer(String name, BroadcastVariableInitializer<T, C> initializer) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Broadcast variables can only be used in DataSet programs");
} // ------------------------------------------------------------------------
// key/value state
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------ @Override
public <T> ValueState<T> getState(ValueStateDescriptor<T> stateProperties) {
KeyedStateStore keyedStateStore = checkPreconditionsAndGetKeyedStateStore(stateProperties);
stateProperties.initializeSerializerUnlessSet(getExecutionConfig());
return keyedStateStore.getState(stateProperties);
} @Override
public <T> ListState<T> getListState(ListStateDescriptor<T> stateProperties) {
KeyedStateStore keyedStateStore = checkPreconditionsAndGetKeyedStateStore(stateProperties);
stateProperties.initializeSerializerUnlessSet(getExecutionConfig());
return keyedStateStore.getListState(stateProperties);
} @Override
public <T> ReducingState<T> getReducingState(ReducingStateDescriptor<T> stateProperties) {
KeyedStateStore keyedStateStore = checkPreconditionsAndGetKeyedStateStore(stateProperties);
stateProperties.initializeSerializerUnlessSet(getExecutionConfig());
return keyedStateStore.getReducingState(stateProperties);
} @Override
public <IN, ACC, OUT> AggregatingState<IN, OUT> getAggregatingState(AggregatingStateDescriptor<IN, ACC, OUT> stateProperties) {
KeyedStateStore keyedStateStore = checkPreconditionsAndGetKeyedStateStore(stateProperties);
stateProperties.initializeSerializerUnlessSet(getExecutionConfig());
return keyedStateStore.getAggregatingState(stateProperties);
} @Override
public <T, ACC> FoldingState<T, ACC> getFoldingState(FoldingStateDescriptor<T, ACC> stateProperties) {
KeyedStateStore keyedStateStore = checkPreconditionsAndGetKeyedStateStore(stateProperties);
stateProperties.initializeSerializerUnlessSet(getExecutionConfig());
return keyedStateStore.getFoldingState(stateProperties);
} @Override
public <UK, UV> MapState<UK, UV> getMapState(MapStateDescriptor<UK, UV> stateProperties) {
KeyedStateStore keyedStateStore = checkPreconditionsAndGetKeyedStateStore(stateProperties);
stateProperties.initializeSerializerUnlessSet(getExecutionConfig());
return keyedStateStore.getMapState(stateProperties);
} private KeyedStateStore checkPreconditionsAndGetKeyedStateStore(StateDescriptor<?, ?> stateDescriptor) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(stateDescriptor, "The state properties must not be null");
KeyedStateStore keyedStateStore = operator.getKeyedStateStore();
Preconditions.checkNotNull(keyedStateStore, "Keyed state can only be used on a 'keyed stream', i.e., after a 'keyBy()' operation.");
return keyedStateStore;
} // ------------------ expose (read only) relevant information from the stream config -------- // /**
* Returns true if checkpointing is enabled for the running job.
*
* @return true if checkpointing is enabled.
*/
public boolean isCheckpointingEnabled() {
return streamConfig.isCheckpointingEnabled();
} /**
* Returns the checkpointing mode.
*
* @return checkpointing mode
*/
public CheckpointingMode getCheckpointMode() {
return streamConfig.getCheckpointMode();
} /**
* Returns the buffer timeout of the job.
*
* @return buffer timeout (in milliseconds)
*/
public long getBufferTimeout() {
return streamConfig.getBufferTimeout();
} }
所有的State都继承自StateDescpritor这个类。简单看一下构造函数。实际上包含了三个参数,
- 名称
- 类型--属于哪一类state
- 默认值
protected StateDescriptor(String name, Class<T> type, T defaultValue) {
this.name = requireNonNull(name, "name must not be null");
requireNonNull(type, "type class must not be null");
try {
this.typeInfo = TypeExtractor.createTypeInfo(type);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Could not create the type information for '" + type.getName() + "'. " +
"The most common reason is failure to infer the generic type information, due to Java's type erasure. " +
"In that case, please pass a 'TypeHint' instead of a class to describe the type. " +
"For example, to describe 'Tuple2<String, String>' as a generic type, use " +
"'new PravegaDeserializationSchema<>(new TypeHint<Tuple2<String, String>>(){}, serializer);'", e);
}
this.defaultValue = defaultValue;
}
再具体的可以自己研究研究,建议工作遇到或者对源码有兴趣可以读读。或者结合实际应用理解下会更快
三、容错机制
1、Flink的核心容错机制是不断的给数据流绘制Snapshots。当系统回滚的时候,这些snapshots就扮演了checkpoints的作用。快照机制受Chandy-Lamport 算法的启发。
读了下论文研究了下这个算法。英文的看不太懂。找了个中文的。
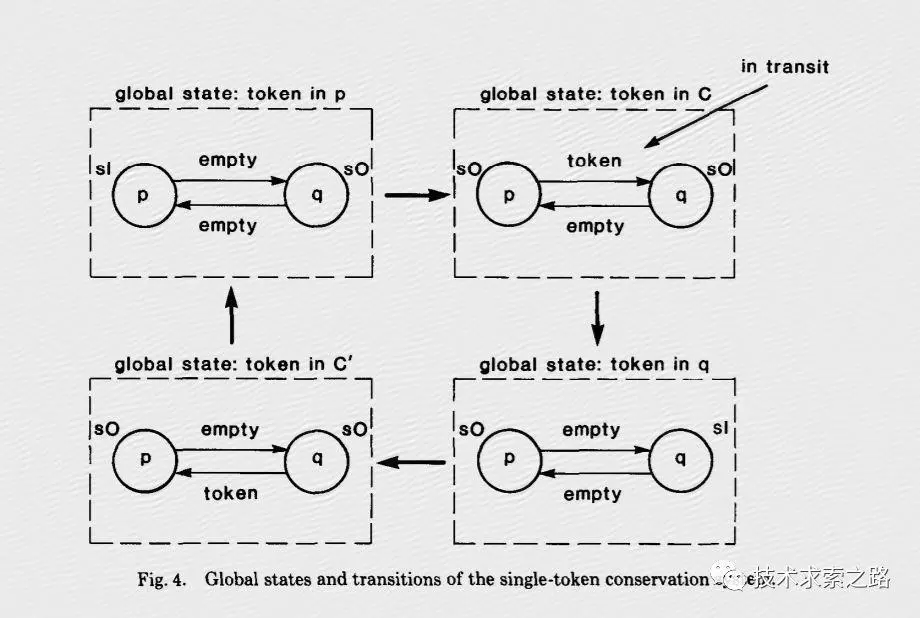
大概就是通过token 和marker来判断是哪里出了问题和需要恢复。
具体可以参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/938001e998f5
Flink学习(三)状态机制于容错机制,State与CheckPoint的更多相关文章
- 总结Flink状态管理和容错机制
本文来自8月11日在北京举行的 Flink Meetup会议,分享来自于施晓罡,目前在阿里大数据团队部从事Blink方面的研发,现在主要负责Blink状态管理和容错相关技术的研发. 本文主要内容如 ...
- Flink状态管理和容错机制介绍
本文主要内容如下: 有状态的流数据处理: Flink中的状态接口: 状态管理和容错机制实现: 阿里相关工作介绍: 一.有状态的流数据处理# 1.1.什么是有状态的计算# 计算任务的结果不仅仅依赖于输入 ...
- Flink的状态编程和容错机制(四)
一.状态编程 Flink 内置的很多算子,数据源 source,数据存储 sink 都是有状态的,流中的数据都是 buffer records,会保存一定的元素或者元数据.例如 : ProcessWi ...
- Flink资料(2)-- 数据流容错机制
数据流容错机制 该文档翻译自Data Streaming Fault Tolerance,文档描述flink在流式数据流图上的容错机制. ------------------------------- ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记(4):Hystrix容错机制
简介 在微服务架构中,微服务之间的依赖关系错综复杂,难免的某些服务会出现故障,导致服务调用方出现远程调度的线程阻塞.在高负载的场景下,如果不做任何处理,可能会引起级联故障,导致服务调用方的资源耗尽甚至 ...
- 入门大数据---Flink学习总括
第一节 初识 Flink 在数据激增的时代,催生出了一批计算框架.最早期比较流行的有MapReduce,然后有Spark,直到现在越来越多的公司采用Flink处理.Flink相对前两个框架真正做到了高 ...
- Flink 容错机制与状态
简介 Apache Flink提供了一种容错机制,可以持续恢复数据流应用程序的状态. 该机制确保即使出现故障,经过恢复,程序的状态也会回到以前的状态. Flink 主持 at least once 语 ...
- 关于 Flink 状态与容错机制
Flink 作为新一代基于事件流的.真正意义上的流批一体的大数据处理引擎,正在逐渐得到广大开发者们的青睐.就从我自身的视角看,最近也是在数据团队把一些原本由 Flume.SparkStreaming. ...
- Storm学习笔记 - 消息容错机制
Storm学习笔记 - 消息容错机制 文章来自「随笔」 http://jsynk.cn/blog/articles/153.html 1. Storm消息容错机制概念 一个提供了可靠的处理机制的spo ...
随机推荐
- vue-router(hash模式)常见问题以及解决方法
问题一:// 动态路由/detail/:id 问题:动态路由跳转的时候,页面是不刷新的,相信很多人都遇到了相同的问题解决方法:在全局的router-view组件上设置一个key值,此key值为一个时间 ...
- React Router路由传参方式总结
首先我们要知道一个前提,路由传递的参数我们可以通过props里面的属性来获取.只要组件是被<Router>组件的<component>定义和指派的,这个组件自然就有了props ...
- 文本分类实战(四)—— Bi-LSTM模型
1 大纲概述 文本分类这个系列将会有十篇左右,包括基于word2vec预训练的文本分类,与及基于最新的预训练模型(ELMo,BERT等)的文本分类.总共有以下系列: word2vec预训练词向量 te ...
- 《通过C#学Proto.Actor模型》之Mailbox
邮箱是Actor模型的一个重要组成部分,负责接收发过来的消息,并保存起来,等待Actor处理.邮箱中维护着两种队列,一种是存系统消息,另一个是存用户消息,系统省是指Started,Stoping,St ...
- zsh : command not found pip3 的解决方案
问题描述 在 zsh 中执行 pip xxx ,出现错误 zsh: command not found: pip3 . 当然我很确定自己是有安装 pip3 的,应该是应该切换了shell,导致环境变量 ...
- iview render input每输入一个字符就会自动跳出焦点
假如你绑定的table的数据是tableData,input数据改变的时候你把整行的数据替换掉,就不会造成table重新渲染,导致input失焦了 h('InputNumber', { props: ...
- LODOP直线px转换mm变斜线
LODOP中打印项顶边距左边距,宽高,可以选择的单位很多,详细可在LODOP官网下载参考LODOP技术手册. 关于LODOP打印直线和虚线,可查看本博客相关博文:Lodop如何打印直线.Lodop打印 ...
- bis和bic命令实现或和异或运算
从20世纪70年代末到80年代末,Digital Equipment的VAX计算机是一种非常流行的机型.它没有布尔运算AND和OR指令,只有bis(位设置)和bic(位清除)这两种指令.两种指令的输入 ...
- Announcing Microsoft Research Open Data – Datasets by Microsoft Research now available in the cloud
The Microsoft Research Outreach team has worked extensively with the external research community to ...
- Google Translation Via Python
没什么好说的,直接送包 https://github.com/mouuff/mtranslate
