Statistics : Data Distribution
1、Normal distribution

In probability theory, the normal (or Gaussian or Gauss or Laplace–Gauss) distribution is a very common continuous probability distribution. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed and is called a normal deviate.
The normal distribution is
useful because of the central limit theorem. In its most general form, under
some conditions (which include finite variance), it states that averages of
samples of observations of random variables independently drawn from
independent distributions converge in distribution to the normal, that is, they
become normally distributed when the number of observations is sufficiently
large. Physical quantities that are expected to be the sum of many independent
processes (such as measurement errors) often have distributions that are nearly
normal. Moreover, many results and methods (such as propagation of uncertainty
and least squares parameter fitting) can be derived analytically in explicit
form when the relevant variables are normally distributed.
The normal distribution is
sometimes informally called the bell curve. However, many other distributions
are bell-shaped (such as the Cauchy, Student's t-, and logistic distributions).
link:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_distribution
https://www.mathsisfun.com/data/standard-normal-distribution.html
2、Poisson Distribution
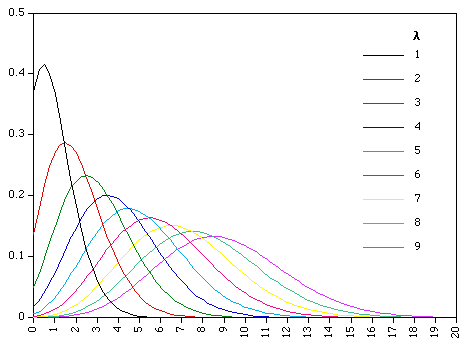
In
probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution (French
pronunciation: ; in English often rendered /ˈpwɑːsɒn/), named after French
mathematician Siméon Denis Poisson, is a discrete probability distribution that
expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed
interval of time or space if these events occur with a known constant rate and
independently of the time since the last event. The Poisson distribution can
also be used for the number of events in other specified intervals such as
distance, area or volume.
For instance, an
individual keeping track of the amount of mail they receive each day may notice
that they receive an average number of 4 letters per day. If receiving any
particular piece of mail does not affect the arrival times of future pieces of
mail, i.e., if pieces of mail from a wide range of sources arrive independently
of one another, then a reasonable assumption is that the number of pieces of
mail received in a day obeys a Poisson distribution. Other examples that may
follow a Poisson distribution include the number of phone calls received by a
call center per hour and the number of decay events per second from a
radioactive source.
link:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_distribution
https://www.umass.edu/wsp/resources/poisson/
3、Chi-squared distribution

In
probability theory and statistics, the chi-square distribution (also
chi-squared or χ2-distribution) with k degrees of freedom is the distribution
of a sum of the squares of k independent standard normal random variables. The
chi-square distribution is a special case of the gamma distribution and is one
of the most widely used probability distributions in inferential statistics,
notably in hypothesis testing or in construction of confidence intervals. When
it is being distinguished from the more general noncentral chi-square distribution,
this distribution is sometimes called the central chi-square distribution.
The chi-square
distribution is used in the common chi-square tests for goodness of fit of an
observed distribution to a theoretical one, the independence of two criteria of
classification of qualitative data, and in confidence interval estimation for a
population standard deviation of a normal distribution from a sample standard
deviation. Many other statistical tests also use this distribution, such as
Friedman's analysis of variance by ranks.
link:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chi-squared_distribution
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Chi-SquaredDistribution.html
https://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda3666.html
4、Beta distribution
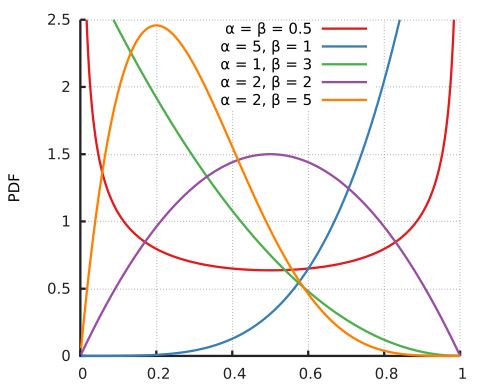
In
probability theory and statistics, the beta distribution is a family of
continuous probability distributions defined on the interval parametrized by two positive shape parameters,
denoted by α and β, that appear as exponents of the random variable and control
the shape of the distribution. It is a special case of the Dirichlet
distribution.
The beta distribution has
been applied to model the behavior of random variables limited to intervals of
finite length in a wide variety of disciplines.
In Bayesian inference, the
beta distribution is the conjugate prior probability distribution for the
Bernoulli, binomial, negative binomial and geometric distributions. For
example, the beta distribution can be used in Bayesian analysis to describe
initial knowledge concerning probability of success such as the probability
that a space vehicle will successfully complete a specified mission. The beta
distribution is a suitable model for the random behavior of percentages and proportions.
The usual formulation of
the beta distribution is also known as the beta distribution of the first kind,
whereas beta distribution of the second kind is an alternative name for the
beta prime distribution.
link:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_distribution
Statistics : Data Distribution的更多相关文章
- 异常:Data = 由于代码已经过优化或者本机框架位于调用堆栈之上,无法计算表达式的值。
做项目的时候,将DataTable序列化成Json,通过ashx向前台返回数据的时候,前台总是获取不到数据,但是程序运行却没问题, 没抛出异常.一时找不到办法,减小输出的数据量,这时前台可以接收到页面 ...
- lombok插件:Data自动get/set方法, Slf4j实现Logger的调用
lombok插件:Data自动get/set方法, Slf4j实现Logger的调用 lombok.Data import lombok.Data; import org.hibernate.anno ...
- 插入图片新方式:data:image
我们在使用<img>标签和给元素添加背景图片时,不一定要使用外部的图片地址,也可以直接把图片数据定义在页面上.对于一些“小”的数据,可以在网页中直接嵌入,而不是从外部文件载入. 如何使用 ...
- EnjoyingSoft之Mule ESB开发教程第六篇:Data Transform - 数据转换
目录 1. 数据转换概念 2. 数据智能感知 - DataSense 3. 简单数据转换组件 3.1 Object to JSON 3.2 JSON to XML 3.3 JSON to Object ...
- Logstash:Data转换,分析,提取,丰富及核心操作
Logstash:Data转换,分析,提取,丰富及核心操作 Logstash plugins Logstash是一个非常容易进行扩张的框架.它可以对各种的数据进行分析处理.这依赖于目前提供的超过200 ...
- Mysql load data infile 导入数据出现:Data truncated for column
[1]Mysql load data infile 导入数据出现:Data truncated for column .... 可能原因分析: (1)数据库表对应字段类型长度不够或修改为其他数据类型( ...
- 错误记录:Data too long for column 'xxx' at row 1
错误记录:Data too long for column 'xxx' at row 1 使用Flask-sqlalchemy操作数据时报错: "Data too long for colu ...
- Generative Modeling by Estimating Gradients of the Data Distribution
目录 概 主要内容 Langevin dynamics Score Matching Denoising Score Matching Noise Conditional Score Networks ...
- C# UTF8的BOM导致XML序列化与反序列化报错:Data at the root level is invalid. Line 1, position 1.
最近在写一个xml序列化及反序列化实现时碰到个问题,大致类似下面的代码: class Program { static void Main1(string[] args) { var test = n ...
随机推荐
- PowerDesigner列名、注释内容互换
资料来源:PowerDesigner列名.注释内容互换 文中一共提供了2种操作的代码. (1)将Name中的字符COPY至Comment中 (2)将Comment中的字符COPY至Name中 使用方法 ...
- C++中对C的扩展学习新增语法——函数重载
函数重载 1.函数重载语法 1.同一个作用域(全局作用域.命名空间作用域.类作用域) 2.参数个数不同 3.参数类型不同 4.参数顺序不同 代码实现: 当函数名字一样的时候,通过参数类型.参数个数.参 ...
- Dev 日志 | 一次 Segmentation Fault 和 GCC Illegal Instruction 编译问题排查 NebulaGraph
摘要 笔者最近在重新整理和编译 Nebula Graph 的第三方依赖,选出两个比较有意思的问题给大家分享一下. Flex Segmentation Fault--Segmentation fault ...
- requests保存图片
1.创建07_save_jpg.py文件 import requests #发送请求respone = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com/img/bd_ ...
- 力扣(LeetCode)颠倒二进制位 个人题解
颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位. 示例 1: 输入: 00000010100101000001111010011100 输出: 0011100101111000001010010100000 ...
- 领扣(LeetCode)最长和谐子序列 个人题解
和谐数组是指一个数组里元素的最大值和最小值之间的差别正好是1. 现在,给定一个整数数组,你需要在所有可能的子序列中找到最长的和谐子序列的长度. 示例 1: 输入: [1,3,2,2,5,2,3,7] ...
- LVM术语及相互关系
*物理存储介质(PhysicalStorageMedia) 指系统的物理存储设备:磁盘,如:/dev/hda./dev/sda等,是存储系统最底层的存储单元. *物理卷(Physical Volume ...
- 深入ObjC GCD中的dispatch group工作原理。
本文是基于GCD的支持库libdispatch的源代码分析的结果或是用于作为源代码阅读的参考,尽量不帖代码,力求用UML图来说明工作流. 本文参考的源代码版本为v501.20.1,如有兴趣请自行到苹果 ...
- .Net Core 使用NPOI导入数据
一.搭建环境 1.新建ASP.NET Core Web 应用程序 2.选择API 3.引用Swashbuckle.AspNetCore NuGet 包进行安装. Swashbuckle.AspNetC ...
- 攻克数通,斩获云计算!誉天Double HCIE学员考证秘笈揭晓
不知不觉,已经过了四个月的时间了,我是六月多报名云计算的,本来是奔着邹Sir去的,但是当时邹sir已经上到HCIE的课程了,只能蹭学弟之前的录屏看.等到七月八号,又正式跟了曾曦老师上了一次完整的课程. ...
