[CVPR2017] Weakly Supervised Cascaded Convolutional Networks论文笔记
p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #042eee }
p.p2 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
p.p3 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 16.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
p.p4 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333; min-height: 16.0px }
p.p5 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 17.0px STIXGeneral; color: #323333 }
p.p6 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 12.0px STIXGeneral; color: #323333 }
p.p7 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 17.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333; min-height: 20.0px }
p.p8 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 17.0px STIXSizeOneSym; color: #323333 }
p.p9 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; text-align: center; font: 17.0px STIXGeneral; color: #323333 }
p.p10 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; text-align: center; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
p.p11 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 9.0px STIXGeneral; color: #323333 }
li.li2 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
span.s1 { text-decoration: underline }
span.s2 { }
span.s3 { vertical-align: -0.5px }
span.s4 { vertical-align: -9.0px }
ul.ul1 { list-style-type: disc }
ul.ul2 { list-style-type: circle }
https://www.csee.umbc.edu/~hpirsiav/papers/cascade_cvpr17.pdf
Weakly Supervised Cascaded Convolutional Networks, Ali Diba, Vivek Sharma, Ali Pazandeh, Hamed Pirsiavash and Luc Van Gool
亮点
- 通过多任务叠加(分类,分割)提高了多物体弱监督检测的正确率
- 通过利用segmentation筛选纯净的proposals,得到了更鲁棒的结果
- 为弱监督分割任务设计比较鲁棒的loss
- 只考虑全局的分类结果和置信度对高的部分
- 通过loss的weights关注到最需要关注的部分
相关工作
One of the most common approaches [7] consists of the following steps:
- generates object proposals,
- extracts features from the proposals,
- applies multiple instance learning (MIL) to the features and finds the box labels from the weak bag (image) labels.
弱监督物体检测难点: 弱监督物体检测对初始化要求很高,不好的初始化可能会使网络陷入局部最优解,解决的办法主要有以下几个:
- improve the initialization [31, 9, 28, 29]
- regularizing the optimization strategies [4, 5, 7]
- [17] employ an iterative self-learning strategy to employ harder samples to a small set of initial samples
- [15] use a convex relaxation of soft-max loss
Majority of the previous works [25, 32] use a large collection of noisy object proposals to train their object detector. In contrast, our method only focuses on a very few clean collection of object proposals that are far more reliable, robust, computationally efficient, and gives better performance
方法
Two-stage: proposal and image classification (conv1 till con5, global pooling) + multiple instance learning (2fc, score layer)

1. image classification: CNN with global average pooling (GAP) [36]中引入,将分类过程中fc层的weights作为原来convolutional layer输出的权重并将所有频道加权得到的图作为class activation map。在这一步中,还产生一个分类的loss LGAP
[36] B. Zhou, A. Khosla, A. Lapedriza, A. Oliva, and A. Torralba. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In CVPR, 2016. 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
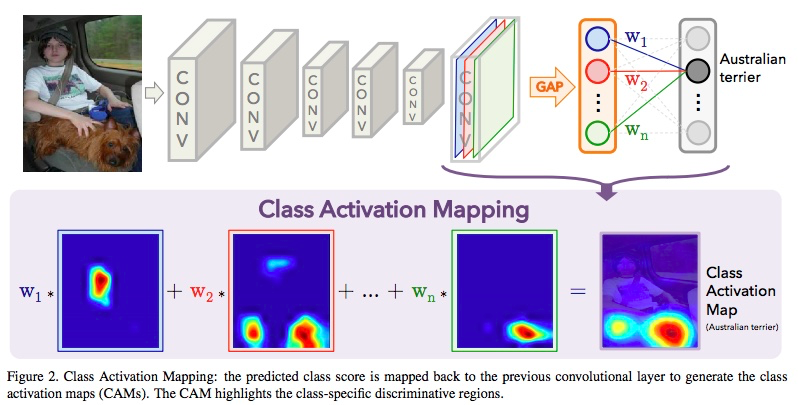
2. multiple instance learning
Proposal: edgeboxs [37] is used to generate an initial set of object proposals. Then we threshold the class activation map [36] to come up with a mask. Finally, we choose the initial boxes with largest overlap with the mask.

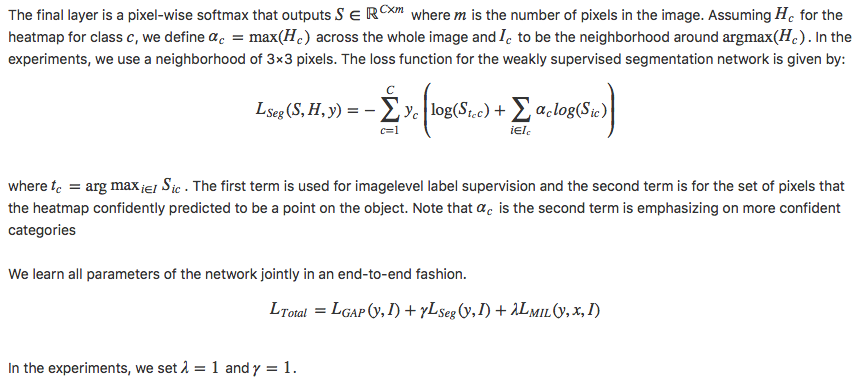
Three-stage: more information about the objects’ boundary learned in a segmentation task can lead to acquisition of a better appearance model and then better object localization.
- 主要思想:分割监督信号帮助提升定位准确率。
- 弱分割监督信号:上一级得到的mask

实验结果
PASCAL VOC 2007
- +3.3% classification compared with [18]
- +1.6% correct localization compared with [27]
- +0.6% compared with [6]
PASCAL VOC 2010
- +3.3% compared with [6]
PASCAL VOC 2012
- +8.8% compared with [18]
- ILSVRC 2013
- +5.5% compared with [18]
Object detection training
- PASCAL VOC 2007 test set: Faster RCNN trained by the pseudo ground-truth (GT) bounding boxes generated by our cascaded networks performs slightly better than our transfered model. (+0.3%)
[6] H. Bilen and A. Vedaldi. Weakly supervised deep detection networks. In CVPR, 2016. 6, 7, 8
[18] D. Li, J.-B. Huang, Y. Li, S. Wang, and M.-H. Yang. Weakly supervised object localization with progressive domain adaptation. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016. 2, 6, 7
[27] K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In ICLR, 2015. 5, 6
p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 16.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
p.p2 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
li.li2 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
span.s1 { }
ul.ul1 { list-style-type: disc }
ul.ul2 { list-style-type: circle }
p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #042eee }
p.p2 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
p.p3 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 16.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
p.p4 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333; min-height: 16.0px }
p.p5 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 17.0px STIXGeneral; color: #323333 }
p.p6 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 12.0px STIXGeneral; color: #323333 }
p.p7 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 17.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333; min-height: 20.0px }
p.p8 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 17.0px STIXSizeOneSym; color: #323333 }
p.p9 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; text-align: center; font: 17.0px STIXGeneral; color: #323333 }
p.p10 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; text-align: center; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
p.p11 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 9.0px STIXGeneral; color: #323333 }
li.li2 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 14.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 }
span.s1 { text-decoration: underline }
span.s2 { }
span.s3 { vertical-align: -0.5px }
span.s4 { vertical-align: -9.0px }
ul.ul1 { list-style-type: disc }
ul.ul2 { list-style-type: circle }
[CVPR2017] Weakly Supervised Cascaded Convolutional Networks论文笔记的更多相关文章
- [CVPR 2016] Weakly Supervised Deep Detection Networks论文笔记
p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 13.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 } p. ...
- [论文阅读] Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks(MTCNN)
相关论文:Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks 概论 用于人脸检测和对 ...
- Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks论文复现笔记
目录 Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks 论文复现笔记 Abstract Introduction Approach Visual ...
- 《Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks》
<Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks> 论文主要的三个贡 ...
- Densely Connected Convolutional Networks 论文阅读
毕设终于告一段落,传统方法的视觉做得我整个人都很奔溃,终于结束,可以看些搁置很久的一些论文了,嘤嘤嘤 Densely Connected Convolutional Networks 其实很早就出来了 ...
- 【Semantic Segmentation】 Instance-sensitive Fully Convolutional Networks论文解析(转)
这篇文章比较简单,但还是不想写overview,转自: https://blog.csdn.net/zimenglan_sysu/article/details/52451098 另外,读这篇pape ...
- 【Detection】R-FCN: Object Detection via Region-based Fully Convolutional Networks论文分析
目录 0. Paper link 1. Overview 2. position-sensitive score maps 2.1 Background 2.2 position-sensitive ...
- [CVPR2015] Is object localization for free? – Weakly-supervised learning with convolutional neural networks论文笔记
p.p1 { margin: 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px 0.0px; font: 13.0px "Helvetica Neue"; color: #323333 } p. ...
- Bag of Tricks for Image Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks论文笔记
一.高效的训练 1.Large-batch training 使用大的batch size可能会减小训练过程(收敛的慢?我之前训练的时候挺喜欢用较大的batch size),即在相同的迭代次数 ...
随机推荐
- Leetcode_101_Symmetric Tree
本文是在学习中的总结,欢迎转载但请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/pistolove/article/details/42087039 Given a binary tree, c ...
- Cocos2D遍历场景图(Scene Graph)
另一个Cocos2D有用的调试特性是打印出递归的打印出节点的孩子们. 你可以添加以下一行到MainScene或GameScene的didLoadFromCCB的方法中: [self.scene wal ...
- JavaScript进阶(十一)JsJava2.0版本
JavaScript进阶(十一)JsJava2.0版本 2007年9月11日,JsJava团队发布了JsJava2.0版本,该版本不仅增加了许多新的类库,而且参照J2SE1.4,大量使用了类的继承和实 ...
- PS图层混合算法之六(差值,溶解, 排除)
差值模式: 查看每个通道中的颜色信息,比较底色和绘图色,用较亮的像素点的像素值减去较暗的像素点的像素值.与白色混合将使底色反相:与黑色混合则不产生变化. 排除模式可生成和差值模式相似的效果,但比差值模 ...
- OpenCV 闭合轮廓检测
这个好像是骨头什么的,但是要求轮廓闭合,于是对图片进行一下膨胀操作,再次检测轮廓就好了. // A closed contour.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include &q ...
- Gradle 1.12用户指南翻译——第三十七章. OSGi 插件
本文由CSDN博客万一博主翻译,其他章节的翻译请参见: http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/gradle-translation.html 翻译项目请关注Githu ...
- objc写一个NSMutableArray不连续索引替换对象的方法
NSMutableArray内置的方法-(void)replaceObjectsAtIndexes:(NSIndexSet*)set withObjects:(NSArray*)objs 只能替换一段 ...
- Java中使用C3P0连接池
先看官网给的范例: import java.sql.*; import javax.naming.*; import javax.sql.DataSource; import com.mchange. ...
- 关于js对象添加属性
字符串类型的(注意要加引号): var obj={}; for(var i=0;i<10;i++){ eval("obj.key"+i+"='"+&quo ...
- Spring Cloud入门教程-Ribbon实现客户端负载均衡
简介 我们继续以之前博客的代码为基础,增加Ribbon组件来提供客户端负载均衡.负载均衡是实现高并发.高性能.可伸缩服务的重要组成部分,它可以把请求分散到一个集群中不同的服务器中,以减轻每个服务器的负 ...
