hdu 5444 Elven Postman
题目连接
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444
Elven Postman
Description
Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long time and their magical prowess are not something to be taken lightly. Also, they live on trees. However, there is something about them you may not know. Although delivering stuffs through magical teleportation is extremely convenient (much like emails). They still sometimes prefer other more “traditional” methods.
So, as a elven postman, it is crucial to understand how to deliver the mail to the correct room of the tree. The elven tree always branches into no more than two paths upon intersection, either in the east direction or the west. It coincidentally looks awfully like a binary tree we human computer scientist know. Not only that, when numbering the rooms, they always number the room number from the east-most position to the west. For rooms in the east are usually more preferable and more expensive due to they having the privilege to see the sunrise, which matters a lot in elven culture.
Anyways, the elves usually wrote down all the rooms in a sequence at the root of the tree so that the postman may know how to deliver the mail. The sequence is written as follows, it will go straight to visit the east-most room and write down every room it encountered along the way. After the first room is reached, it will then go to the next unvisited east-most room, writing down every unvisited room on the way as well until all rooms are visited.
Your task is to determine how to reach a certain room given the sequence written on the root.
For instance, the sequence 2, 1, 4, 3 would be written on the root of the following tree.
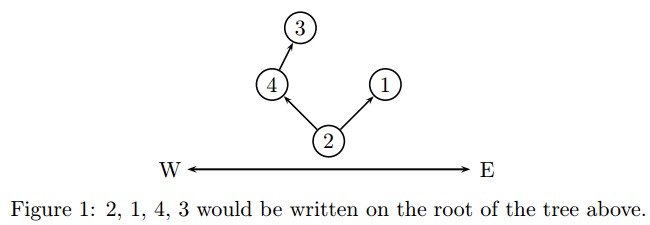
Input
First you are given an integer $T\ (T \leq 10)$ indicating the number of test cases.
For each test case, there is a number $n\ (n \leq 1000)$ on a line representing the number of rooms in this tree. n integers representing the sequence written at the root follow, respectively $a_1, . . . , a_n$ where $a_1, . . . , a_n ∈ \{1, . . . , n\}$.
On the next line, there is a number $q$ representing the number of mails to be sent. After that, there will be $q$ integers $x_1, . . . , x_q$ indicating the destination room number of each mail.
Output
For each query, output a sequence of move ($E$ or $W$) the postman needs to make to deliver the mail. For that $E$ means that the postman should move up the eastern branch and $W$ the western one. If the destination is on the root, just output a blank line would suffice.
Note that for simplicity, we assume the postman always starts from the root regardless of the room he had just visited.
Sample Input
2
4
2 1 4 3
3
1 2 3
6
6 5 4 3 2 1
1
1
Sample Output
E
WE
EEEEE
直接用二叉树模拟即可。。
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using std::set;
using std::sort;
using std::pair;
using std::swap;
using std::multiset;
#define pb(e) push_back(e)
#define sz(c) (int)(c).size()
#define mp(a, b) make_pair(a, b)
#define all(c) (c).begin(), (c).end()
#define iter(c) decltype((c).begin())
#define cls(arr, val) memset(arr, val, sizeof(arr))
#define cpresent(c, e) (find(all(c), (e)) != (c).end())
#define rep(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < (int)n; i++)
#define tr(c, i) for(iter(c) i = (c).begin(); i != (c).end(); ++i)
const int N = 1010;
const int INF = ~0u >> 1;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
struct Node {
int v;
Node *ch[2];
inline void set(int dat, Node *p) {
v = dat, ch[0] = ch[1] = p;
}
};
struct BST {
Node *root, *tail, *null, stack[N];
inline void init() {
tail = &stack[0];
null = tail++;
null->set(INF, NULL);
root = null;
}
inline Node *newNode(int dat) {
Node *p = tail++;
p->set(dat, null);
return p;
}
inline void insert(Node *&x, int dat) {
if (x == null) { x = newNode(dat); return; }
insert(x->ch[dat > x->v], dat);
}
inline void insert(int dat) {
insert(root, dat);
}
inline void find(int dat) {
Node *x = root;
while (x->v != dat) {
if (dat < x->v) {
putchar('E');
x = x->ch[0];
} else {
putchar('W');
x = x->ch[1];
}
}
putchar('\n');
}
}go;
int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.txt", "w+", stdout);
#endif
int t, n, v, q;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
go.init();
scanf("%d", &n);
rep(i, n) {
scanf("%d", &v);
go.insert(v);
}
scanf("%d", &q);
while (q--) {
scanf("%d", &v);
go.find(v);
}
}
return 0;
}
hdu 5444 Elven Postman的更多相关文章
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(长春网路赛——平衡二叉树遍历)
题目链接:pid=5444http://">http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Time Limi ...
- Hdu 5444 Elven Postman dfs
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid= ...
- 2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online HDU 5444 Elven Postman【二叉排序树的建树和遍历查找】
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman 二叉树
Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others) Problem Descrip ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(二叉树)——2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online
Problem Description Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman (2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online)
Elven Postman Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long time ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman 二叉排序树
HDU 5444 题意:给你一棵树的先序遍历,中序遍历默认是1...n,然后q个查询,问根节点到该点的路径(题意挺难懂,还是我太傻逼) 思路:这他妈又是个大水题,可是我还是太傻逼.1000个点的树,居 ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(根据先序遍历和中序遍历求后序遍历)2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online
很坑的一道题,读了半天才读懂题,手忙脚乱的写完(套上模板+修改模板),然后RE到死…… 题意: 题面上告诉了我们这是一棵二叉树,然后告诉了我们它的先序遍历,然后,没了……没了! 反复读题,终于在偶然间 ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman (二叉树,暴力搜索)
题意:给出一颗二叉树的先序遍历,默认的中序遍历是1..2.……n.给出q个询问,询问从根节点出发到某个点的路径. 析:本来以为是要建树的,一想,原来不用,其实它给的数是按顺序给的,只要搜结点就行,从根 ...
随机推荐
- 微信公众号发起微信支付 c#
tenpay.dll: MD5Util.cs using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Syst ...
- 为知笔记 Markdown 新手指南
为知笔记 Markdown 新手指南 http://www.wiz.cn/feature-markdown.html 时序图,流程图详细流程图语法 http://adrai.github.io/flo ...
- NSSet、NSMutableSet
NSSet和NSArray功能性质一样,用于存储对象,属于集合:只能添加cocoa对象,基本数据类型需要装箱. NSSet . NSMutableSet是无序的集合,在内存中存储方式是不连续的,而NS ...
- 第4章 sed命令
1 sed命令基本用法 sed(stream editor)是流编辑器,可对文本文件和标准输入进行编辑: sed只是对缓冲区中原始文件的副本进行编辑,并不编辑原始的文件,如果需要保存改动内容,可以选择 ...
- SVN中文件属性
从SVN中checkout代码,然后设置crontab 定时执行脚本,发现permission denied 查看发现脚本没有可执行权限 但是,之前项目中的代码是有该权限的,于是猜想应该可以对SVN中 ...
- eclipse删除已经记录的用户名和密码
1.从windows > preference > Team > SVN #SVN Interface这个位置看看. 2.如果是用的JavaHL, 删除C:\Users\[YourU ...
- sql语句小练习二
1.创建一个数据库StudentManage, 初始化大小10M,不足以1M每次增长 create database StudentManage on ( name = 'StudentManag ...
- Solaris磁盘设备
Solaris的磁盘分区称为分片(slice),在磁盘上,一个环形就是一个分区分片的命名通常是c#t#d#s#c:Controller number,控制器标号,c0就是第一个控制器t:Taget n ...
- 安装JAVA JDK注意事项
1 WIN8系统 安装JDK 我安装的是1.6版本, 64位的 : 2 安装好后 cmd 输入 java -version 正常 java 命令 正常 javac 命令不正常 提 ...
- js 定位到指定位置
<script> //滚动定位到product function scroll() { var scroll_offset = $(&quo ...
