bcftools
beftools非常复杂,大概有20个命令,每个命令下面还有N多个参数
annotate .. edit VCF files, add or remove annotations call .. SNP/indel calling (former "view") cnv .. Copy Number Variation caller concat .. concatenate VCF/BCF files from the same set of samples consensus .. create consensus sequence by applying VCF variants convert .. convert VCF/BCF to other formats and back csq .. haplotype aware consequence caller filter .. filter VCF/BCF files using fixed thresholds gtcheck .. check sample concordance, detect sample swaps and contamination index .. index VCF/BCF isec .. intersections of VCF/BCF files merge .. merge VCF/BCF files files from non-overlapping sample sets mpileup .. multi-way pileup producing genotype likelihoods norm .. normalize indels plugin .. run user-defined plugin polysomy .. detect contaminations and whole-chromosome aberrations query .. transform VCF/BCF into user-defined formats reheader .. modify VCF/BCF header, change sample names roh .. identify runs of homo/auto-zygosity sort .. sort VCF/BCF files stats .. produce VCF/BCF stats (former vcfcheck) view .. subset, filter and convert VCF and BCF files
下面讲一下过滤参数
1、bcftools filter(以-i参数为例)
- -i, --include EXPRESSION :
- include only sites for which EXPRESSION is true. For valid expressions see EXPRESSIONS.(根据正则保留)
- 其中包括:
- 1.1、numerical constants, string constants, file names (this is currently supported only to filter by the ID column)
1, 1.0, 1e-4 "String" @file_name
1.2、算术运算
+,*,-,/
1.3、comparison operators
== (same as =), >, >=, <=, <, !=
1.4、regex操作符“~”和它的否定“!~”。表达式区分大小写,除非添加“/i”。
INFO/HAYSTACK ~ "needle" INFO/HAYSTACK ~ "NEEDless/i"
1.5、圆括号
(, )
1.6、逻辑运算符。参见下面的示例和有关“&&”与“&”以及“||”与“|”之间区别的过滤教程。
&&, &, ||, |
1.7、信息标签,格式标签,列名
INFO/DP or DP FORMAT/DV, FMT/DV, or DV FILTER, QUAL, ID, CHROM, POS, REF, ALT[0]
1.8、1 (or 0) to test the presence (or absence) of a flag
FlagA=1 && FlagB=0
1.9、"." to test missing values
DP=".", DP!=".", ALT="."
2.0、missing genotypes can be matched regardless of phase and ploidy (".|.", "./.", ".") using these expressions
GT~"\.", GT!~"\."
2.1、sample genotype: reference (haploid or diploid), alternate (hom or het, haploid or diploid), missing genotype, homozygous, heterozygous, haploid, ref-ref hom, alt-alt hom, ref-alt het, alt-alt het, haploid ref, haploid alt (case-insensitive)
GT="ref" GT="alt" GT="mis" GT="hom" GT="het" GT="hap" GT="RR" GT="AA" GT="RA" or GT="AR" GT="Aa" or GT="aA" GT="R" GT="A"
2.2、TYPE for variant type in REF,ALT columns (indel,snp,mnp,ref,bnd,other,overlap). Use the regex operator "\~" to require at least one allele of the given type or the equal sign "=" to require that all alleles are of the given type. Compare
TYPE="snp" TYPE~"snp" TYPE!="snp" TYPE!~"snp"
2.3、array subscripts (0-based), "*" for any element, "-" to indicate a range. Note that for querying FORMAT vectors, the colon ":" can be used to select a sample and an element of the vector, as shown in the examples below
INFO/AF[0] > 0.3 .. first AF value bigger than 0.3 FORMAT/AD[0:0] > 30 .. first AD value of the first sample bigger than 30 FORMAT/AD[0:1] .. first sample, second AD value FORMAT/AD[1:0] .. second sample, first AD value DP4[*] == 0 .. any DP4 value FORMAT/DP[0] > 30 .. DP of the first sample bigger than 30 FORMAT/DP[1-3] > 10 .. samples 2-4 FORMAT/DP[1-] < 7 .. all samples but the first FORMAT/DP[0,2-4] > 20 .. samples 1, 3-5 FORMAT/AD[0:1] .. first sample, second AD field FORMAT/AD[0:*], AD[0:] or AD[0] .. first sample, any AD field FORMAT/AD[*:1] or AD[:1] .. any sample, second AD field (DP4[0]+DP4[1])/(DP4[2]+DP4[3]) > 0.3 CSQ[*] ~ "missense_variant.*deleterious"
2.4、with many samples it can be more practical to provide a file with sample names, one sample name per line
GT[@samples.txt]="het" & binom(AD)<0.01
2.5、function on FORMAT tags (over samples) and INFO tags (over vector fields): maximum; minimum; arithmetic mean (AVG is synonymous with MEAN); median; standard deviation; sum; string length; absolute value; number of elements (matching columns for FORMAT tags or number of fields for INFO tags).
MAX, MIN, AVG, MEAN, MEDIAN, STDEV, SUM, STRLEN, ABS, COUNT
2.6、two-tailed binomial test. Note that for N=0 the test evaluates to a missing value and when FORMAT/GT is used to determine the vector indices, it evaluates to 1 for homozygous genotypes.
binom(FMT/AD) .. GT can be used to determine the correct index binom(AD[0],AD[1]) .. or the fields can be given explicitly phred(binom()) .. the same as binom but phred-scaled
2.7、variables calculated on the fly if not present: number of alternate alleles; number of samples; count of alternate alleles; minor allele count (similar to AC but is always smaller than 0.5); frequency of alternate alleles (AF=AC/AN); frequency of minor alleles (MAF=MAC/AN); number of alleles in called genotypes; number of samples with missing genotype; fraction of samples with missing genotype; indel length (deletions negative, insertions positive)
N_ALT, N_SAMPLES, AC, MAC, AF, MAF, AN, N_MISSING, F_MISSING, ILEN
2.8、the number (N_PASS) or fraction (F_PASS) of samples which pass the expression
N_PASS(GQ>90 & GT!="mis") > 90 F_PASS(GQ>90 & GT!="mis") > 0.9
2.9、custom perl filtering. Note that this command is not compiled in by default, see the section Optional Compilation with Perl in the INSTALL file for help and misc/demo-flt.pl for a working example. The demo defined the perl subroutine "severity" which can be invoked from the command line as follows:
perl:path/to/script.pl; perl.severity(INFO/CSQ) > 3
注意事项:
字符串比较和正则表达式不区分大小写;变量和函数名不区分大小写,但是flag区分大小写。例如,"qual"可以代替"qual", "strlen()"可以代替"strlen()",但不是“dp”而是“DP”。当查询多个值时,将测试所有元素并对结果使用OR逻辑。例如,查询“TAG=1,2,3,4”时,计算如下:
-i 'TAG[*]=1' .. true, the record will be printed -i 'TAG[*]!=1' .. true -e 'TAG[*]=1' .. false, the record will be discarded -e 'TAG[*]!=1' .. false -i 'TAG[0]=1' .. true -i 'TAG[0]!=1' .. false -e 'TAG[0]=1' .. false -e 'TAG[0]!=1' .. true
举例:
MIN(DV)>5 MIN(DV/DP)>0.3 MIN(DP)>10 & MIN(DV)>3 FMT/DP>10 & FMT/GQ>10 .. both conditions must be satisfied within one sample FMT/DP>10 && FMT/GQ>10 .. the conditions can be satisfied in different samples QUAL>10 | FMT/GQ>10 .. true for sites with QUAL>10 or a sample with GQ>10, but selects only samples with GQ>10 QUAL>10 || FMT/GQ>10 .. true for sites with QUAL>10 or a sample with GQ>10, plus selects all samples at such sites TYPE="snp" && QUAL>=10 && (DP4[2]+DP4[3] > 2) COUNT(GT="hom")=0 .. no homozygous genotypes at the site AVG(GQ)>50 .. average (arithmetic mean) of genotype qualities bigger than 50 ID=@file .. selects lines with ID present in the file ID!=@~/file .. skip lines with ID present in the ~/file MAF[0]<0.05 .. select rare variants at 5% cutoff POS>=100 .. restrict your range query, e.g. 20:100-200 to strictly sites with POS in that range.
shell 扩展:
注意表达式必须经常引用,因为在shell中有些字符有特殊的含义。一个用单引号括起来的表达式的例子,它导致整个表达式按照预期传递给程序:
bcftools view -i '%ID!="." & MAF[0]<0.01'
------------------------过滤Filtering-------------
1、按照固定列(fixed columns)过滤
固定列,例如“QUAL, FILTER, INFO”可以直接过滤。例如:
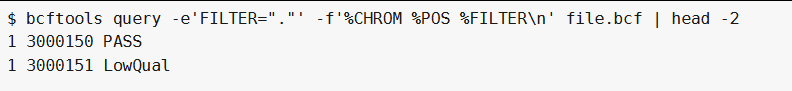
bcftools query -e'FILTER="."' -f'%CHROM %POS %FILTER\n' file.bcf #过滤掉FILTER字段中为.的行
bcftools query -i'QUAL>20 && DP>10' -f'%CHROM %POS %QUAL %DP\n' file.bcf | head -2 #只保留质量值大于20,且覆盖深度高于10的位点
2、FORMAT columns
在过滤FORMAT字段的时候,OR 逻辑用于所有samples。When filtering FORMAT tags, the OR logic is applied with multiple samples,而不是单个sample.例如,如果我们想删除任何样本中带有未知基因型的位点,表达式-i 'GT!="会不起作用,必须用相反的逻辑 -e 'GT ="."' :
bcftools query -i 'GT!="."' #不行 bcftools query -e 'GT ="."' #相反逻辑才可行

3、FORMAT列与 布尔值(&& vs & and || vs |)
我们希望一个sample或多个samples具有足够大的覆盖率(DP>10)和基因型质量(GQ>20)的snp位点:
bcftools query -i'FMT/DP>10 & FMT/GQ>20' -f'%POS[\t%SAMPLE:DP=%DP GQ=%GQ]\n' file.bcf ##-i 'FMT/DP>10和FMT/GQ>20'在同一个sample中选择满足条件的位点:

另一方面,如果我们需要在同一sample中两个条件都满足但不一定相同样品,我们使用&&操作符而不是&:
bcftools query -i'FMT/DP>10 && FMT/GQ>20' -f'%POS[\t%SAMPLE:DP=%DP GQ=%GQ]\n' file.bcf
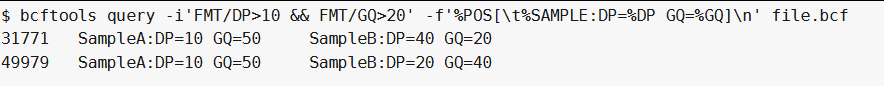
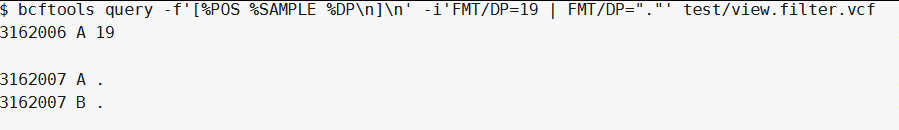
|操作符可以只选择匹配的样本:
bcftools query -f'[%POS %SAMPLE %DP\n]\n' -i 'FMT/DP=19 | FMT/DP="."' test/view.filter.vcf
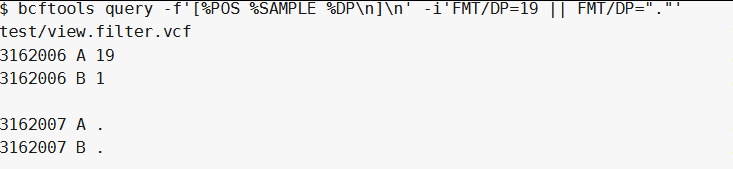
whole samples record when || is used(就是有一个样本符合该位点,那么该位点所有的样本记录都会被显示出来):
bcftools query -f '[%POS %SAMPLE %DP\n]\n' -i 'FMT/DP=19 || FMT/DP="."' test/view.filter.vcf
过滤:
bcftools filter -i 'SVLEN<100000 | SVLEN< -50 & DV>10' -Oz --threads 8 -o B1952.filter.clean.vcf.gz B1952.ngmlr_sniffle.vcf #例如过滤-50<绝对SVLEN<10000
重要网址:
http://samtools.github.io/bcftools/howtos/filtering.html
bcftools的更多相关文章
- bcftools合并vcf文件
见命令: bcftools merge A.vcf.gz B.vcf.gz C.vcf.gz -Oz -o ABC.vcf.gz 参考链接:http://vcftools.sourceforge.ne ...
- bcftools或vcftools提取指定区段的vcf文件(extract specified position )
下载安装bcftools 见如下命令: bcftools filter 1000Genomes.vcf.gz --regions 9:4700000-4800000 > 4700000-4800 ...
- 使用bcftools提取指定样本的vcf文件(extract specified samples in vcf format)
1.下载安装bcftools. 2.准备样本ID文件,这里命名为samplelistname.txt,一个样本一行,如下所示: sample1 sample2 sample3 3.输入命令: bcft ...
- bcftools将vcf生成bgzip和index格式
利用bcftools软件将vcf格式生成gz格式和index格式,需要用到“-Oz”和“index”命令,具体如下: /bcftools-1.8/bin/bcftools view ExAC.vcf ...
- 【Bcftools】合并不同sample的vcf文件,通过bcftools
通过GATK calling出来的SNP如果使用UnifiedGenotype获得的SNP文件是分sample的,但是如果使用vcftools或者ANGSD则需要Vcf文件是multi-sample的 ...
- 【BCFTOOLS】按样本拆分VCF文件
在对vcf的操作有这样三个软件: Vcftools:主要用于群体分析,文本处理的功能不是很强大,虽然这个软件也可以拆分样本,但是这种拆分不涉及文件的处理,只是保留在分析流程里. GATK .x:这个软 ...
- samtools+bcftools 进行SNP calling
两个软件的作用:1.samtools mpileup 主要是用于收集BAM文件中的信息,这个位点上有多少条read匹配,匹配read的碱基是什么,并将这些信息存储在BCF文件中.2.bcftools ...
- bcftools 提取vcf(snp/indel)文件子集
做群体变异检测后,通常会有提取子集的操作,之前没有发现bcftools有这个功能,都是自己写脚本操作,数据量一上来,速度真的是让人无语凝噎.这里记录下提取子vcf文件的用法,软件版本:bcftools ...
- linux 安装SAMtools,bcftools,htslib,sratoolkit,bedtools,GATK,TrimGalore,qualimap,vcftools,bwa
--------------------安装Samtools---------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
随机推荐
- css兄弟选择器,+ ~选择器的区别
壹 ❀ 引 实习生在写搜索框下拉提示时,遇到了不知道怎么解决的问题,所以来问我.效果不难,鼠标选中输入框(focus)时,展示搜索关键字相关提示,看了眼dom结构是这样的: 在她的理解里面,选中父元 ...
- RMAN详细教程(三):备份脚本的组件和注释
RMAN详细教程(一):基本命令代码 RMAN详细教程(二):备份.检查.维护.恢复 RMAN详细教程(三):备份脚本的组件和注释 RMAN详细教程(四):备份脚本实战操作 一.基本组件: 1.Ser ...
- 反射2-spring boot jpa 注入model即实现查询
spring boot jpa 使用方法:将对应的model类注入即可// fixed parameter type private Specification<TargetModel> ...
- 【shell脚本】自动磁盘分区,格式化,挂载===autoMount.sh
#!/bin/bash # 自动对磁盘分区.格式化.挂载 # 对虚拟机的 vdb 磁盘进行分区格式化,使用<<将需要的分区指令导入给程序 fdisk # n(新建分区),p(创建主分区), ...
- Elasticsearch Query DSL 语言介绍
目录 0. 引言 1. 组合查询 2. 全文搜索 2.1 Match 2.2 Match Phase 2.3 Multi Match 2.4 Query String 2.5 Simple Query ...
- vs未能正确加载CSharpPackage包,未能正确加载“Microsoft.VisualStudio.Editor.Implementation.EditorPackage”包
VS2017打开项目时提示未能正确加载CSharpPackage包, 可以使用 devenv命令工具来解决,操作如下 打开vs2017开发人员命令提示符(请使用管理员身份运行),如图 敲入 deve ...
- 【踩坑系列】VS2019提示 ' the package could not be found in c\users\username\nuget\packages\. '
解决步骤 1.删除对应项目下的 obj 文件夹 2.重新生成该项目
- DevExpress 使用 GridControl 时,数据源无法立即更新的问题
背景 在使用 DevExpress 的 GridControl 为其实现 Checkbox 列,发现如果勾选了三行的数据,在遍历 GridControl 绑定的数据源时 Checkbox 列的数据仅有 ...
- Java关键字之abstract、final、static用法
abstract:即抽象的,可以修饰类.方法: 修饰类:当有一个方法为抽象方法时,这个类就是抽象类,抽象类不能被new,它是一个不完整的类. 修饰方法:这个方法就是抽象的,即只能方法的定义,没有方法的 ...
- 敏捷软件开发_UML<一>
敏捷软件开发_UML 所看书籍是:敏捷软件开发_原则.模式与实践_C#版(美)马丁著,这本书写的非常棒,感谢作者.该归纳总结的过程按照我读的顺序写. UML 在建造桥梁,零件,自动化设备之前需要建 ...

