堆溢出---glibc malloc
成功从来没有捷径。如果你只关注CVE/NVD的动态以及google专家泄露的POC,那你只是一个脚本小子。能够自己写有效POC,那就证明你已经是一名安全专家了。今天我需要复习一下glibc中内存的相关知识,以巩固我对堆溢出的理解和分析。带着以下问题去阅读本章:
- dlmalloc – General purpose allocator
- ptmalloc2 – glibc
- jemalloc – FreeBSD and Firefox
- tcmalloc – Google
- libumem – Solaris
我们以glibc为例探讨堆的运行机制,主要是因为服务器绝大部分都和glibc有关,研究glibc有广泛意义。
系统调用:malloc本身需要调用brk或mmap完成内存分配操作
线程:ptmalloc2的前身是dlmalloc,它们最大的区别是ptmalloc2支持线程,它提升了内存分配的效率。在dlmalloc中,如果有2个线程同时调用 malloc,只有一个线程可以进入关键区,线程之间共享同一个freelist数据结构。在ptmaloc2中,每一个线程都拥有单独的堆区段,也就意味着每个线程都有自己的freelist结构体。没有线程之间的共享和争用,性能自然提高不少。Per thread arena用来特指为每个线程维护独立的堆区段和freelist结构体的方式。
/* Per thread arena example. */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h> void* threadFunc(void* arg) {
printf("Before malloc in thread 1\n");
getchar();
char* addr = (char*) malloc();
printf("After malloc and before free in thread 1\n");
getchar();
free(addr);
printf("After free in thread 1\n");
getchar();
} int main() {
pthread_t t1;
void* s;
int ret;
char* addr; printf("Welcome to per thread arena example::%d\n",getpid());
printf("Before malloc in main thread\n");
getchar();
addr = (char*) malloc();
printf("After malloc and before free in main thread\n");
getchar();
free(addr);
printf("After free in main thread\n");
getchar();
ret = pthread_create(&t1, NULL, threadFunc, NULL);
if(ret)
{
printf("Thread creation error\n");
return -;
}
ret = pthread_join(t1, &s);
if(ret)
{
printf("Thread join error\n");
return -;
}
return ;
}
分析:主线程在malloc调用之前,没有任何堆区和栈区被分配
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::
Before malloc in main thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
-0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p :
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
主线程在调用malloc之后,从下图中我们可以看出堆区域被分配在0804b000-0806c000区域,这是通过调用brk调整内存中止点来建立堆。此外,尽管申请了1000字节,但分配了132KB的堆内存。这个连续区域被称为Arena。主线程建立的就称为Main Arena。未来分配内存的请求会持续使用Arena区域直到用尽。如果用尽,可以调整内存中止点来扩大Top trunk。相似的,也可以相应的收缩以防止top chunk有太多的空间。(Top trunk是Arena最顶部的chunk)
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/lsploits/hof/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
-0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p :
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
主线程 Free之后,内存并未归还给OS,而是交由glibc malloc管理,放在Main Arena的bin中。(freelist数据结构体就是bin)之后所有的空间申请,都会在bin中寻求满足。无法满足时才再次向内核获得空间。
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
After free in main thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/lsploits/hof/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
-0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
b7e05000-b7e07000 rw-p :
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在调用thread1中malloc之前,thread1的堆区域并未建立,但线程栈已建立。
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
After free in main thread
Before malloc in thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
-0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
b7604000-b7605000 ---p :
b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p : [stack:]
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
在thread1中malloc调用之后,线程堆区段建立了。位于b7500000-b7521000,大小132KB。这显示和主线程不同,线程malloc调用的是mmap系统调用,而非sbrk。尽管用户请求1000字节,1M的堆内存被映射到了进程地址空间。但只有132KB被设置为可读写权限,并被设置为该线程的堆空间。这个连续的内存空间是Thread Arena。
当用户内存请求大小超过128KB时,不论请求是从主线程还是子线程,内存分配都是由mmap系统调用来完成的。
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
After free in main thread
Before malloc in thread
After malloc and before free in thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
-0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
b7500000-b7521000 rw-p :
b7521000-b7600000 ---p :
b7604000-b7605000 ---p :
b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p : [stack:]
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
Thread1在free之后,被分配的内存区并未交还给操作系统,而是归还给glicbc分配器,实际上它交给了线程Arena bin.
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ ./mthread
Welcome to per thread arena example::
Before malloc in main thread
After malloc and before free in main thread
After free in main thread
Before malloc in thread
After malloc and before free in thread
After free in thread
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$ cat /proc//maps
- r-xp : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
-0804a000 r--p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804a000-0804b000 rw-p : /home/sploitfun/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread/mthread
0804b000-0806c000 rw-p : [heap]
b7500000-b7521000 rw-p :
b7521000-b7600000 ---p :
b7604000-b7605000 ---p :
b7605000-b7e07000 rw-p : [stack:]
...
sploitfun@sploitfun-VirtualBox:~/ptmalloc.ppt/mthread$
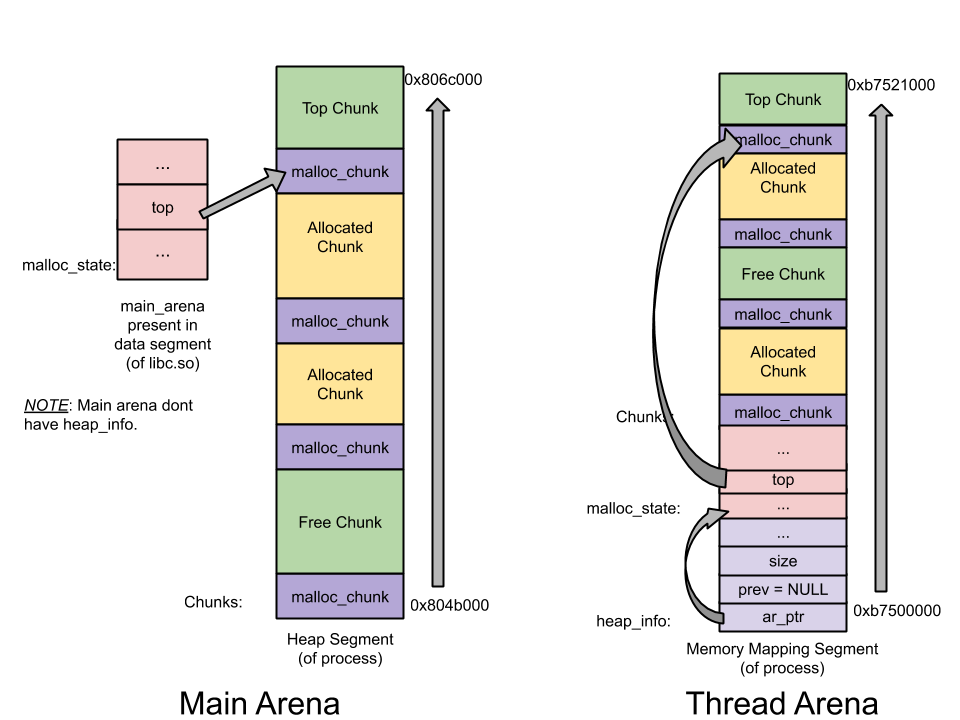
Arena:
在上面的例子中,主线程对应的是Main Arena,子线程对应的是Thread Arena。那线程和Arena是否是一一对应的呢?不是。实际上线程数可以多于核数,因此,让一个线程拥有一个Arena有些奢侈。应用程序Arena的数量是和核数相关的,具体如下:
For bit systems:
Number of arena = * number of cores.
For bit systems:
Number of arena = * number of cores.
Multiple Arena:
举例说明:一个单核32位系统有4个线程(1主3子)。那4个线程只有2个Arena。Glibc内存分配器确保Multiple Arena在线程之间共享
- 主线程首次调用malloc时一定是创建了Main Arena
- 当子线程1和子线程2首次调用malloc时,会给它们都建立一个新的Arena。此时Arena和线程是一一对应的
- 当子线程3首次调用 malloc,此时会计算Arena的限制。已超出Arena数量限制,要重用Main Arena, Thread1 Arena或Thread2 Arena
- 重用:
- 遍历存在的Arena,找到一个后试图去lock它
- 成功lock,比如是Main Arena,给用户返回Arena
- 没有空闲的Arena,就排队等待
- 当Thread3二次调用 malloc时,malloc将使用最近访问的Arena(可能是main arena)。如果main arena是空闲的就使用它,如果忙时就Block等待。
多堆:
Heap_info: 堆头。一个线程Arena拥有多个堆,每个堆有它自己的头。之所以有多个堆,是因为开始的时候只有一个堆,但随着堆区空间用尽,新堆会由mmap重新建立,而且地址空间是不连续的,新旧堆无法合并
malloc_state: Arena Header - 一个线程Arena有多个堆,但那些堆只有一个Arena头。Arena头包含了bins,top chunk和last remainder chunk等信息
malloc_chunk: Chunk Header - 一个堆被分为很多chunks,多个用户请求导致多个chunk。每个chunk有它自己的头部信息
注意:
- Main Arena没有多个堆,因此没有heap_info结构。当main arena空间耗尽,sbrk的堆区被延展
- 和线程Arena不同,Main Arena的Arena头并非由sbrk调用而产生的堆区的一部分。它是全局变量,存在于libc.so的数据区



Chunk的类型:
- Allocated chunk
- Free chunk
- Top chunk
- Last Remainder chunk
Allocated Trunk:

prev_size: 前一个chunk为空闲区,则该区域包含前一区域的大小。如果非空闲,则该域包含前一区域的用户数据
size: 被分配空间的大小 。后三比特域包含标志位
- PREV_INUSE (P) – 前一个chunk是否被占用
- IS_MMAPPED (M) – 是否是mmap分配
- NON_MAIN_ARENA (N) – 是否属于thread arena
注意:
- 对于allocated chunk, 其他域如 fd, bk不被使用. 这里只存储用户数据
- 用户请求的内存空间包含了malloc_chunk信息,因此实际使用的空间会小于用户请求大小。
Free Trunk:

prev_size: 两个空闲区不能毗邻,当两个chunk空闲豕毗邻,则会合并为一个空闲区。因此通常前一个chunk是非空闲的,prev_size是前一个chunk的用户数据
size: 空间大小
fd: Forward pointer – 同一bin中的下一个chunk(非物理空间)
bk: Backward pointer – 同一bin中的前一个chunk(非物理空间)
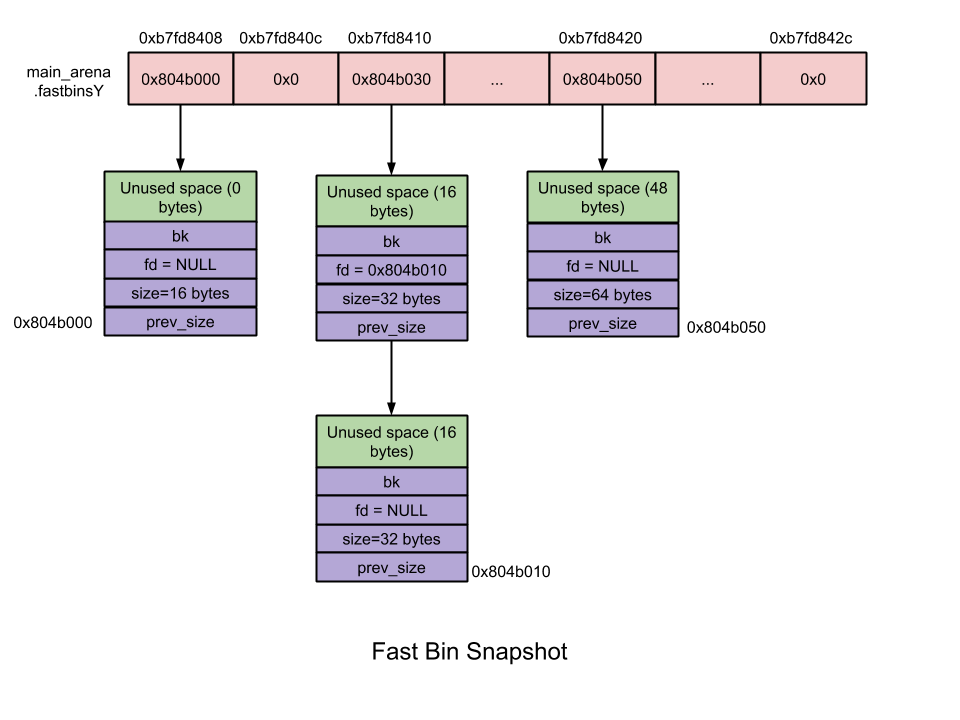
Bins: 根据大小不同,有如下bin
- Fast bin
- Unsorted bin
- Small bin
- Large bin
fastbinsY: 这个array是fastbin列表
bins: 共有126 个bins
- Bin 1 – Unsorted bin
- Bin 2 to Bin 63 – Small bin
- Bin 64 to Bin 126 – Large bin
Fast Bin: 大小在16~80字节之间.
- 数量 – 10
- 每个fastbin有一个空闲chunk的单链表. 之所以用单链表是因为在链表中没有删除操作。添加和删除都在表的顶部 – LIFO.
- Chunk大小 – 8字节对齐
- 首个fastbin包含16字节的binlist, 第2个fastbin包含24 bytes的binlist,以此类推
- 同一fastbin中的chunk大小是一致的
- 在malloc初始化时, 最大的fast bin 大小设置为64比特,而非80比特.
- 不合并 – 毗邻chunk不合并. 不合并会导致碎片,但效率提高
- malloc(fast chunk) –
- 初始态 fast bin max size 和 fast bin indices 为空,因此尽管用户请求fast chunk,是small bin code提供服务而非fast bin code。
- 之后当fastbin不为空,fast bin index通过计算激活相应的binlist
- 激活后的binlist中可以给用户提供内存
- free(fast chunk) –
- 计算Fast bin index以激活相应binlist
- 释放后的chunk被放入刚才激活的binlist 中
Unsorted Bin: 当small chunk 或 large chunk被释放,不是将其归还给相应的bin中,而是添加至unsorted bin。这对性能有所提升
- 数量 – 1
- 循环双链表
- Chunk 大小 – 大小无限制
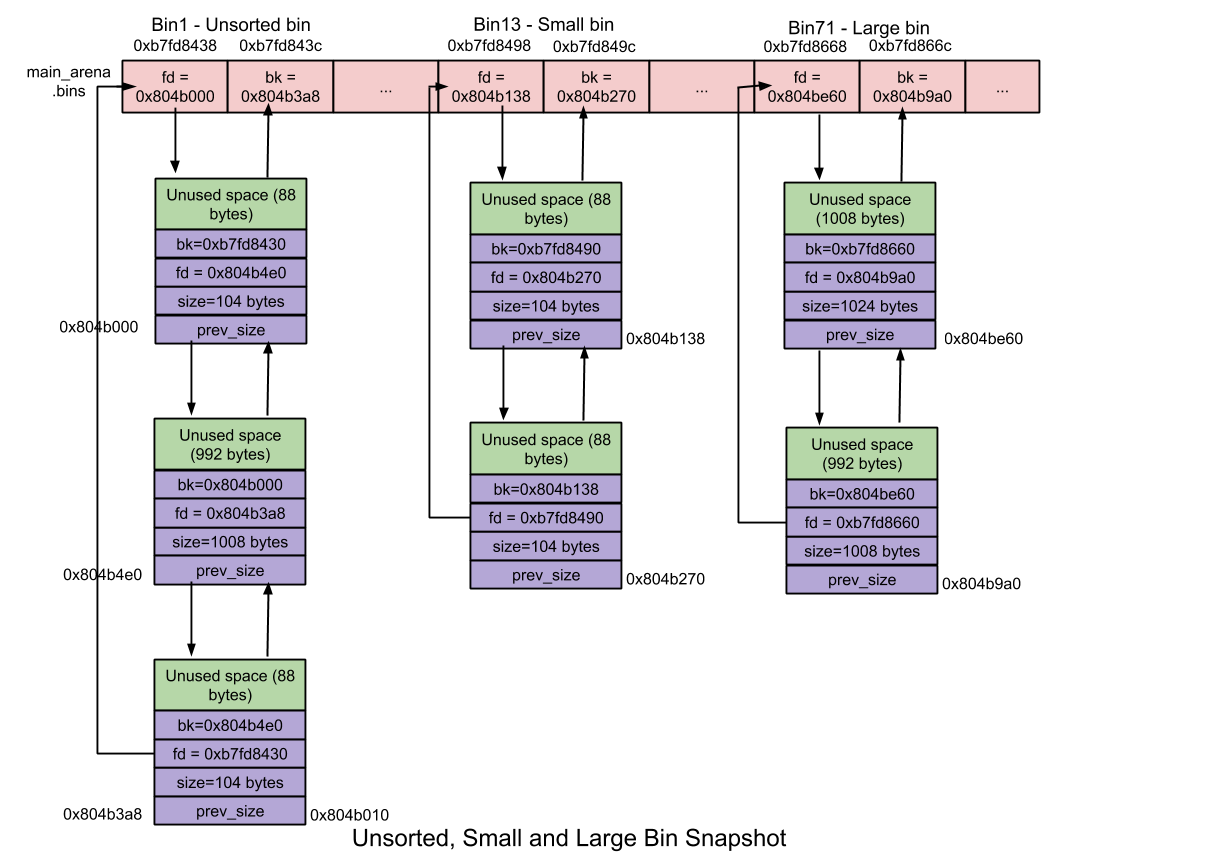
Small Bin:大小小于512字节的块称为小块。small bins在内存分配和释放方面比large bins快(但比fast bins慢)。
- 数量– 62
- 每个small bin都包含一个循环的空闲块的双向链接列表(又称垃圾箱列表)。使用双链表是因为在小垃圾箱链接的中间可能会发生块移除的操作。FIFO。
- 块大小 – 8字节对齐:
- 小bin包含大小为8个字节的块的binlist。first small bin包含大小为16个字节的块,second small bin包含大小为24个字节的块,依此类推……
- small bin 内的块大小相同
- 合并– 两个空闲的chunk不能彼此相邻,将它们合并为一个空闲的块。合并消除了外部碎片,但它放慢了速度!!
- malloc(small chunk)–
- 初始,所有small bin都将为NULL,尽管用户请求一个small chunk, unsorted bin code 会为其服务,而不是smll bin code
- 同样,第一次调用malloc的过程中,将初始化malloc_state中发现的small bin和large bin数据结构(bin),即,bin指向自身,表示它们为空。
- 稍后,当small bin不为空时,将删除其对应的binlist 中的last chunk并将其返回给用户。
- free (small chunk) –
- 释放该块时,请检查其上一个或下一个块是否空闲,如果有,则将它们从各自的链接列表中取消链接,然后将新合并的块添加到未排序的bin链接列表的开头
Large Bin:大小大于512的块称为大块。存放大块的垃圾箱称为大垃圾箱。大存储区在内存分配和释放方面比小存储区慢。
垃圾箱数量– 63
每个大垃圾箱都包含一个循环的空闲块的双向链接列表(又称垃圾箱)。使用双链表是因为在大仓中,可以在任何位置(前,中或后)添加和删除块。
在这63个垃圾箱中:
32个bin包含大小为64个字节的块的binlist。即)第一个大容器(Bin 65)包含大小为512字节至568字节的块的binlist,第二个大容器(Bin 66)包含大小为576字节至632字节的块的binlist,依此类推…
16个bin包含大小为512字节的块的binlist。
8个bin包含大小为4096字节的块的binlist。
4个bin包含大小为32768字节的块的binlist。
2个bin包含大小为262144个字节的块的binlist。
1箱包含一块剩余的大小。
与小垃圾箱不同,大垃圾箱中的块大小不相同。因此,它们以降序存储。最大的块存储在前端,而最小的块存储在其binlist的后端。
合并–两个空闲的块不能彼此相邻,将它们合并为一个空闲的块。
malloc(大块)–
最初,所有大容器都将为NULL,因此即使用户请求了大块而不是大容器代码,下一个最大的容器代码也会尝试为其服务。
同样在第一次调用malloc的过程中,将初始化malloc_state中发现的小bin和大bin数据结构(bin),即,bin指向自身,表示它们为空。
稍后,当大容器为非空时,如果最大的块大小(在其Binlist中)大于用户请求的大小,则将Binlist从后端移动到前端,以找到大小接近/等于用户请求的大小的合适块。一旦找到,该块将分为两个块
用户块(具有用户请求的大小)–返回给用户。
剩余块(剩余大小)–添加到未排序的垃圾箱。
如果最大的块大小(在其binlist中)小于用户请求的大小,请尝试使用下一个最大的(非空)容器来满足用户请求。下一个最大的bin代码扫描binmap,以查找不为空的下一个最大的bin,如果找到任何这样的bin,则从该binlist中检索合适的块并将其拆分并返回给用户。如果找不到,请尝试使用顶部块满足用户请求。
free(大块)–其过程类似于free(小块)
TOP Chunk: Arena顶部的chunk称为top chunk. 它不属于任何bin。它在当用户需求无法满足时使用。如果top chunk size 比用户请求大小大,那top chunk被分为两个
- 用户块
- 剩下的块
剩下的块成为新的top chunk。如果top chunk 大小小于用户请求大小,则top chunk调用sbrk(Main arena)或mmap(thread arena)系统调用进行延展
Last Remainder Chunk: 即最近一次切割后剩下的那个chunk. Last remainder chunk 可帮助提升性能。连续的small chunk请求可能会导致分配的位置相近。
在很多arena的chunk中,哪个能够成为last reminder chunk?
当一个用户请求small chunk,small bin和unsorted bin都无法满足,就会扫描binmaps进而找寻next largest bin. 正如较早提及的,找到the next largest bin,它将会分为2个chunk,user chunk返回给用户,remainder chunk 添加至unsorted bin. 除此之外,它成为最新的last remainder chunk.
堆溢出---glibc malloc的更多相关文章
- Linux堆溢出漏洞利用之unlink
Linux堆溢出漏洞利用之unlink 作者:走位@阿里聚安全 0 前言 之前我们深入了解了glibc malloc的运行机制(文章链接请看文末▼),下面就让我们开始真正的堆溢出漏洞利用学习吧.说实话 ...
- linux下堆溢出unlink的一个简单例子及利用
最近认真学习了下linux下堆的管理及堆溢出利用,做下笔记:作者作为初学者,如果有什么写的不对的地方而您又碰巧看到,欢迎指正. 本文用到的例子下载链接https://github.com/ctfs/w ...
- 堆溢出学习笔记(linux)
本文主要是linux下堆的数据结构及堆调试.堆溢出利用的一些基础知识 首先,linux下堆的数据结构如下 /* This struct declaration is misleading (but a ...
- stm32 堆溢出
STM32 堆溢出 遇到的问题 最近在给旧项目添加了段代码,程序经常到某个状态就突然崩溃了,也不一定是在运行新代码的时候崩溃.检查了几遍代码,数组越界访问,除数为0,内存泄露等常见的问题都不存在. 原 ...
- Linux 堆溢出原理分析
堆溢出与堆的内存布局有关,要搞明白堆溢出,首先要清楚的是malloc()分配的堆内存布局是什么样子,free()操作后又变成什么样子. 解决第一个问题:通过malloc()分配的堆内存,如何布局? 上 ...
- 【转载】利用一个堆溢出漏洞实现 VMware 虚拟机逃逸
1. 介绍 2017年3月,长亭安全研究实验室(Chaitin Security Research Lab)参加了 Pwn2Own 黑客大赛,我作为团队的一员,一直专注于 VMware Worksta ...
- vmware漏洞之一——转:利用一个堆溢出漏洞实现VMware虚拟机逃逸
转:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27733895?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral 小结: vmware通过Backd ...
- 理解 glibc malloc:主流用户态内存分配器实现原理
https://blog.csdn.net/maokelong95/article/details/51989081 Understanding glibc malloc 修订日志: 2017-03- ...
- 由STL map调用clear后,内存不返还给操作系统的问题出发,探讨glibc malloc/free行为(转)
1. 问题 我们的程序有几十个线程,每个线程拥有一个std::map,每个线程都要向自己的std::map中插入大量的数据,但每个数据只有几十字节:当使用完std::map,调用map.clear() ...
随机推荐
- Selenium系列(十四) - Web UI 自动化基础实战(1)
如果你还想从头学起Selenium,可以看看这个系列的文章哦! https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/category/1680176.html 其次,如果你不懂前端基础知识, ...
- sql MariaDB 安装contos
安装和运行MySQL数据库(MariaDB) centos 平台 1.安装和运行 yum install mariadb mariadb-server - 安装 systemctl start mar ...
- Python——图像手绘效果
1.图像的RGB色彩模式 PIL PIL, Python Image Library PIL库是一个具有强大图像处理能力的第三方库 在命令行下的安装方法: pip install pillow fro ...
- OpenWrite技术自媒体界的JVM一次编辑、随处发布
原文 :https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/KUtJ2dwhBRuJ2G_-PkQFEA 最懂你的科技自媒体管理平台 [实用小工具推荐]给科技或技术同学们推荐一款比较好用的工具,可以 ...
- Codeforces 631 (Div. 2) D. Dreamoon Likes Sequences 位运算^ 组合数 递推
https://codeforces.com/contest/1330/problem/D 给出d,m, 找到一个a数组,满足以下要求: a数组的长度为n,n≥1; 1≤a1<a2<⋯&l ...
- 1014 Waiting in Line (30 分)
Suppose a bank has N windows open for service. There is a yellow line in front of the windows which ...
- Java多线程并发工具类-信号量Semaphore对象讲解
Java多线程并发工具类-Semaphore对象讲解 通过前面的学习,我们已经知道了Java多线程并发场景中使用比较多的两个工具类:做加法的CycliBarrier对象以及做减法的CountDownL ...
- Python魔法缓存,以数字开始
Python魔法缓存,以数字开始 众所周知,Python是弱类型的脚本语言,变量的定义是不用声明类型的. a = 1 Python所有数字的本质都是对象, 他们是不可改变的数据类型,这意味着改变数字数 ...
- PTA | 1008 数组元素循环右移问题 (20分)
一个数组A中存有N(N>0)个整数,在不允许使用另外数组的前提下,将每个整数循环向右移M(M>=0)个位置,即将A中的数据由(A0 A1--AN-1)变换为(AN-M -- AN-1 A0 ...
- RHCS概述
RHCS概述 创建RHCS集群环境 创建高可用Apache服务 1 创建RHCS集群环境 1.1 问题 准备四台KVM虚拟机,其三台作为集群节点,一台安装luci并配置iSCSI存储服务,实现如下功能 ...
