使用caffe训练自己的CNN
现在有这样的一个场景:给一张行人的小矩形框图片, 根据该行人的特征识别出性别。
分析:
(1),行人的姿态各异,变化多端。很难提取图像的特定特征
(2),正常人肉眼判别行人的根据是身材比例,头发长度等。(如果是冬天的情况下,行人穿着厚实,性别识别更加难)
solution:
针对难以提取特定特征的图像,可以采用卷积神经网络CNN去自动提取并训练。
数据准备:
采用 PETA数据集,Pedestrain Attribute Recognition At Far Distance。 该数据集一共包含了19000张标记了行人穿着及性别信息的图片。
Peta dataset source url: http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/PETA.html
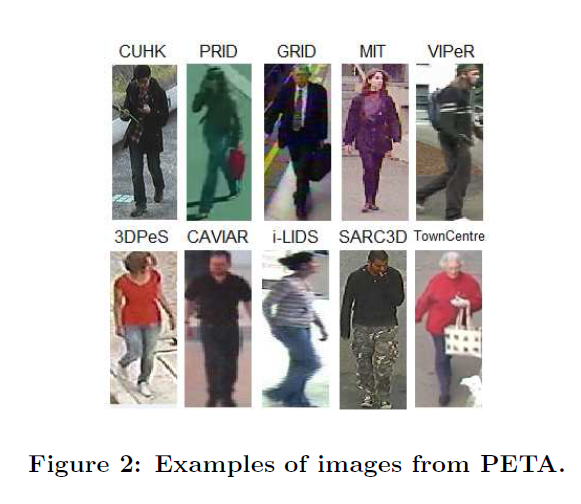
数据处理:
针对下载解压之后的数据集,采用的流程是:
(1)对每一张图片进行resize, resize到特定的大小(实验中定为50*150),
(2)对正类负类样本的不均衡情况,进行rebalance处理,实验中对少数类样本进行随机选择n张进行data augmentation之后重新加入到dataset中。
(3)划分training set和testing set, 根据train/test ratio将整个数据样本随机分为两部分。
(4)对training set 进行data augmentation 处理。 扩大训练数据量。 (操作包括: 翻转,滤波等)
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- encoding: utf-8 -*- #########
## The python code to preprocess the images and resize them into (50, 150)
## Date: 2016-09-19
######### import os, sys, cv2
import numpy as np
import random image_cnt = 0
MIN_HEIGHT = 120
MIN_WIDTH = 40
targetLabel = [] positive_cnt = 0
negative_cnt = 0 def readImage( filePath , targetDir ):
global image_cnt, positive_cnt, negative_cnt
global targetLabel
if not os.path.isdir( filePath ):
print('{} is not a dir'.format(filePath))
return None
listFile = os.listdir( filePath )
labelDict = {}
with open( filePath + 'Label.txt', 'r') as reader:
for line in reader:
lines = line.split()
for i in range(1, len(lines)):
if lines[i] == 'personalMale':
label = 1
elif lines[i] == 'personalFemale':
label = 0
else:
continue
labelDict[lines[0]] = label
break for i in range(len(listFile)):
if len(listFile[i]) > 4 and (listFile[i][-4:] == '.bmp' or listFile[i][-4:] == '.jpg' or \
listFile[i][-4:] == '.png' or listFile[i][-5:] == '.jpeg'):
imageName = filePath + listFile[i]
img = cv2.imread( imageName )
if not img.data:
continue
height, width = img.shape[:2]
if height < MIN_HEIGHT or width < MIN_WIDTH:
continue
fileName = str( image_cnt ) + '.jpeg'
identity = listFile[i].find('_')
if identity == -1:
identity = len(listFile[i])
idd = listFile[i][:identity]
if labelDict.has_key( idd ) :
targetLabel.append([ fileName, labelDict[idd]])
if labelDict[idd] == 0:
negative_cnt += 1
else:
positive_cnt += 1
img = cv2.resize(img, (50, 150), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
cv2.imwrite(targetDir + fileName, img)
image_cnt += 1
else:
print('file {} do not have label'.format(listFile[i]) ) ####### pyramid operator
def MinAndEnlarge(img, Minus_pixel = 3):
img = img[(3*Minus_pixel):(150 - 3*Minus_pixel), Minus_pixel:(50 - Minus_pixel), :]
img = cv2.resize(img, (50, 150), interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC )
return img ####### rotate operator
def Flip(img, operator = 1):
if operator == 1:
img = cv2.flip(img, 1)
else:
img = cv2.flip(img, 0)
return img ####### median blurring the image
def Blur(img, kernel_size=5):
img = cv2.medianBlur(img, kernel_size)
return img def EnlargeData( filePath , targetDir ):
global image_cnt, targetLabel
total_sample = len(targetLabel)
for i in range(total_sample):
img = cv2.imread( filePath + targetLabel[i][0] )
fileLabel = targetLabel[i][1]
if not img.data:
print('no exits image file {}'.format( filePath + targetLabel[i][0]) )
#
img1 = MinAndEnlarge(img, 3)
fileName = str(image_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img1 )
image_cnt += 1
targetLabel.append( [fileName, fileLabel] )
#
img2 = Flip(img1)
fileName = str(image_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img2 )
image_cnt += 1
targetLabel.append( [fileName, fileLabel] )
#
img3 = Blur(img, 5)
fileName = str(image_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img3 )
image_cnt += 1
targetLabel.append( [fileName, fileLabel] )
#
img4 = Blur(img1, 5)
fileName = str(image_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img4 )
image_cnt += 1
targetLabel.append([fileName, fileLabel])
#
img5 = Blur(img2, 5)
fileName = str(image_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img5 )
image_cnt += 1
targetLabel.append([fileName, fileLabel])
print('The total number of images is {}'.format(image_cnt)) def saveLabel( targetDir ):
global targetLabel
with open(targetDir + 'label.txt', 'w') as writer:
for i in range(len(targetLabel)):
writer.write( str( targetLabel[i][0] ) + ' ' + str(targetLabel[i][1]) + '\n' ) ##### ReBalance operator
####### num (the number of minority class should added)
####### n_or_p (the label of minority class)
####### op_chose( 1--symmetrical flip; 0--rotate image; )
def ReBalance( targetDir, num, n_or_p, op_chose = 0):
global targetLabel, image_cnt
total_sample = len(targetLabel)
Contain = {}
while 1:
if num <= 0:
break
key_id = random.randint(0, total_sample-1)
if Contain.has_key( key_id ) or targetLabel[key_id][1] != n_or_p:
continue
img = cv2.imread( targetDir + targetLabel[key_id][0] )
if op_chose == 0:
img = cv2.flip(img, 1)
elif op_chose == 1:
img = cv2.flip(img, 0)
fileName = str(image_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite(targetDir + fileName, img)
image_cnt += 1
targetLabel.append([fileName, n_or_p])
num -= 1
print('Finish add {} images'.format(image_cnt - total_sample))
print('Now the class is balanced and total num is {}'.format(image_cnt))
print('image_cnt is {} and len(_targetLabel_) is {} '.format(image_cnt, len(targetLabel))) def divide( targetDir, trainDir, testDir, test_ratio = 0.20):
global targetLabel
total_sample = len(targetLabel)
assert( test_ratio < 1)
test_num = int(total_sample * test_ratio )
test_half_num = test_num // 2; ml_cnt = 0; fm_cnt = 0
testLabel = [] ; trainLabel = []
for i in range(total_sample):
if ml_cnt < test_half_num and targetLabel[i][1] == 1:
ml_cnt += 1
img = cv2.imread( targetDir + targetLabel[i][0] )
cv2.imwrite( testDir + targetLabel[i][0], img )
testLabel.append(targetLabel[i])
elif fm_cnt < test_half_num and targetLabel[i][1] == 0:
fm_cnt += 1
img = cv2.imread( targetDir + targetLabel[i][0] )
cv2.imwrite( testDir + targetLabel[i][0], img )
testLabel.append(targetLabel[i])
else:
img = cv2.imread( targetDir + targetLabel[i][0] )
cv2.imwrite( trainDir + targetLabel[i][0], img )
trainLabel.append(targetLabel[i])
# train
with open( trainDir + 'label.txt', 'w') as writer:
for i in range(len(trainLabel)):
writer.write( str( trainLabel[i][0] ) + ' ' + str(trainLabel[i][1]) + '\n' )
with open( testDir + 'label.txt', 'w') as writer:
for i in range(len(testLabel)):
writer.write( str(testLabel[i][0]) + ' ' + str(testLabel[i][1]) + '\n')
print('has divide into train with {} samples and test with {} samples'.format(len(trainLabel), len(testLabel)) )
return trainLabel, testLabel def DivideSet( targetDir, trainDir, testDir, test_ratio = 0.20):
global targetLabel
total_sample = len(targetLabel)
assert( test_ratio < 1 )
test_num = int(test_ratio * total_sample)
test_half_num = test_num //2 ; ml_cnt = test_half_num; fm_cnt = test_half_num
testLabel = [] ; trainLabel = [] ; testDict = {}
while ml_cnt > 0 or fm_cnt > 0:
idd = random.randint(0, total_sample-1)
if testDict.has_key( targetLabel[idd][0] ):
continue
if targetLabel[idd][1] == 1 and ml_cnt > 0:
img = cv2.imread( targetDir + targetLabel[idd][0] )
cv2.imwrite( testDir + targetLabel[idd][0], img )
testLabel.append( targetLabel[idd] )
testDict[targetLabel[idd][0]] = idd
ml_cnt -= 1
if targetLabel[idd][1] == 0 and fm_cnt > 0:
img = cv2.imread( targetDir + targetLabel[idd][0] )
cv2.imwrite( testDir + targetLabel[idd][0], img )
testLabel.append( targetLabel[idd] )
testDict[targetLabel[idd][0]] = idd
fm_cnt -= 1
for i in range(total_sample):
if not testDict.has_key( targetLabel[i][0] ):
trainLabel.append( targetLabel[i] )
img = cv2.imread( targetDir + targetLabel[i][0] )
cv2.imwrite( trainDir + targetLabel[i][0], img )
## save the trainset and testset
with open( trainDir + 'label.txt', 'w') as writer:
for i in range(len(trainLabel)):
writer.write( str( trainLabel[i][0] ) + ' ' + str(trainLabel[i][1]) + '\n' )
with open( testDir + 'label.txt', 'w') as writer:
for i in range(len(testLabel)):
writer.write( str(testLabel[i][0]) + ' ' + str(testLabel[i][1]) + '\n')
print('has divide into train with {} samples and test with {} samples'.format(len(trainLabel), len(testLabel)) )
return trainLabel, testLabel def EnlargeTrain( fileDir, targetDir, trainLabel , start_cnt):
total_sample = len(trainLabel)
new_cnt = start_cnt
for i in range(total_sample):
img = cv2.imread( fileDir + trainLabel[i][0] )
fileLabel = trainLabel[i][1]
if not img.data:
print('no exits image file {}'.format( fileDir + trainLabel[i][0]) )
continue
#
img1 = MinAndEnlarge(img, 3)
fileName = str(new_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img1 )
new_cnt += 1
trainLabel.append( [fileName, fileLabel] )
#
img2 = Flip(img1)
fileName = str(new_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img2 )
new_cnt += 1
trainLabel.append( [fileName, fileLabel] )
#
img3 = Blur(img, 5)
fileName = str(new_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img3 )
new_cnt += 1
trainLabel.append( [fileName, fileLabel] )
#
img4 = Blur(img1, 5)
fileName = str(new_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img4 )
new_cnt += 1
trainLabel.append([fileName, fileLabel])
#
img5 = Blur(img2, 5)
fileName = str(new_cnt) + '.jpeg'
cv2.imwrite( targetDir + fileName, img5 )
new_cnt += 1
trainLabel.append([fileName, fileLabel])
print('The total number of training images is {}'.format(new_cnt))
with open( targetDir + 'label.txt', 'w') as writer:
for i in range(len(trainLabel)):
writer.write( str( trainLabel[i][0] ) + ' ' + str(trainLabel[i][1]) + '\n' )
print('The trainLabel size is {}'.format(len(trainLabel)) ) if __name__ == '__main__':
fileHead = '/home/zhangyd/source/PETA_dataset/'
filePath = ['3DPeS', 'CAVIAR4REID', 'CUHK', 'GRID','MIT', 'PRID','SARC3D','TownCentre', 'VIPeR','i-LID']
savePath = '/home/zhangyd/source/peta/'
for i in range(len(filePath)):
path = fileHead + filePath[i] + '/archive/'
print ('runing dataset {}'.format(filePath[i]) )
readImage( path, savePath )
print ('The cnt is {}'.format( image_cnt ))
#EnlargeData( savePath, savePath )
saveLabel( savePath )
print( 'we have {} positive labels and {} negative labels '.format( positive_cnt, negative_cnt ))
if positive_cnt > negative_cnt:
add_num = positive_cnt - negative_cnt
ReBalance( savePath, add_num, 0, 0)
else:
add_num = negative_cnt - positive_cnt
ReBalance( savePath, add_num, 1, 0)
print('The total dataset is in {}'.format(savePath))
TrainsavePath = '/home/zhangyd/source/peta_v1/petaTrain/'
TestsavePath = '/home/zhangyd/source/peta_v1/petaTest/'
trainLabel, testLabel = DivideSet(savePath, TrainsavePath, TestsavePath, 0.2 )
start_cnt = len(targetLabel)
EnlargeTrain( TrainsavePath, TrainsavePath, trainLabel, start_cnt )
print('the end')
实验
使用caffe的create_lmdb.sh 转换图像数据 成 imbd数据集。
定义 prototxt 等信息。
CNN 的结构是:
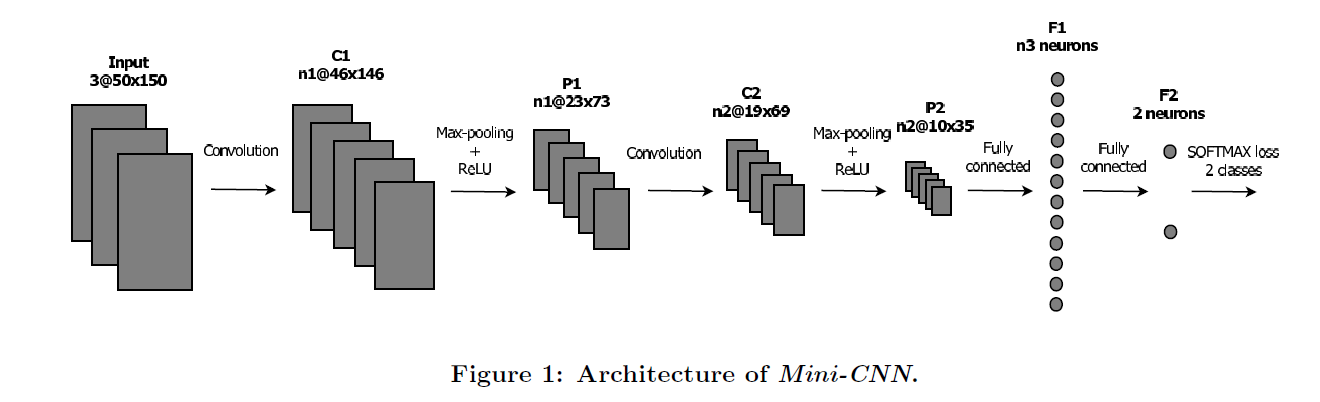
训练的参数设置:
# The train/test net protocol buffer definition
net: "examples/peta/petanet_train_test.prototxt"
# test_iter specifies how many forward passes the test should carry out.
# In the case of MNIST, we have test batch size 100 and 100 test iterations,
# covering the full 10,000 testing images.
test_iter: 100
# Carry out testing every 500 training iterations.
test_interval: 500
# The base learning rate, momentum and the weight decay of the network.
base_lr: 0.01
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 0.0005
# The learning rate policy
lr_policy: "inv"
gamma: 0.0001
power: 0.75
# Display every 100 iterations
display: 100
# The maximum number of iterations
max_iter: 10000
# snapshot intermediate results
snapshot: 5000
snapshot_prefix: "examples/peta/petanet"
# solver mode: CPU or GPU
solver_mode: GPU
使用论文《Learned vs. Hand-Crafted Features for Pedestrian Gender Recognition》中的网络结构,取得了较好的训练结果:
I0922 00:07:32.204310 16398 solver.cpp:337] Iteration 10000, Testing net (#0)
I0922 00:07:34.001411 16398 solver.cpp:404] Test net output #0: accuracy = 0.8616
I0922 00:07:34.001471 16398 solver.cpp:404] Test net output #1: loss = 0.721973 (* 1 = 0.721973 loss)
I0922 00:07:34.001479 16398 solver.cpp:322] Optimization Done.
I0922 00:07:34.001485 16398 caffe.cpp:254] Optimization Done.
实验分析:
因为网络不大,网络也比较简单,在GPU下进行训练,消耗的显存大概是几百M,不到1G的显存。网络结构经典,也取得较好的训练结果。
我的拓展: 自己设计的CNN网络
吸取了GoogleNet的网络特征, 引入inception, 重新设计网络。
是两个 inception 组成, 后面加上一个FC层。
其中Snapshot的网络结构prototxt文件是:
name: "petaNet"
layer {
name: "data"
type: "Input"
top: "data"
input_param {
shape: {
dim: 1
dim: 3
dim: 50
dim: 150
}
}
} ### ------------ layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param {
lr_mult: 1
}
param {
lr_mult: 2
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 3
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "conv1"
} ##-------
# Inception 3a
##------- layer {
name: "inc1_conv1"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "inc1_conv1"
type: "Convolution"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 7
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc1_conv1_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc1_conv1"
top: "inc1_conv1"
} layer {
name: "inc1_conv2_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "inc1_conv2_1"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 3
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc1_conv2_1_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc1_conv2_1"
top: "inc1_conv2_1"
} layer {
name: "inc1_conv2_2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "inc1_conv2_1"
top: "inc1_conv2_2"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 3
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc1_conv2_2_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc1_conv2_2"
top: "inc1_conv2_2"
} layer {
name: "inc1_conv2_3"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "inc1_conv2_2"
top: "inc1_conv2_3"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 3
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc1_conv2_3_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc1_conv2_3"
top: "inc1_conv2_3"
} layer {
name: "inc1_conv3_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "inc1_conv3_1"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc1_conv3_1_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc1_conv3_1"
top: "inc1_conv3_1"
} layer {
name: "inc1_conv3_2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "inc1_conv3_1"
top: "inc1_conv3_2"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 3
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc1_conv3_2_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc1_conv3_2"
top: "inc1_conv3_2"
} layer {
name: "inc1_concat"
type: "Concat"
bottom: "inc1_conv1"
bottom: "inc1_conv2_3"
bottom: "inc1_conv3_2"
top: "inc1_concat"
} #-----end of Inception 3a layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "inc1_concat"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
} ##------
# Inception 2B
##------ layer {
name: "inc2_conv1_1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "inc2_conv1_1"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 120
kernel_size: 3
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc2_conv1_1_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc2_conv1_1"
top: "inc2_conv1_1"
} layer {
name: "inc2_conv1_2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "inc2_conv1_1"
top: "inc2_conv1_2"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 120
kernel_size: 3
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc2_conv1_2_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc2_conv1_2"
top: "inc2_conv1_2"
} layer {
name: "inc2_conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "inc2_conv2"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
convolution_param {
num_output: 120
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
}
layer {
name: "inc2_conv2_relu"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "inc2_conv2"
top: "inc2_conv2"
} layer {
name: "inc2_concat"
type: "Concat"
bottom: "inc2_conv1_2"
bottom: "inc2_conv2"
top: "inc2_concat"
} ##----end of Inception 2B layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "inc2_concat"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
} layer {
name: "fc1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "fc1"
param { lr_mult: 1 }
param { lr_mult: 2 }
inner_product_param {
num_output: 2
weight_filler { type: "xavier" }
bias_filler { type: "constant" }
}
} #### ---------- layer {
name: "prob"
type: "Softmax"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "prob"
}
取得的效果比论文中的网络结构差点, 训练结果是:
I0927 00:11:42.485725 20295 solver.cpp:317] Iteration 10000, loss = 0.0678897
I0927 00:11:42.485771 20295 solver.cpp:337] Iteration 10000, Testing net (#0)
I0927 00:12:06.291497 20295 solver.cpp:404] Test net output #0: accuracy = 0.8448
I0927 00:12:06.291554 20295 solver.cpp:404] Test net output #1: loss = 0.614111 (* 1 = 0.614111 loss)
I0927 00:12:06.291563 20295 solver.cpp:322] Optimization Done.
I0927 00:12:06.291568 20295 caffe.cpp:254] Optimization Done.
实验分析:
因为该网络的组成较为复杂, inception包含着较大的子网络, 因为训练的时候,需要消耗GPU显存为3G多。训练时间也较长些。
reference:
Learned vs. Hand-Crafted Features for Pedestrian Gender Recognition Grigory Antipov,Sid-Ahmed Berrani
使用caffe训练自己的CNN的更多相关文章
- caffe︱深度学习参数调优杂记+caffe训练时的问题+dropout/batch Normalization
一.深度学习中常用的调节参数 本节为笔者上课笔记(CDA深度学习实战课程第一期) 1.学习率 步长的选择:你走的距离长短,越短当然不会错过,但是耗时间.步长的选择比较麻烦.步长越小,越容易得到局部最优 ...
- 使用caffe训练mnist数据集 - caffe教程实战(一)
个人认为学习一个陌生的框架,最好从例子开始,所以我们也从一个例子开始. 学习本教程之前,你需要首先对卷积神经网络算法原理有些了解,而且安装好了caffe 卷积神经网络原理参考:http://cs231 ...
- 实践详细篇-Windows下使用Caffe训练自己的Caffemodel数据集并进行图像分类
三:使用Caffe训练Caffemodel并进行图像分类 上一篇记录的是如何使用别人训练好的MNIST数据做训练测试.上手操作一边后大致了解了配置文件属性.这一篇记录如何使用自己准备的图片素材做图像分 ...
- Caffe训练AlexNet网络,精度不高或者为0的问题结果
当我们使用Caffe训练AlexNet网络时,会遇到精度一值在低精度(30%左右)升不上去,或者精度总是为0,如下图所示: 出现这种情况,可以尝试使用以下几个方法解决: 1.数据样本量是否太少,最起码 ...
- caffe训练自己的图片进行分类预测--windows平台
caffe训练自己的图片进行分类预测 标签: caffe预测 2017-03-08 21:17 273人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 分类: caffe之旅(4) 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未 ...
- [caffe] caffe训练tricks
Tags: Caffe Categories: Tools/Wheels --- 1. 将caffe训练时将屏幕输出定向到文本文件 caffe中自带可以画图的工具,在caffe路径下: ./tools ...
- 自己定义CNN网络模型并使用caffe训练
caffe自带的例子中对mnist手写体数字训练使用的卷积神经网络是在lenet_train_test.prototxt中定义的,隐含层包含了2个卷积层,2个池化层,2个全连接层,1个激活函数层.网络 ...
- python+caffe训练自己的图片数据流程
1. 准备自己的图片数据 选用部分的Caltech数据库作为训练和测试样本.Caltech是加州理工学院的图像数据库,包含Caltech101和Caltech256两个数据集.该数据集是由Fei-Fe ...
- Caffe训练好的网络对图像分类
对于训练好的Caffe 网络 输入:彩色or灰度图片 做minist 下手写识别分类,不能直接使用,需去除均值图像,同时将输入图像像素归一化到0-1直接即可. #include <caffe/c ...
随机推荐
- 学习zepto.js(对象方法)[5]
继续说. clone: 该方法不接收任何参数,会返回对象中的所有元素集合,但不会对象绑定的事件. var $temp = $("div").clone(); //并不接收任何参数. ...
- sharepoint powershell 批量处理匿名访问
配置Web Application启用匿名访问 Add-PSSnapin -Name Microsoft.SharePoint.PowerShell -ErrorAction SilentlyCont ...
- iOS开发中的http浅析
至于为什么要进行HTTP请求我就不说了.本文主要对HTTP协议做了一些介绍,主要针对网络编程和面试. 先从流程开始说起 APP <---> 服务器 <---> 后台 1) ...
- cordova for ios: Unable to simultaneously satisfy constraints.
使用cordova开发ios项目的时候,在上传图片碰到一个问题.使用html的<input type="file"/>标签来选择照片或者拍照片,引起了布局报错,然后图片 ...
- Android 手机卫士--md5加密过程
在之前的文章中,我们将用户的密码使用SharedPreferences存储,我们打开/data/data/com.wuyudong.mobilesafe/shared_prefs文件夹下的 confi ...
- LruCache缓存
LruCache通常用于实现内存缓存,采用的缓存算法是LRU(Least Recently Used)即近期最少使用算法,其核心思想是:当缓存满的时候,会优先淘汰那些近期最少使用的缓存对象. 1.Lr ...
- 【Swift 2.0】实现简单弹幕功能
前言 简单实现弹幕功能,表跟我谈效率,但也有用队列控制同时弹的数量. 声明 欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处:) 博客园:http://www.cnblogs.com 农民伯伯: http://over ...
- EventBus3.0源码解析
本文主要介绍EventBus3.0的源码 EventBus是一个Android事件发布/订阅框架,通过解耦发布者和订阅者简化 Android 事件传递. EventBus使用简单,并将事件发布和订阅充 ...
- Android中asset和raw的区别
:assets 文件夹是存放不进行编译加工的原生文件,即该文件夹里面的文件不会像 xml, java 文件被预编译,可以存放一些图片,html,js, css 等文件.
- 基于Ruby的watir-webdriver自动化测试方案与实施(二)
接着基于Ruby的watir-webdriver自动化测试方案与实施(一) http://www.cnblogs.com/Javame/p/4159360.html 继续 ... ... 回顾 软 ...
