LEETCODE —— Linked List Cycle [Floyd's cycle-finding algorithm]
Linked List Cycle
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if head is None:
return False
rabbit = turtle = head
while rabbit.next and rabbit.next.next:
turtle = turtle.next
rabbit = rabbit.next.next
if rabbit == turtle:
return True
return False
佛洛依德龟兔算法
|
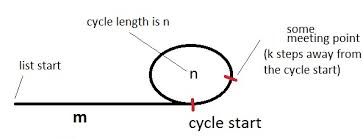
Let me try to clarify the cycle detection algorithm that is provided at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cycle_detection#Tortoise_and_hare in my own words. I refer to the figure How it works Let's have a tortoise and a hare (name of the pointers) pointing to the beginning of the list with a cycle. Let's hypothesize that if we move tortoise 1 step at a time, and hare 2 steps at a time, they will eventually meet at a point. Let's show that first of all this hypothesis is true. The figure illustrates a list with a cycle. The cycle has a length of n and we are initially m steps away from the cycle. Also let's say that the meeting point is k steps away from the cycle beginning and tortoise and hare meets after a total of i steps. The following 2 conditions must hold: 1) i = m + p * n + k 2) 2i = m + q * n + k The first one says that tortoise moves i steps and in these i steps it first gets to the cycle. Then it goes through the cycle p times for some positive number p. Finally it goes over k more nodes until it meets hare. A similar is true for hare. It moves 2i steps and in these 2i steps it first gets to the cycle. Then it goes through the cycle q times for some positive number q. Finally it goes over k more nodes until it meets tortoise. Therefore, 2 ( m + p * n + k ) = m + q * n + k => 2m + 2pn + 2k = m + nq + k => m + k = ( q - 2p ) n Among m, n, k, p, q, the first two are properties of the given list. If we can show that there is at least one set of values for k, q, p that makes this equation true we show that the hypothesis is correct. One such solution set is as follows: p = 0 q = m k = m n - m We can verify that these values work as follows: m + k = ( q - 2p ) n => m + mn - m = ( m - 2*0) n => mn = mn. For this set, i is i = m + p n + k => m + 0 * n + mn - m = mn. Of course, you should see that this is not necessarily the smallest i possible. In other words, tortoise and hare might have already met before many times. However, since we show that they meet at some point at least once we can say that the hypothesis is correct. So they would have to meet if we move one of them 1 step, and the other one 2 steps at a time. Now we can go to the second part of the algorithm which is how to find the beginning of the cycle. Cycle Beginning Once tortoise and hare meet, let's put tortoise back to the beginning of the list and keep hare where they met (which is k steps away from the cycle beginning). The hypothesis is that if we let them move at the same speed (1 step for both), the first time they ever meet again will be the cycle beginning. Let's prove this hypothesis. Let's first assume some oracle tells us what m is. Then, if we let them move m + k steps, tortoise would have to arrive at the point they met originally (k steps away from the cycle beginning - see in the figure). Previously we showed that m + k = (q - 2p) n. Since m + k steps is a multiple of cycle length n, hare, in the mean time, would go through the cycle (q-2p) times and would come back to the same point (k steps away from the cycle beginning). Now, instead of letting them move m + k steps, if we let them move only m steps, tortoise would arrive at the cycle beginning. Hare would go be k steps short of completing (q-2p) rotations. Since it started k steps in front of the cycle beginning, hare would have to arrive at the cycle beginning. As a result, this explains that they would have to meet at the cycle beginning after some number of steps for the very first time (very first time because tortoise just arrived at the cycle after m steps and it could never see hare which was already in the cycle). Now we know that the number of steps we need to move them until they meet turns out to be the distance from the beginning of the list to the cycle beginning, m. Of course, the algorithm does not need to know what m is. It will just move both tortoise and hare one step at a time until they meet. The meeting point has to be the cycle start and the number of steps must be the distance (m) to the cycle beginning. Assuming we know the length of the list, we can also, compute the length of the cycle of subtracting m from the list length. |
LEETCODE —— Linked List Cycle [Floyd's cycle-finding algorithm]的更多相关文章
- LeetCode Linked List Cycle II 和I 通用算法和优化算法
Linked List Cycle II Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cyc ...
- Floyd's Cycle Detection Algorithm
Floyd's Cycle Detection Algorithm http://www.siafoo.net/algorithm/10 改进版: http://www.siafoo.net/algo ...
- LeetCode & linked list bug
LeetCode & linked list bug add-two-numbers shit test /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * ...
- [LeetCode] Linked List Cycle II 单链表中的环之二
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Foll ...
- [LeetCode] Linked List Cycle 单链表中的环
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it. Follow up: Can you solve it without using ex ...
- [LeetCode]Linked List Cycle II解法学习
问题描述如下: Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return nu ...
- LeetCode——Linked List Cycle
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it. Follow up: Can you solve it without using ex ...
- LeetCode——Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Foll ...
- [算法][LeetCode]Linked List Cycle & Linked List Cycle II——单链表中的环
题目要求 Linked List Cycle Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it. Follow up: Can you so ...
随机推荐
- 用Window Authentication的方式去连接SQLServer
用Window Authentication的方式去连接SQLServer Connection String: jdbc:sqlserver://${serverName};databaseName ...
- linux 两个文件合并
可以使用cat命令,有两种实现的方式,一种将两个文件合并的到一个新的文件,另一种将一个文件追加到另一个文件的末尾. 方法一:使用cat命令从文件中读入两个文件,然后将重定向到一个新的文件.这种方法可以 ...
- Bpmx实施经验
Bpmx是一个较大的平台,直接发布的话会有内存问题,经查阅一些资料,java1.5没有解决好之前版本的历史问题,所以在垃圾处理gc上有很多配置需要手动完成,之后的版本同上. Bpmx平台自带的文档中部 ...
- Android Activity中获取当前焦点的控件,自动化输入EditText
获取焦点的view对象 View view=getWindow().getDecorView().findFocus(); 如果是EditText if(view instanceof EditTex ...
- 最优雅,高效的javascript字符串拼接
这种方式是es6的语法.使用键盘1左边的那个字符 `` 拼接, 再加上js自带的模板引擎拼接字符串非常快速.这东西也没什么高深的,看几个例子就懂了. console.log(`<xml> ...
- Git进行代码管理的心得
git从网上下载安装后 直接可在开始菜单中找到 打开可以看到一个类似命令窗口的东西 用代码进行用户名和邮箱的设置 虽然不知道为什么但是教程叫我这么做 (ˇˍˇ) 然后似乎就可以用了 进入文件夹 输入对 ...
- php数组常见的几种遍历方法
1.foreach遍历 $arr[] = array('first'=>green,'second'=>'yellow','third'=>'blue'); foreach($arr ...
- android SDK 离线下载更新
http://blog.csdn.net/harvic880925/article/details/37913801 前言:在公司配置eclipse做android开发,真是烦死了,不知公司做了哪门子 ...
- 填补Resources和WWW加载本地资源的坑
总的来说Resources和WWW加载本地资源坑比较多,大多与路径有关. 下面代码构成了一个路径的预读模块: 此模块主要解决的坑是:Resources或WWW加载本地的文件夹中的多个文件时,无法获取文 ...
- vim ---- 一键自动indent的命令
当用vim拷贝某一段代码到另一个程序的时候,往往indent会有一些问题.. 下面这个强大的命令能够让你一键让代码有很好的格式. gg=G 例子:

 in my explanation.
in my explanation.