手写promise之分步解析
promise是es6推出适用于异步请求的构造函数,帮助解决回调地狱的问题,以下内容将自定义实现promise,只包括基本使用,所以一些边界情况考虑没有在内。
如果对promise用法还不熟悉的朋友可移步
Promise的理解与使用(一)
Promise的理解和使用(二)
executor
首先建立promise的基本结构
定义构造函数
promise的executor部分是放到主线程中直接执行的
class icePromise {
constructor(executor){
const resolve = () => {
console.log('resolve被调用')
}
const reject = () => {
console.log('reject被调用')
}
}
executor(resolve, reject)
}
const promise = new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
resolve()
})
定义状态
1、定义常量
const STATUS_PENDING = 'pending'
const STATUS_FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const STATUS_REJECTED = 'rejected'
2、通过构造函数创建实例时,就应该需要状态,所以在类中定义
this.status = STATUS_PENDING
3、resolve和reject方法里通过状态判断
当为pending时,才能执行resolve或者reject方法,执行前先修改状态
then方法
onFulfilled/onRejected中要执行then里面的回调函数,将两个函数绑定到实例的属性上
1、在类中定义一个then方法
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
this.onFulfilled = onFulfilled
this.onRejected = onRejected
}
2、在resolve和reject中分别执行this.onFulfilled和this.onRejected中
此时会报错,因为executor会立刻执行,而then里面的函数是微任务,
会在主线程执行完成之后执行
3、resolve和reject中加入 queueMicrotask (微任务)
整体架构的初版就完成了
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.onFulfilled(value);
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.onRejected(reason);
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
this.onFulfilled = onFulfilled;
this.onRejected = onRejected;
}
}
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("resolve");
reject("reject");
});
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("success1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("fail1", reason);
}
);
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("success2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("fail2", reason);
}
);
返回两次promise的状态,只执行第一个resolve,then方法中对应执行的成功或者失败的函数也正确
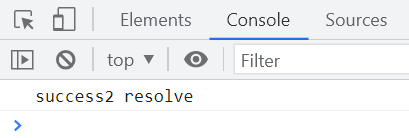
但存在的问题是,执行两次then方法,只执行了第二个,以下对then方法进行优化。
then
解决多次调用then方法的问题
1、constructor中定义变量用于收集所有的成功/失败的回调函数
this.onFulfilledCallbacks = []
this.onRejectedCallbacks = []
2、 在then方法中通过push添加到数组中
this.onFulfilledCallbacks.push()
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push()
3、在resolve和reject中遍历
this.onFulfilledCallbacks和this.onRejectedCallbacks中的方法
此时代码如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(onFulfilled);
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected);
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("resolve---");
reject("----reject");
});
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err2", reason);
}
);
// 确定状态后再调用
setTimeout(() => {
promise.then(
(res) => {
console.log("res3", res);
},
(err) => {
console.log("err3", err);
}
);
}, 1000);
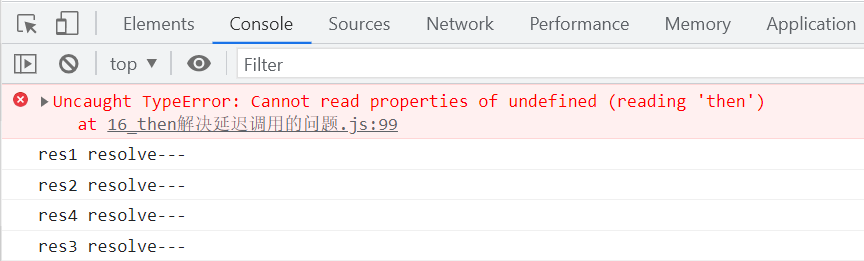
解决then的多次调用的问题,但仍有其它的问题,一个是resolve和reject方法同时执行,二是通过定时器延迟执行的promise的then方法没有输出响应结果

解决延迟调用的问题
1、保存value和reason
this.value = undefined
this.reason = undefined
resolve和reject方法分别给this.value和this.reason赋值
2、then方法中进行状态的判断
当状态为pending时,继续向onFulfilledCallbacks、onRejectedCallbacks数组中添加函数;当状态不为pending时,直接执行onFulfilled或onRejected方法
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
onRejected(this.reason);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(onFulfilled);
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected);
}
3、pending状态的变化
① queueMicrotask中判断不为pending则return
② 修改pending状态
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
onRejected(this.reason);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(onFulfilled);
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(onRejected);
}
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("resolve---");
reject("----reject");
});
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err2", reason);
}
);
// 确定状态后再调用
setTimeout(() => {
promise.then(
(res) => {
console.log("res3", res);
},
(err) => {
console.log("err3", err);
}
);
}, 1000);
promise.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res4", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err4", reason);
}
).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res5", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err5", reason);
}
)
解决了resolve和reject多次调用及计时器延迟调用的问题,但此时发现then无法进行链式调用
解决链式调用的问题
1、then方法里返回一个 new icePromise,将判断逻辑放进去
2、this.onFulfilledCallbacks 和 this.onRejectedCallbacks 传入回调函数,
回调函数返回resolve或者reject函数的执行结果
3、封装工具函数,用于处理try catch
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("resolve---");
reject("----reject");
});
promise
.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err2", reason);
}
)
.then(
(res) => {
console.log("res3", res);
},
(err) => {
console.log("err3", err);
}
);
此时then函数就已经可以链式调用啦,基本功能已经实现~
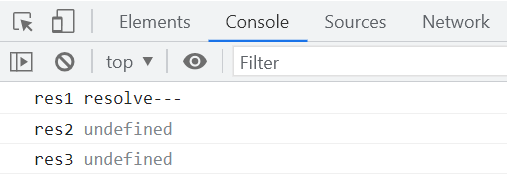
catch
catch函数接收一个失败的回调
1、调用then方法,将onRejected方法加到第二个promise的回调中
catch(onRejected){
this.then(null, onRejected)
}
2、then方法中对传入的 onRejected进行判断,当没有传递时,就抛出异常
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
整体实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
}
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
reject("----reject");
resolve("resolve---");
});
// 测试代码
promise
.then((value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
})
.then((value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log("catch", error);
});
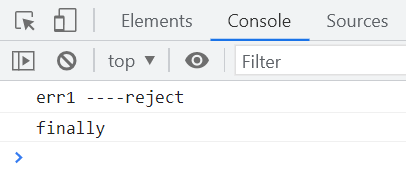
执行结果如下
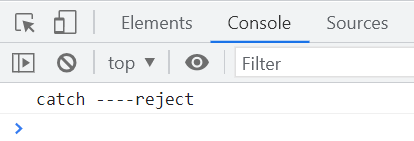
finally
finally方法无论执行resolve或者reject的方法后都会执行
finally(onFinally){
this.then(()=>{
onFinally()
}, ()=>{
onFinally()
})
}
整体实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
this.then(
() => {
onFinally();
},
() => {
onFinally();
}
);
}
}
// 测试代码
const promise = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
reject("----reject");
});
promise
.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
.finally(() => {
console.log("finally");
});
resolve/reject
resolve和reject是Promise的类方法,也可以通过调用then方法来实现
static resolve(value){
return new icePromise((resolve)=>resolve(value))
}
static reject(reason){
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>reject(reason))
}
完整实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
this.then(
() => {
onFinally();
},
() => {
onFinally();
}
);
}
static resolve(value) {
return new Promise((onResolve) => {
onResolve(value);
});
}
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((onResolve, onRejected) => {
onRejected(reason);
});
}
}
// 测试代码
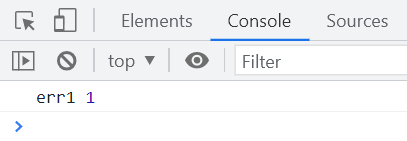
const promise = Promise.reject(1);
promise
.then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
)
执行结果如下
all/allSettled
all和allSettled方法都是promise的类方法
1、all方法
只要有一个promise执行reject的方法就会执行reject,当所有promise都返回resolve时,才执行resolve方法。
2、allSettled方法
当所有promise都执行完成时,才执行resolve方法,返回所有promise的状态和结果。
static all(promise){
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
const values = []
promises.forEach(promise => {
promise.then(res => {
values.push(res)
if (values.length === promises.length) {
resolve(values)
}
}, err => {
reject(err)
})
})
})
})
}
static allSettled(promise){
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
const values = []
promise.then(res=>{
values.push({ status: '', value: '' })
if(values.length === promise.length){
resolve(values)
}
}, err=>{
values.push({ status: '', value: '' })
if(values.length === promise.length){
resolve(values)
}
})
})
}
完整实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
this.then(
() => {
onFinally();
},
() => {
onFinally();
}
);
}
static resolve(value) {
return new Promise((onResolve) => {
onResolve(value);
});
}
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((onResolve, onRejected) => {
onRejected(reason);
});
}
static all(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(
(value) => {
result.push(value);
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(reason) => {
reject(reason);
}
);
});
});
}
static allSettled(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(
(value) => {
result.push({
status: STATUS_FULFILLED,
value,
});
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(reason) => {
result.push({
status: STATUS_REJECTED,
reason,
});
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
}
);
});
});
}
}
// 测试代码
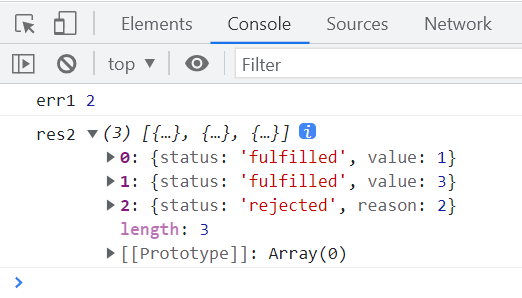
const promise1 = IcePromise.resolve(1);
const promise2 = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(2);
});
});
const promise3 = IcePromise.resolve(3);
IcePromise.all([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
);
IcePromise.allSettled([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res2", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err2", reason);
}
);
执行结果如下
race/any
race和any都是promise的类方法。
1、race方法
只要有一个promise执行完成,就会返回它所执行的结果
2、any方法
① 有fulfilled状态,会等到这个fullfilled执行完成,执行resolve,结果为value
② 如果所有的Promise都是reject的,那么也会等到所有的Promise都变成rejected状态后报一个AggregateError的错误。
static race(promises){
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
promises.forEach(promise=>{
promise.then(resolve, reject)
})
})
}
static any(promises){
const reasons = []
return new icePromise((resolve, reject)=>{
promises.forEach(promise=>{
promise.then(resolve, err=>{
reasons.push(err)
if(reasons.length === promises.length){
reject(new AggregateError(reasons))
}
})
})
})
}
整体实现如下
const STATUS_PENDING = "pending";
const STATUS_FULFILLED = "fulfilled";
const STATUS_REJECTED = "rejected";
const respondWithCatchError = (fn, value, resolve, reject) => {
try {
const result = fn(value);
resolve(result);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
};
class IcePromise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = STATUS_PENDING;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
const resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.value);
});
});
}
};
const reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status !== STATUS_PENDING) return;
this.status = STATUS_REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => {
fn(this.reason);
});
});
}
};
executor(resolve, reject);
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
const defaultOnFulfilled = (value) => {
return value;
};
const defaultOnRejected = (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
onFulfilled = onFulfilled || defaultOnFulfilled;
onRejected = onRejected || defaultOnRejected;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === STATUS_FULFILLED && onFulfilled) {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_REJECTED && onRejected) {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
}
if (this.status === STATUS_PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onFulfilled, this.value, resolve, reject);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
respondWithCatchError(onRejected, this.reason, resolve, reject);
});
}
});
}
catch(onRejected) {
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
finally(onFinally) {
this.then(
() => {
onFinally();
},
() => {
onFinally();
}
);
}
static resolve(value) {
return new Promise((onResolve) => {
onResolve(value);
});
}
static reject(reason) {
return new Promise((onResolve, onRejected) => {
onRejected(reason);
});
}
static all(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(
(value) => {
result.push(value);
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(reason) => {
reject(reason);
}
);
});
});
}
static allSettled(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(
(value) => {
result.push({
status: STATUS_FULFILLED,
value,
});
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
},
(reason) => {
result.push({
status: STATUS_REJECTED,
reason,
});
if (result.length === promises.length) {
resolve(result);
}
}
);
});
});
}
static race(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(resolve, reject);
});
});
}
static any(promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const reasons = [];
promises.forEach((promise) => {
promise.then(resolve, (reason) => {
reasons.push(reason);
if (reasons.length === promises.length) {
reject(new AggregateError(reasons));
}
});
});
});
}
}
// 测试代码
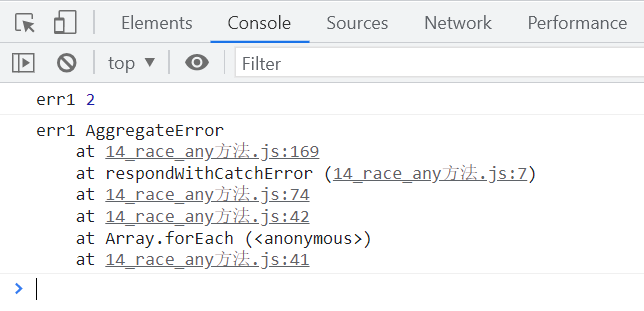
const promise1 = new IcePromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject(1);
});
});
const promise2 = IcePromise.reject(2);
const promise3 = IcePromise.reject(3);
IcePromise.race([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
);
IcePromise.any([promise1, promise2, promise3]).then(
(value) => {
console.log("res1", value);
},
(reason) => {
console.log("err1", reason);
}
);
以上就是自定义promise的所有代码啦,关于js高级,还有很多需要开发者掌握的地方,可以看看我写的其他博文,持续更新中~
手写promise之分步解析的更多相关文章
- 手写Promise A+ 规范
基于ES6语法手写promise A+ 规范,源码实现 class Promise { constructor(excutorCallBack) { this.status = 'pending'; ...
- 手写promise
写在前面: 在目前的前端分开中,我们对于异步方法的使用越来越频繁,那么如果处理异步方法的返回结果,如果优雅的进行异步处理对于一个合格的前端开发者而言就显得尤为重要,其中在面试中被问道最多的就是对Pro ...
- 手写Promise看着一篇就足够了
目录 概要 博客思路 API的特性与手写源码 构造函数 then catch Promise.resolved Promise.rejected Promise.all Promise.race 概要 ...
- 手写Promise中then方法返回的结果或者规律
1. Promise中then()方法返回来的结果或者规律 我们知道 promise 的 then 方法返回来的结果值[result]是由: 它指定的回调函数的结果决定的 2.比如说下面这一段代码 l ...
- 前端面试题之手写promise
前端面试题之Promise问题 前言 在我们日常开发中会遇到很多异步的情况,比如涉及到 网络请求(ajax,axios等),定时器这些,对于这些异步操作我们如果需要拿到他们操作后的结果,就需要使用到回 ...
- [转]史上最最最详细的手写Promise教程
我们工作中免不了运用promise用来解决异步回调问题.平时用的很多库或者插件都运用了promise 例如axios.fetch等等.但是你知道promise是咋写出来的呢? 别怕-这里有本promi ...
- 手写 Promise
在上一章节中我们了解了 Promise 的一些易错点,在这一章节中,我们会通过手写一个符合 Promise/A+ 规范的 Promise 来深入理解它,并且手写 Promise 也是一道大厂常考题,在 ...
- 手写Promise简易版
话不多说,直接上代码 通过ES5的模块化封装,向外暴露一个属性 (function(window){ const PENDING = 'pending'; const RESOLVED = 'fulf ...
- 史上最简单的手写Promise,仅17行代码即可实现Promise链式调用
Promise的使用相比大家已经孰能生巧了,我这里就不赘述了 先说说我写的Promise的问题吧,无法实现宏任务和微任务里的正确执行(也就是在Promise里面写setTimeout,setInter ...
- js手写'Promise'
/* * pending:初始化成功 * fulfilled:成功 * rejected:失败 * */ function Promise(executor) {// 执行器 this.status ...
随机推荐
- OpenAI CLIP 关键点 - 连接图像和文字
标签: #CLIP #Image2Text #Text2Image #OpenAI 创建时间:2023-04-21 00:17:52 基本原理 CLIP是一个图像分类模型. 准备训练数据:准备大量的文 ...
- 理解 React 中的 useEffect、useMemo 与 useCallback
useEffect 先理解 useEffect 有助于学习 useMemo 和 useCallback.因为 useMemo 和 useCallback 的实现实际上都是基于 useEffect 的. ...
- #Python基础 DateFrame 查看数据信息
一:导入案例数据及X-MIND 二:实例 2.1 显示摘要信息 2.2显示描述性统计信息 2.3显示 前后n行 2.4显示索引.列信息 2.5显示每列的数据类型
- 获取android app 的Activity 和 Package
开头 appium 配置, sdk 配置,jdk配置,adb配置,python配置是我们app 自动化测试必不可少的配置,当然这种配置网上有很多,我们在这里就不展开说了. 直接就开始自动化脚本的dem ...
- 2022-07-20:以下go语言代码是关于json 和 context的,输出什么?A:{};B:{“a“:“b“};C:{“Context“:0};D:不确定。 package main imp
2022-07-20:以下go语言代码是关于json 和 context的,输出什么?A:{}:B:{"a":"b"}:C:{"Context&quo ...
- 2021-03-12:go中,如何确定有没有内存泄露,系统里怎么去监控整体的运行情况,日志是怎么处理的?
2021-03-12:go中,如何确定有没有内存泄露,系统里怎么去监控整体的运行情况,日志是怎么处理的? 福哥答案2021-03-12: runtime/pprof:采集程序(非 Server)的运行 ...
- mysql报错Unknown collation: utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
mysql报错Unknown collation: utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci 解决方案: 将文件内的所有 utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci 换成 utf8_general_ci utf ...
- 【GiraKoo】Android监听屏幕尺寸变化通知
[GiraKoo]Android监听屏幕尺寸变化通知 Android系统中存在多种情况可能导致屏幕尺寸发生变化.例如:横竖屏切换,虚拟按键,分屏,键盘弹出等. App有的时候需要了解屏幕的真实尺寸,D ...
- ET介绍——CSharp协程
什么是协程 说到协程,我们先了解什么是异步,异步简单说来就是,我要发起一个调用,但是这个被调用方(可能是其它线程,也可能是IO)出结果需要一段时间,我不想让这个调用阻塞住调用方的整个线程,因此传给被调 ...
- 在.net项目中添加Husky.Net提交验证
参考:C# 项目添加 husky - jesn - 博客园 (cnblogs.com) 官方文档:Getting Started | Husky.Net (alirezanet.github.io) ...
