Andrew NG 机器学习编程作业3 Octave
问题描述:使用逻辑回归(logistic regression)和神经网络(neural networks)识别手写的阿拉伯数字(0-9)
一、逻辑回归实现:
数据加载到octave中,如下图所示:
①样本数据的可视化
随机选择100个样本数据,使用Octave可视化的结果如下:
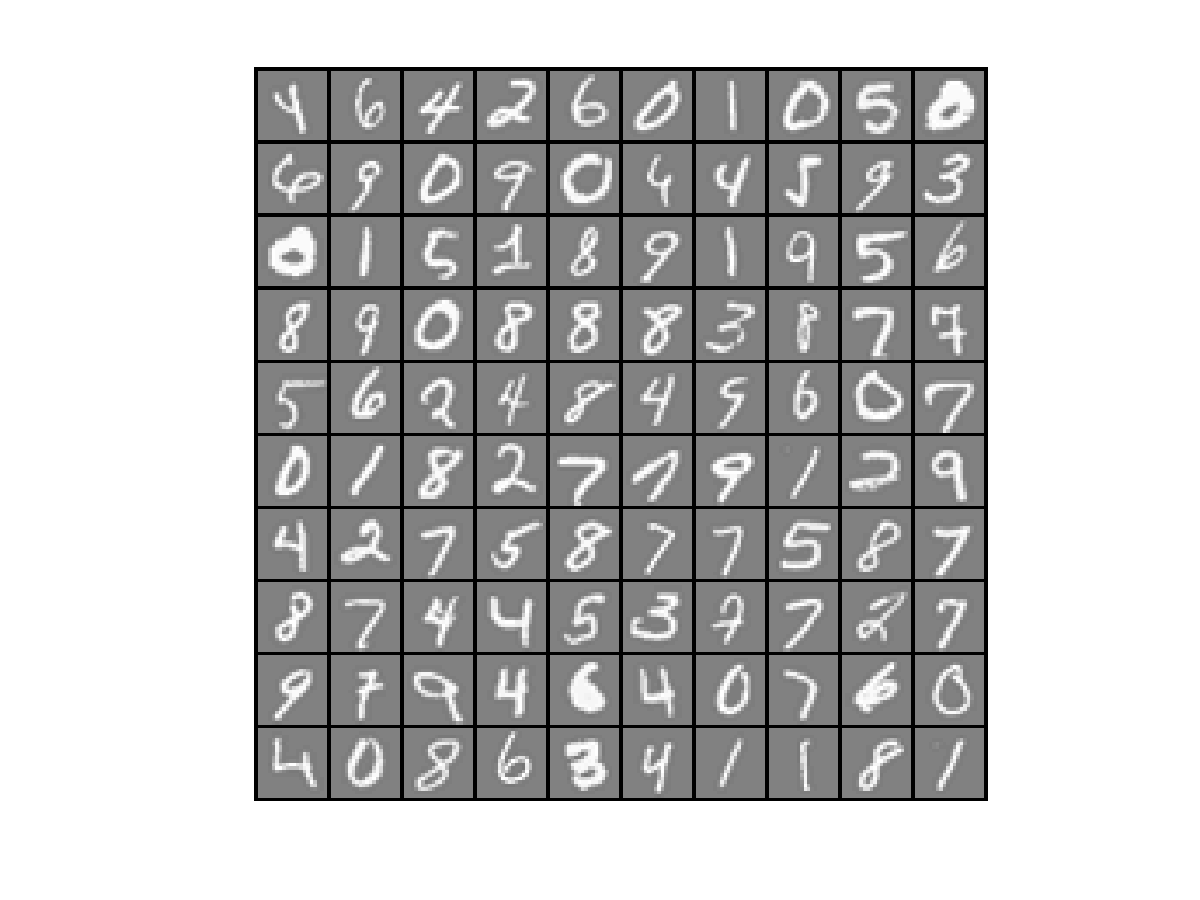
②使用逻辑回归来实现多分类问题(one-vs-all)
所谓多分类问题,是指分类的结果为三类以上。比如,预测明天的天气结果为三类:晴(用y==1表示)、阴(用y==2表示)、雨(用y==3表示)
分类的思想,其实与逻辑回归分类(默认是指二分类,binary classification)很相似,对“晴天”进行分类时,将另外两类(阴天和下雨)视为一类:(非晴天),这样,就把一个多分类问题转化成了二分类问题。示意图如下:(图中的圆圈 表示:不属于某一类的 所有其他类)
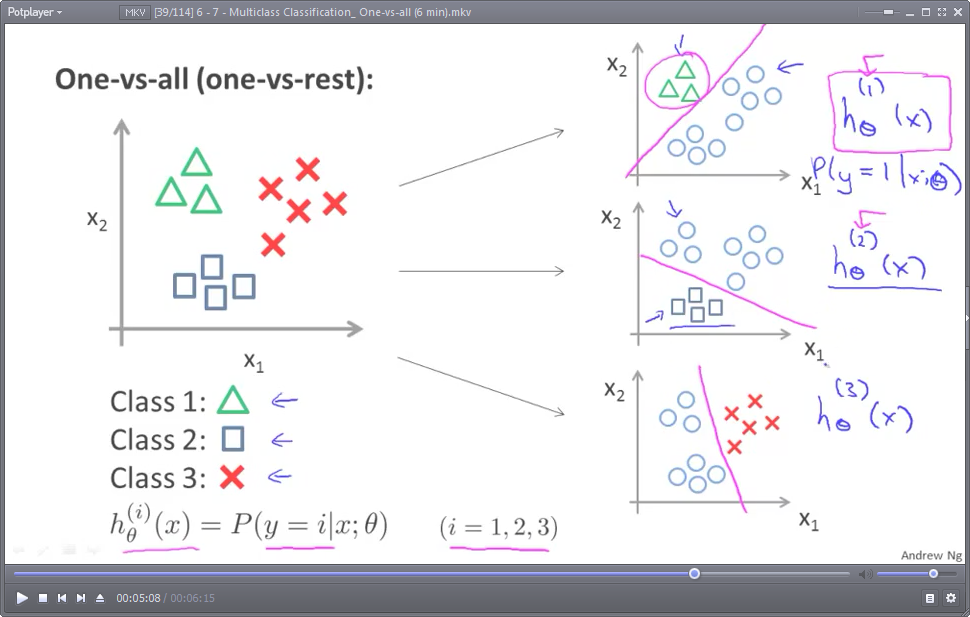
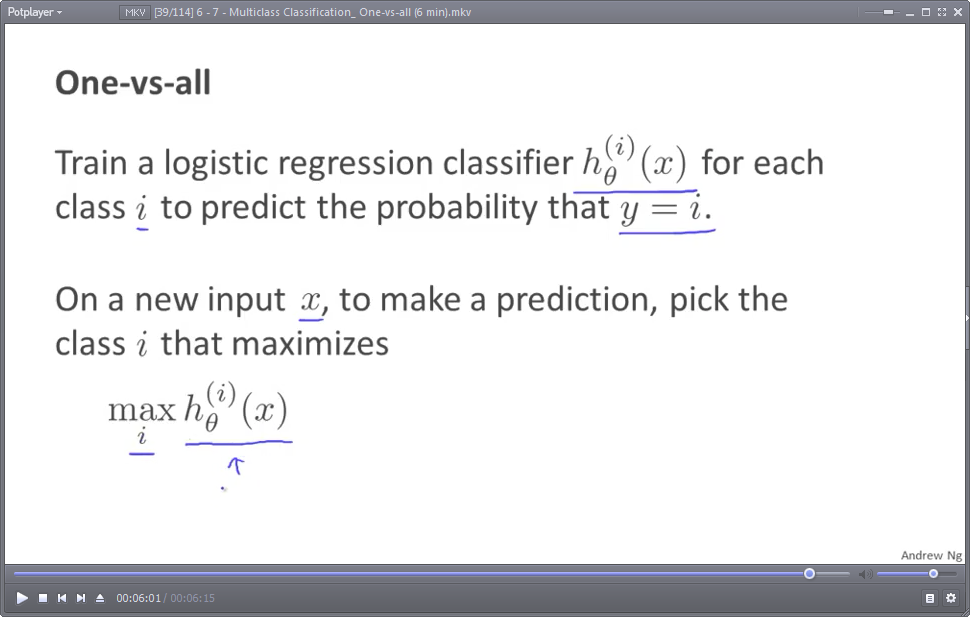
对于N分类问题(N>=3),就需要N个假设函数(预测模型),也即需要N组模型参数θ(θ一般是一个向量)
然后,对于每个样本实例,依次使用每个模型预测输出,选取输出值最大的那组模型所对应的预测结果作为最终结果。
因为模型的输出值,在sigmoid函数作用下,其实是一个概率值。,注意:hθ(1)(x),hθ(2)(x),hθ(3)(x)三组 模型参数θ 一般是不同的。比如:
hθ(1)(x),输出 预测为晴天(y==1)的概率
hθ(2)(x),输出 预测为阴天(y==2)的概率
hθ(3)(x),输出 预测为雨天(y==3)的概率
③Octave代码实现
对于上面的识别阿拉伯数字的问题,一共需要训练出10个逻辑回归模型,每个逻辑回归模型对应着识别其中一个数字。
我们一共有5000个样本,样本的预测结果值就是:y=(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10),其中 10 代表 数字0
我们使用fmincg库函数 来求解使得代价函数取最小值的 模型参数θ
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
%ONEVSALL trains multiple logistic regression classifiers and returns all
%the classifiers in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta
%corresponds to the classifier for label i
% [all_theta] = ONEVSALL(X, y, num_labels, lambda) trains num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers and returns each of these classifiers
% in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta corresponds
% to the classifier for label i % Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2); % You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the following code to train num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers with regularization
% parameter lambda.
%
% Hint: theta(:) will return a column vector.
%
% Hint: You can use y == c to obtain a vector of 1's and 0's that tell you
% whether the ground truth is true/false for this class.
%
% Note: For this assignment, we recommend using fmincg to optimize the cost
% function. It is okay to use a for-loop (for c = 1:num_labels) to
% loop over the different classes.
%
% fmincg works similarly to fminunc, but is more efficient when we
% are dealing with large number of parameters.
%
% Example Code for fmincg:
%
% % Set Initial theta
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
%
% % Set options for fminunc
% options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
%
% % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
% % This function will return theta and the cost
% [theta] = ...
% fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), ...
% initial_theta, options);
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1); options = optimset('GradObj','on','MaxIter',50); for c = 1:num_labels %num_labels 为逻辑回归训练器的个数,num of logistic regression classifiers
all_theta(c, :) = fmincg(@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c),lambda)), initial_theta,options );
end % ========================================================================= end
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda)
%LRCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with
%regularization
% J = LRCOSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Hint: The computation of the cost function and gradients can be
% efficiently vectorized. For example, consider the computation
%
% sigmoid(X * theta)
%
% Each row of the resulting matrix will contain the value of the
% prediction for that example. You can make use of this to vectorize
% the cost function and gradient computations.
%
% Hint: When computing the gradient of the regularized cost function,
% there're many possible vectorized solutions, but one solution
% looks like:
% grad = (unregularized gradient for logistic regression)
% temp = theta;
% temp(1) = 0; % because we don't add anything for j = 0
% grad = grad + YOUR_CODE_HERE (using the temp variable)
% J = ( log( sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * y + log( 1-sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * (1 - y) )/(-m) + (lambda / (2*m)) * ( ( theta( 2:length(theta) ) )' * theta(2:length(theta)) ); grad = ( X' * ( sigmoid(X*theta)-y ) )/m + ( lambda / m ) * ( [0; ones( length(theta) - 1 , 1 )].*theta ); % ============================================================= grad = grad(:); end
下面来解释一下 for循环:
num_labels 为分类器个数,共10个,每个分类器(模型)用来识别10个数字中的某一个。
我们一共有5000个样本,每个样本有400中特征变量,因此:模型参数θ 向量有401个元素。
initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1); % 模型参数θ的初始值(n == 400)
all_theta是一个10*401的矩阵,每一行存储着一个分类器(模型)的模型参数θ 向量,执行上面for循环,就调用fmincg库函数 求出了 所有模型的参数θ 向量了。
求出了每个模型的参数向量θ,就可以用 训练好的模型来识别数字了。对于一个给定的数字输入(400个 feature variables) input instance,每个模型的假设函数hθ(i)(x) 输出一个值(i = 1,2,...10)。取这10个值中最大值那个值,作为最终的识别结果。比如g(hθ(8)(x))==0.96 比其它所有的 g(hθ(i)(x)) (i = 1,2,...10,但 i 不等于8) 都大,则识别的结果为 数字 8
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label for a trained one-vs-all classifier. The labels
%are in the range 1..K, where K = size(all_theta, 1).
% p = PREDICTONEVSALL(all_theta, X) will return a vector of predictions
% for each example in the matrix X. Note that X contains the examples in
% rows. all_theta is a matrix where the i-th row is a trained logistic
% regression theta vector for the i-th class. You should set p to a vector
% of values from 1..K (e.g., p = [1; 3; 1; 2] predicts classes 1, 3, 1, 2
% for 4 examples) m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters (one-vs-all).
% You should set p to a vector of predictions (from 1 to
% num_labels).
%
% Hint: This code can be done all vectorized using the max function.
% In particular, the max function can also return the index of the
% max element, for more information see 'help max'. If your examples
% are in rows, then, you can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max
% for each row.
% [~,p] = max( X * all_theta',[],2); % 求矩阵(X*all_theta')每行的最大值,p 记录矩阵每行的最大值的索引 % ========================================================================= end
二、神经网络实现
由于逻辑回归是线性分类(它的假设函数是一个线性函数,就是划一条直线,把数据分成了两类。
对于一些复杂的类别,逻辑回归就解决不了了。比如下面这个图片中的分类。(无法通过 划直线 将 叉叉 和 圆圈 分开)
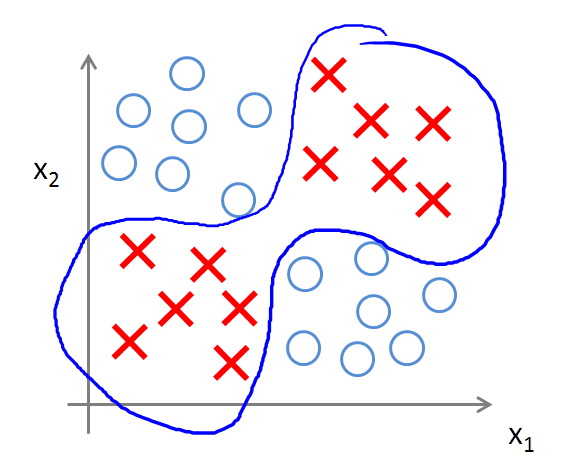
而神经网络,则能够实现很复杂的非线性分类问题。
对于神经网络而言,同样有一个训练样本矩阵 X,同时还有一个模型参数 Theta 矩阵,通过某种算法将 模型参数矩阵 训练好之后(求出 Theta 矩阵),再使用前向传播算法( feedforward propagation algorithm)(感觉就像是矩阵相乘嘛), 就可以对输入的测试样本进行预测了。
本作业中, 模型参数 Theta 矩阵是已经训练好了的,直接 load 即可。如下所示:

function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network
% p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label of X given the
% trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2) % Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned neural network. You should set p to a
% vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
%
% Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
% function can also return the index of the max element, for more
% information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
% can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
% % 模拟实现前向传播算法
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
a_super_2 = sigmoid(Theta1 * X');
a_super_2 = [ones(1,m); a_super_2];% add bias unit
a_super_3 = sigmoid(Theta2 * a_super_2);
%==================================
[~,p] = max( a_super_3' ,[], 2 ); % 对样本的结果进行预测,与逻辑回归的预测类似,选取输出的最大值 作为最终的预测结果 % ========================================================================= end
注意:我们正是通过 max 函数,求得矩阵 a_super3′ 的每一行的最大值。将每一行的中的最大值 的索引 赋值给向量p。其中,a_super3′ 是一个5000行乘10列的矩阵
向量p就是预测的结果向量。而由于 a_super3′ 有10列,故 p 中每个元素的取值范围为[1,10],即分别代表了数字 0-9(其中10 表示 0)
测试代码如下:
rp = randperm(m);
>>
>> for i = 1:m
% Display
fprintf('\nDisplaying Example Image\n');
displayData(X(rp(i), :)); pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X(rp(i),:));
fprintf('\nNeural Network Prediction: %d (digit %d)\n', pred, mod(pred, 10)); % Pause with quit option
s = input('Paused - press enter to continue, q to exit:','s');
if s == 'q'
break
end
end
例如下图所示的数字:


Andrew NG 机器学习编程作业3 Octave的更多相关文章
- Andrew NG 机器学习编程作业5 Octave
问题描述:根据水库中蓄水标线(water level) 使用正则化的线性回归模型预 水流量(water flowing out of dam),然后 debug 学习算法 以及 讨论偏差和方差对 该线 ...
- Andrew NG 机器学习编程作业4 Octave
问题描述:利用BP神经网络对识别阿拉伯数字(0-9) 训练数据集(training set)如下:一共有5000个训练实例(training instance),每个训练实例是一个400维特征的列向量 ...
- Andrew NG 机器学习编程作业2 Octave
问题描述:用逻辑回归根据学生的考试成绩来判断该学生是否可以入学 这里的训练数据(training instance)是学生的两次考试成绩,以及TA是否能够入学的决定(y=0表示成绩不合格,不予录取:y ...
- Andrew NG 机器学习编程作业6 Octave
问题描述:使用SVM(支持向量机 )实现一个垃圾邮件分类器. 在开始之前,先简单介绍一下SVM ①从逻辑回归的 cost function 到SVM 的 cost function 逻辑回归的假设函数 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 4—反向传播神经网络
课程笔记 Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 9_Neural Networks learning 作业说明 Exercise 4,Week 5,实现反向传播 ba ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业: Linear Regression
编程作业有两个文件 1.machine-learning-live-scripts(此为脚本文件方便作业) 2.machine-learning-ex1(此为作业文件) 将这两个文件解压拖入matla ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Logistic Regression
编程作业文件: machine-learning-ex2 1. Logistic Regression (逻辑回归) 有之前学生的数据,建立逻辑回归模型预测,根据两次考试结果预测一个学生是否有资格被大 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Regularized Linear Regression and Bias/Variance
作业文件: machine-learning-ex5 1. 正则化线性回归 在本次练习的前半部分,我们将会正则化的线性回归模型来利用水库中水位的变化预测流出大坝的水量,后半部分我们对调试的学习算法进行 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习编程作业:Support Vector Machines
作业: machine-learning-ex6 1. 支持向量机(Support Vector Machines) 在这节,我们将使用支持向量机来处理二维数据.通过实验将会帮助我们获得一个直观感受S ...
随机推荐
- hdu 2859 Phalanx (最大对称子矩阵)
Problem Description Today is army day, but the servicemen are busy with the phalanx for the celebrat ...
- 前端基础-- CSS
CSS知识 CSS(Cascading Style Sheet,层叠样式表)定义如何显示HTML元素. 当浏览器读到一个样式表,它就会按照这个样式表来对文档进行格式化(渲染).Css之车更丰富的文档外 ...
- 阶乘函数(factorial)——结果在整型范围内的阶乘计算
定义: 在数学中,正整数的阶乘(英语:factorial)是所有小于及等于该数的正整数的积,计为n!,例如5的阶乘计为5!,其值为120: \[ 5!=5\times 4\times 3\times ...
- Django(十)COOKIE和session
https://www.cnblogs.com/haiyan123/p/7763169.html from django.shortcuts import render,redirect # Crea ...
- webpack 非严格模式设置 npm i babel-plugin-transform-remove-strict-mode
安装插件:npm i babel-plugin-transform-remove-strict-mode 在.babelrc文件的插件项添加:"transform-remove-strict ...
- Python基础-元组、列表、字典
元组tuple 元组被称为只读列表,即数据可以被查询,但不能被修改,所以,字符串的切片操作同样适用于元组.例:(1,2,3)("a","b","c&q ...
- snpeff注释变异(variants)
1.进入网站http://snpeff.sourceforge.net/,下载snpeff: wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/snpeff/files/snp ...
- hdu 3613"Best Reward"(Manacher算法)
传送门 题意: 国王为了犒劳立下战功的大将军Li,决定奖给Li一串项链,这个项链一共包含26中珠子"a~z",每种珠子都有 相应的价值(-100~100),当某个项链可以构成回文时 ...
- 使用PreparedStatement 查询一条数据 封装成一个学生的Student1对象
package cn.lijun.entity; public class Student1 { private int id; private String sname; private int g ...
- 【转载】 qml: MouseArea重叠问题;
原文: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_15024587/article/details/80000443 MouseArea控件大家应该是很熟悉的了. 使用起来也是非常方便的说 ...
