2023-05-05:给定一个无向、连通的树 树中有 n 个标记为 0...n-1 的节点以及 n-1 条边 。 给定整数 n 和数组 edges , edges[i] = [ai, bi]表示树中的
2023-05-05:给定一个无向、连通的树
树中有 n 个标记为 0...n-1 的节点以及 n-1 条边 。
给定整数 n 和数组 edges ,
edges[i] = [ai, bi]表示树中的节点 ai 和 bi 之间有一条边。
返回长度为 n 的数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] :
树中第 i 个节点与所有其他节点之间的距离之和。
输入: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4],[2,5]]。
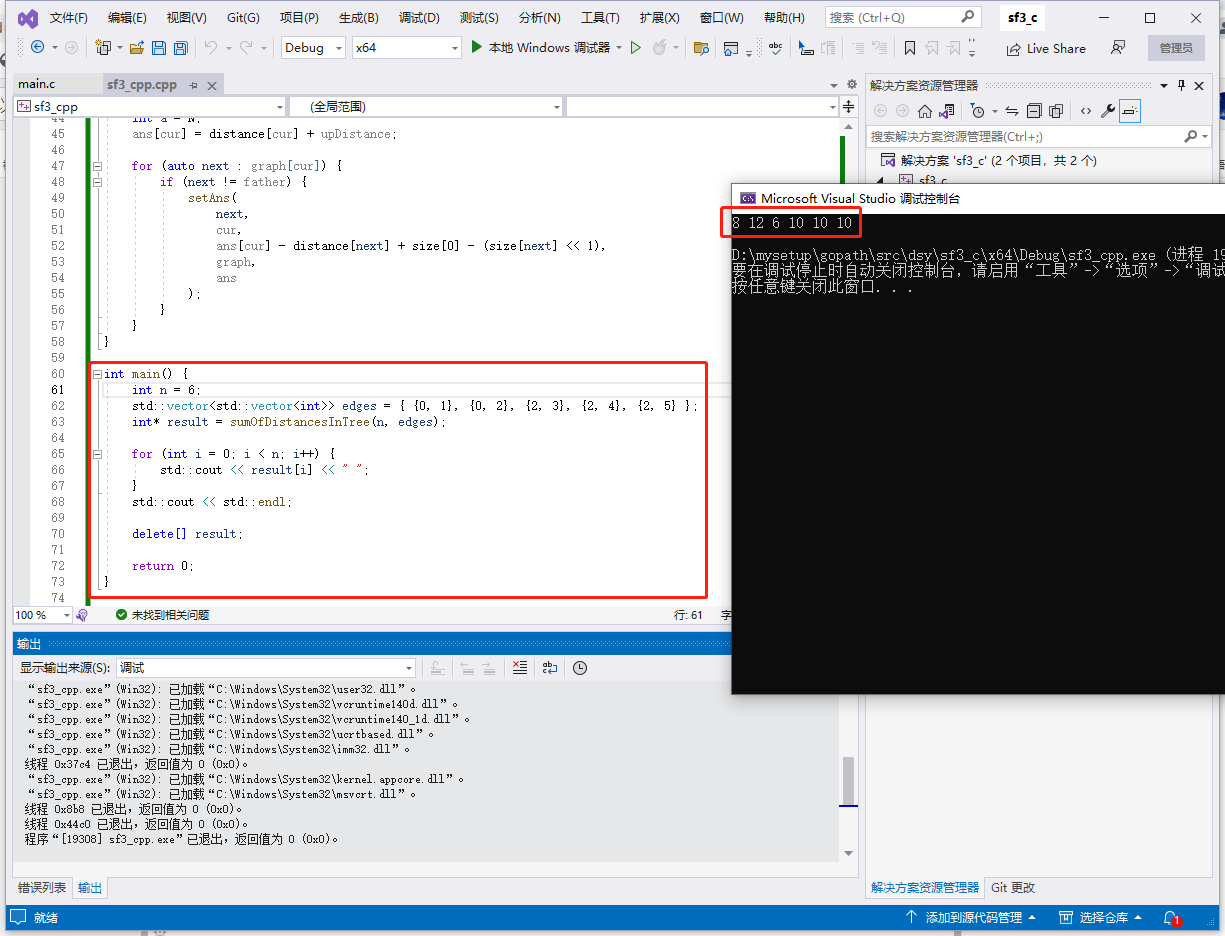
输出: [8,12,6,10,10,10]。
答案2023-05-05:
思路:
给定一棵无向、连通的树,要求计算每个节点到其他所有节点的距离之和。
可以通过遍历树,对于每个节点分别计算它到其他节点的距离之和。对于每个节点,利用它的子节点信息来更新它到其他节点的距离之和,然后递归地更新它的子节点。最终得到所有节点的距离之和。
具体实现如下:
1.构造图
通过给定的 edges 数组构造无向图。
2.遍历树,计算每个节点到其他节点的距离之和
从根节点开始递归遍历树,对于每个节点,首先初始化它到其他节点的距离之和为 0,然后递归地处理它的子节点。处理完所有子节点之后,计算该节点到其他节点的距离之和,并将该节点的大小(即包括自身在内的节点数)保存下来。
3.递归更新节点到其他节点的距离之和
从根节点开始递归遍历树,对于每个节点,首先计算它到其他节点的距离之和,并将其保存在 ans 数组中。然后递归地处理它的子节点,将它们对应的距离之和更新到 upDistance 中,并计算每个子节点到其他节点的距离之和。
总时间复杂度:O(n)
总空间复杂度:O(n)
go完整代码如下:
package main
import "fmt"
var N int = 30001
var size [30001]int
var distance [30001]int
func sumOfDistancesInTree(n int, edges [][]int) []int {
graph := make([][]int, n)
for i := range graph {
graph[i] = []int{}
}
for _, edge := range edges {
u := edge[0]
v := edge[1]
graph[u] = append(graph[u], v)
graph[v] = append(graph[v], u)
}
collect(0, -1, graph)
ans := make([]int, n)
setAns(0, -1, 0, graph, ans)
return ans
}
func collect(cur int, father int, graph [][]int) {
size[cur] = 1
distance[cur] = 0
for _, next := range graph[cur] {
if next != father {
collect(next, cur, graph)
distance[cur] += distance[next] + size[next]
size[cur] += size[next]
}
}
}
func setAns(cur int, father int, upDistance int, graph [][]int, ans []int) {
ans[cur] = distance[cur] + upDistance
for _, next := range graph[cur] {
if next != father {
setAns(
next,
cur,
ans[cur]-distance[next]+size[0]-(size[next]<<1),
graph,
ans,
)
}
}
}
func main() {
n := 6
edges := [][]int{{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}}
result := sumOfDistancesInTree(n, edges)
fmt.Println(result)
}
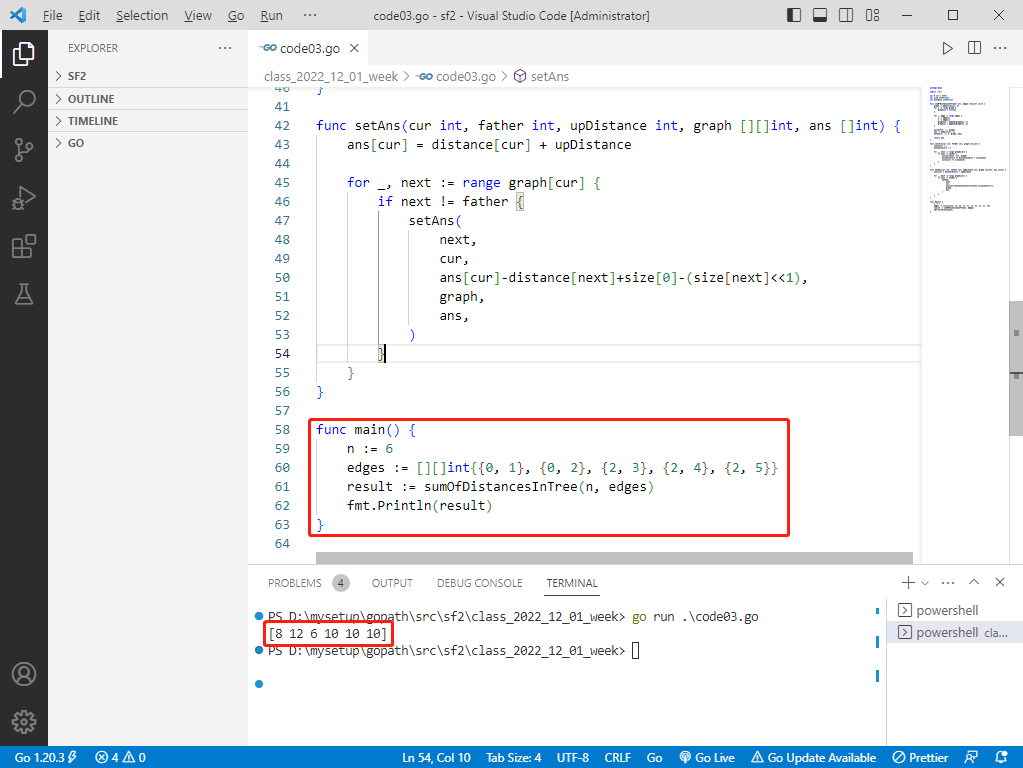
rust完整代码如下:
const N: usize = 30001;
static mut SIZE: [i32; N] = [0; N];
static mut DISTANCE: [i32; N] = [0; N];
pub fn sum_of_distances_in_tree(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut graph: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![vec![]; n as usize];
for edge in edges {
let u = edge[0] as usize;
let v = edge[1] as usize;
graph[u].push(v as i32);
graph[v].push(u as i32);
}
unsafe {
collect(0, -1, &graph);
let mut ans: Vec<i32> = vec![0; n as usize];
set_ans(0, -1, 0, &graph, &mut ans);
ans
}
}
unsafe fn collect(cur: usize, father: i32, graph: &Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
SIZE[cur] = 1;
DISTANCE[cur] = 0;
for next in &graph[cur] {
let next = *next as usize;
if next != father as usize {
collect(next, cur as i32, graph);
DISTANCE[cur] += DISTANCE[next] + SIZE[next];
SIZE[cur] += SIZE[next];
}
}
}
fn set_ans(cur: usize, father: i32, up_distance: i32, graph: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, ans: &mut Vec<i32>) {
unsafe {
ans[cur] = DISTANCE[cur] + up_distance;
for next in &graph[cur] {
let next = *next as usize;
if next != father as usize {
set_ans(
next,
cur as i32,
ans[cur] - DISTANCE[next] + SIZE[0] - (SIZE[next] << 1),
graph,
ans,
);
}
}
}
}
fn main() {
let n = 6;
let edges = vec![vec![0, 1], vec![0, 2], vec![2, 3], vec![2, 4], vec![2, 5]];
let result = sum_of_distances_in_tree(n, edges);
println!("{:?}", result);
}
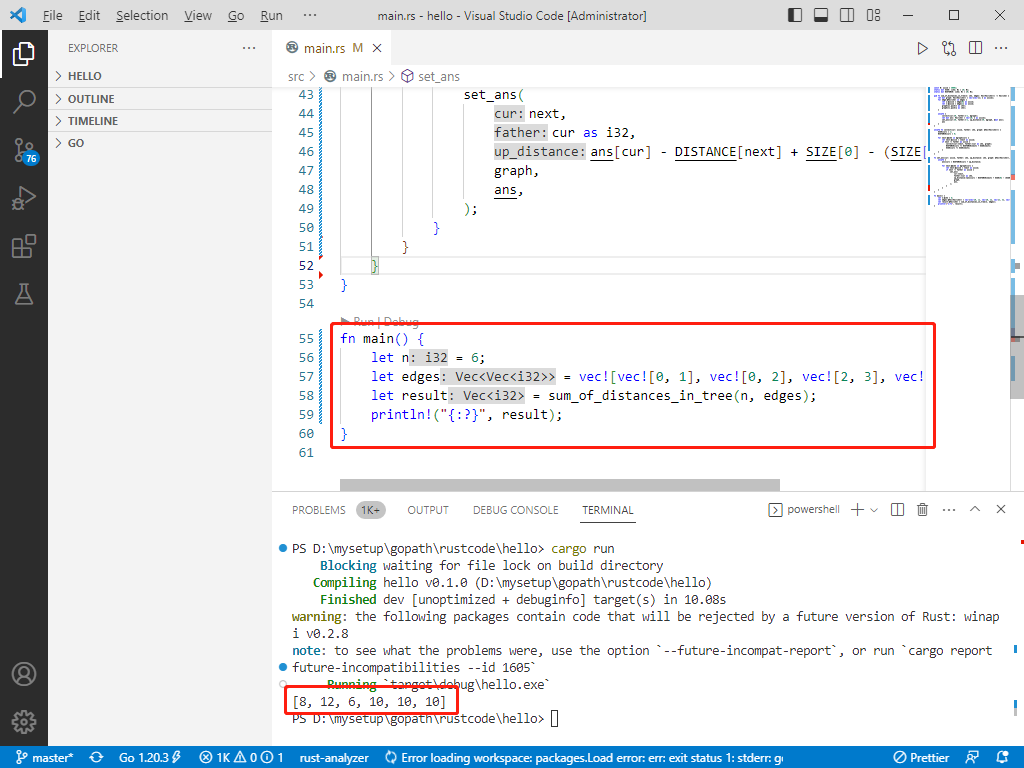
c完整代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 30001
int size[N];
int distance[N];
void collect(int cur, int father, int** graph, int n);
void setAns(int cur, int father, int upDistance, int** graph, int* ans);
int* sumOfDistancesInTree(int n, int edges[][2]) {
int** graph = malloc(n * sizeof(*graph));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = malloc((n + 1) * sizeof(**graph));
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
graph[i][j] = -1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
if (graph[u][0] == -1) {
graph[u][0] = 0;
}
if (graph[v][0] == -1) {
graph[v][0] = 0;
}
int j = 0;
while (graph[u][++j] != -1);
graph[u][j] = v;
j = 0;
while (graph[v][++j] != -1);
graph[v][j] = u;
}
collect(0, -1, graph, n);
int* ans = malloc(n * sizeof(int));
setAns(0, -1, 0, graph, ans);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
free(graph[i]);
}
free(graph);
return ans;
}
void collect(int cur, int father, int** graph, int n) {
size[cur] = 1;
distance[cur] = 0;
int j = 1;
while (graph[cur][j] != -1) {
int next = graph[cur][j];
if (next != father) {
collect(next, cur, graph, n);
distance[cur] += distance[next] + size[next];
size[cur] += size[next];
}
j++;
}
}
void setAns(int cur, int father, int upDistance, int** graph, int* ans) {
ans[cur] = distance[cur] + upDistance;
int j = 1;
while (graph[cur][j] != -1) {
int next = graph[cur][j];
if (next != father) {
setAns(
next,
cur,
ans[cur] - distance[next] + size[0] - (size[next] << 1),
graph,
ans
);
}
j++;
}
}
int main() {
int n = 6;
int edges[][2] = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5} };
int* result = sumOfDistancesInTree(n, edges);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", result[i]);
}
printf("\n");
free(result);
return 0;
}
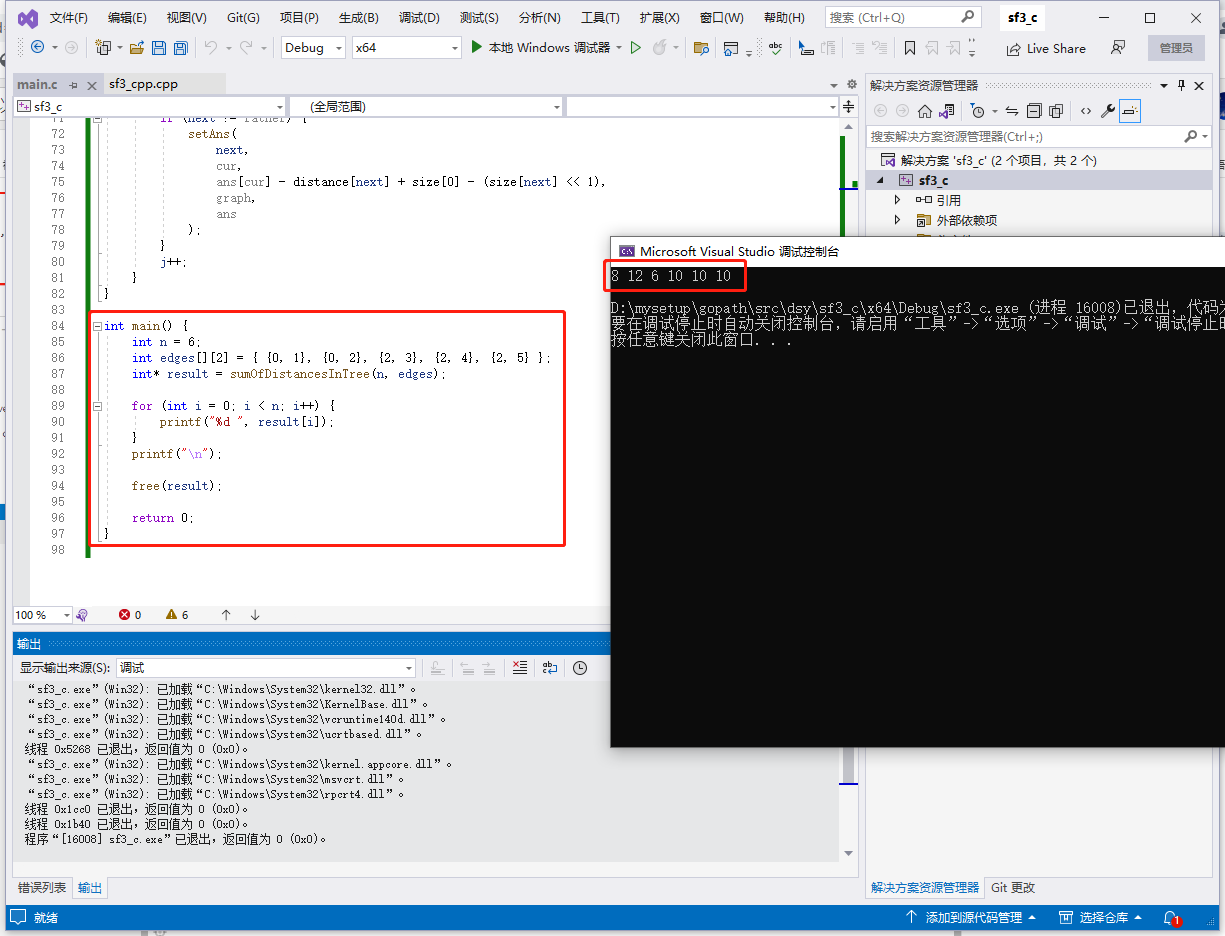
c++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
//using namespace std;
const int N = 30001;
static int size[N];
static int distance[N];
void collect(int cur, int father, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& graph);
void setAns(int cur, int father, int upDistance, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& graph, int* ans);
int* sumOfDistancesInTree(int n, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& edges) {
std::vector<std::vector<int>> graph(n);
for (auto edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
collect(0, -1, graph);
int* ans = new int[n];
setAns(0, -1, 0, graph, ans);
return ans;
}
void collect(int cur, int father, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& graph) {
size[cur] = 1;
distance[cur] = 0;
for (auto next : graph[cur]) {
if (next != father) {
collect(next, cur, graph);
distance[cur] += distance[next] + size[next];
size[cur] += size[next];
}
}
}
void setAns(int cur, int father, int upDistance, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& graph, int* ans) {
int a = N;
ans[cur] = distance[cur] + upDistance;
for (auto next : graph[cur]) {
if (next != father) {
setAns(
next,
cur,
ans[cur] - distance[next] + size[0] - (size[next] << 1),
graph,
ans
);
}
}
}
int main() {
int n = 6;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> edges = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5} };
int* result = sumOfDistancesInTree(n, edges);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
std::cout << result[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
delete[] result;
return 0;
}
2023-05-05:给定一个无向、连通的树 树中有 n 个标记为 0...n-1 的节点以及 n-1 条边 。 给定整数 n 和数组 edges , edges[i] = [ai, bi]表示树中的的更多相关文章
- Two sum(给定一个无重复数组和目标值,查找数组中和为目标值的两个数,并输出其下标)
示例: nums = [1,2,5,7] target = [6] return [0,2] Python解决方案1: def twoSum(nums, target): ""&q ...
- 给定一个数列a1,a2,a3,...,an和m个三元组表示的查询,对于每个查询(i,j,k),输出ai,ai+1,...,aj的升序排列中第k个数。
给定一个数列a1,a2,a3,...,an和m个三元组表示的查询,对于每个查询(i,j,k),输出ai,ai+1,...,aj的升序排列中第k个数. #include <iostream> ...
- 给定一个二叉搜索树(BST),找到树中第 K 小的节点
问题:给定一个二叉搜索树(BST),找到树中第 K 小的节点. 出题人:阿里巴巴出题专家:文景/阿里云 CDN 资深技术专家. 考察点: 1. 基础数据结构的理解和编码能力 2. 递归使用 参考答案 ...
- 给定一个十进制的正整数,写下从1开始,到N的所有整数,然后数一下其中出现“1”的个数。
一.题目: n给定一个十进制的正整数,写下从1开始,到N的所有整数,然后数一下其中出现“1”的个数. n要求: n写一个函数 f(N) ,返回1 到 N 之间出现的 “1”的个数.例如 f(12) ...
- Gym 101064 D Black Hills golden jewels 【二分套二分/给定一个序列,从序列中任意取两个数形成一个和,两个数不可相同,要求求出第k小的组合】
D. Black Hills golden jewels time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
- 【leetcode-03】给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的最长子串的长度
开个新坑,leetcode上面做题目.下面是题目描述: <!-- 给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的最长子串的长度. 示例 1: 输入: "abcabcbb" 输出 ...
- AI+BI的未来
术语与缩写解释 缩写.术语 解 释 BI 商业智能(Business Intelligence,简称:BI),又称商业智慧或商务智能,指用现代数据仓库技术.线上分析处理技术.数据挖掘和数据展现技 ...
- 2021.08.05 P2168 荷马史诗(哈夫曼树模板)
2021.08.05 P2168 荷马史诗(哈夫曼树模板) [P2168 NOI2015] 荷马史诗 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn) 重点: 1.k叉哈夫曼树如果子结 ...
- 算法:Manacher,给定一个字符串str,返回str中最长回文子串的长度。
[题目] 给定一个字符串str,返回str中最长回文子串的长度 [举例] str="123", 1 str="abc1234321ab" 7 [暴力破解] 从左 ...
- 给定一个double类型的数组arr,其中的元素可正可负可0,返回子数组累乘的最大乘积。例如arr=[-2.5,4,0,3,0.5,8,-1],子数组[3,0.5,8]累乘可以获得最大的乘积12,所以返回12。
分析,是一个dp的题目, 设f[i]表示以i为结尾的最大值,g[i]表示以i结尾的最小值,那么 f[i+1] = max{f[i]*arr[i+1], g[i]*arr[i+1],arr[i+1]} ...
随机推荐
- PHP 二维按照某个字段对数组排序
function arraySort($arr, $keys, $type = 'asc') {//二维按照某个字段对数组排序 $keysvalue = $new_array = array(); f ...
- HDF格式遥感影像批量转为TIFF格式:ArcPy实现
本文介绍基于Python中ArcPy模块,实现大量HDF格式栅格图像文件批量转换为TIFF格式的方法. 首先,来看看我们想要实现的需求. 在一个名为HDF的文件夹下,有五个子文件夹:每一个 ...
- c++ 内存顺序
搞懂无锁编程的重要一步是完全理解内存顺序! 本教程由作者和ChatGPT通力合作完成. 都有哪几种? c++的内存模型共有6种 memory_order_relaxed memory_order_co ...
- 在CentOS上编译最新版linux内核(linux-5.19.9)
从官网下载最新版的Linux内核源码,本教程使用linux-5.19.9进行编译. 实验环境(CentOS-Stream-8) $ uname -a Linux localhost.localdoma ...
- Kattis mapcolouring(状压dp)
刚知道vj上查看别人代码,看不到汉字...我理解的都注明后边了. #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long #define met(a, ...
- Flex布局原理【转载】
引言 CSS3中的 Flexible Box,或者叫flexbox,是用于排列元素的一种布局模式. 顾名思义,弹性布局中的元素是有伸展和收缩自身的能力的. 相比于原来的布局方式,如float.posi ...
- 4种API性能恶化根因分析
摘要:服务发生性能恶化时,需要投入大量人力分析性能异常根因,分析成本高,耗时长.我们提出了一种先在异常调用链内部分析候选根因,再在全局拓扑环境下对候选根因进行汇聚的二级分析方法,克服了调用链之间异常相 ...
- JVM 问题排查工具
更多内容,前往 IT-BLOG Java 开发人员肯定都知道 JDK的 bin 目录中有 "java.exe"."javac.exe" 这两个命令行工具.下面主 ...
- 用ACDSee查看Office文档?No!有中文解决方案吗?暂未发现!
看图软件选择 用过不少看图软件,20年前就觉得ACDSee实在太好用了,界面漂亮.速度快.格式多.体积小! 后来图像格式越来越丰富,ACDSee版本也越来越新,体积越来越大. 看图软件也越来越繁杂,免 ...
- Revit BIM模型在ArcGIS Pro中的数据组织及转换成SLPK后的图层结构解析
ArcGIS Pro对Revit 数据有自己的一套分层方式. 在ArcGIS Pro中打开bim文件会发现都是按照相同的方式组织数据: 将rvt格式数据转换成SLPK格式后的数据结构(将slpk数据直 ...
