Hadoop vs Elasticsearch – Which one is More Useful
Difference Between Hadoop and Elasticsearch
Hadoop is a framework that helps in handling the voluminous data in a fraction of seconds, where traditional ways are failing to handle. It takes the support of multiple machines to run the process parallelly in a distributed manner. Elasticsearch works like a sandwich between Logstash and Kibana. Where Logstash is accountable to fetch the data from any data source, elastic search analyzes the data and finally, kibana gives the actionable insights out of it. This solution makes applications, more powerful to work in complex search requirements or demands.
Now let us look forward to the topic in detail:
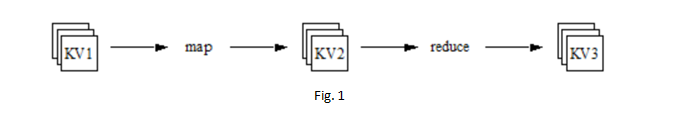
Its unique way of data management (specially designed for Big data), which includes an end to end process of storing, processing and analyzing. This unique way is termed as MapReduce. Developers write the programs in the MapReduce framework, to run the extensive data in parallel across distributed processors.
The question then arises, after data gets distributed for processing into different machines, how output gets accumulated in a similar fashion?
The answer is, MapReduce generates a unique key which gets appended with distributed data in various machines. MapReduce keeps track of the processing of data. And once it is done, that unique key is used to put all processed data together. This gives the feel of all work done on a single machine.
Scalability and reliability are perfectly taken care of in MapReduce of Hadoop. Below are some functionalities of MapReduce:
- The map then Reduce: To run a job, it gets broken into individual chunks which are called task. Mapper function will always run first for all the tasks, then only reduce function will come into the picture. The entire process will be called completed only when reduce function completes its work for all distributed tasks.
- Fault Tolerant: Take a scenario, when one node goes down while processing the task? The heartbeat of that node doesn’t reach to the engine of MapReduce or say Master node. Then, in that case, the Master node assigns that task to some different node to finish the task. Moreover, the unprocessed and processed data are kept in HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System), which is storage layer of Hadoop with default replication factor of 3. This means, if one node goes down there are still two nodes alive with the same data.
- Flexibility: You can store any type of data: structured, semi-structured or unstructured.
- Synchronization: Synchronization is inbuilt characteristic of Hadoop. This makes sure, reduce will start only if all mapper function is done with its task. “Shuffle” and “Sort” is the mechanism which makes the job’s output smoother.Elasticsearch is a JSON based simple, yet powerful analytical tool for document indexing and powerful full-text search.
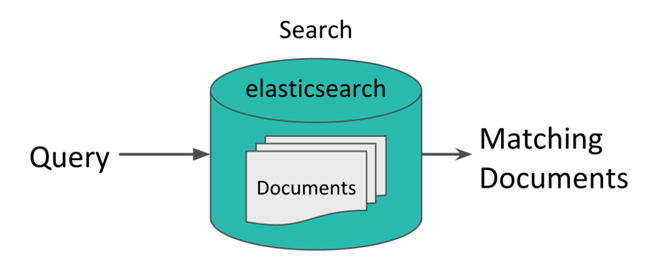
Fig. 2
In ELK, all the components are open source. ELK taking great momentum in IT environment for log analysis, web analytics, business intelligence, compliance analysis etc. ELK is apt for business where ad hoc requests come and data needs to be quickly analyzed and visualized.
4.5 (1,535 ratings)
$299 $599
View Course
ELK is a great tool to go with for Tech startups who can’t afford to purchase a license for log analysis product like Splunk. Moreover, open source products have always been the focus in IT industry.
Head To Head Comparisons Between Hadoop vs Elasticsearch (Infographics)
Below is the top 9 comparisons between Hadoop vs Elasticsearch
 Key Difference Between Hadoop vs Elasticsearch
Key Difference Between Hadoop vs Elasticsearch
Below are the lists of points, describe the key differences between Hadoop and Elasticsearch:
- Hadoop has distributed filesystem which is designed for parallel data processing, while ElasticSearch is the search engine.
- Hadoop provides far more flexibility with a variety of tools, as compared to ES.
- Hadoop can store ample of data, whereas ES can’t.
- Hadoop can handle extensive processing and complex logic, where ES can handle only limited processing and basic aggregation kind of logic.
Hadoop vs Elasticsearch Comparison Table
| Basis of Comparison | Hadoop | Elasticsearch |
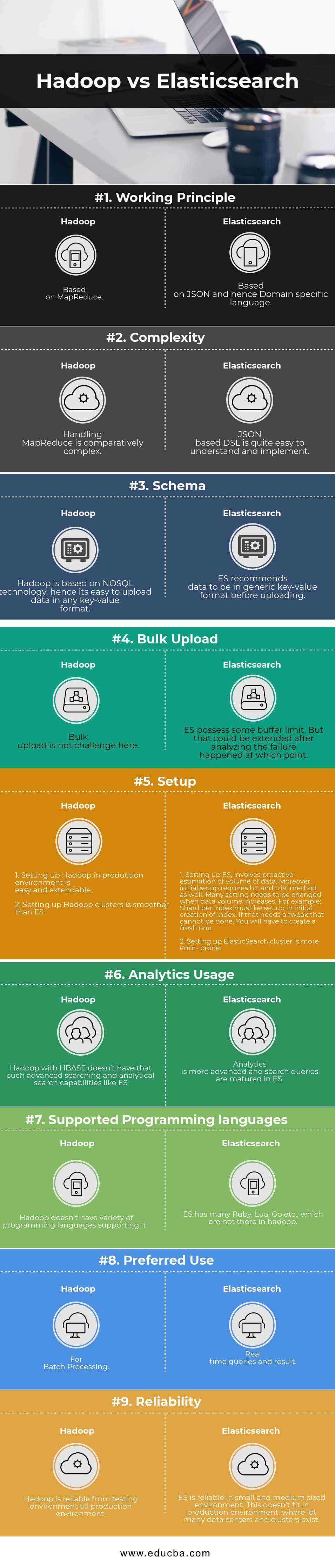
| Working Principle | Based on MapReduce | Based on JSONand hence Domain-specific language |
| Complexity | Handling MapReduce is comparatively complex | JSON based DSL is quite easy to understand and implement |
| Schema | Hadoop is based on NoSQLtechnology, hence its easy to upload data in any key-value format | ES recommends data to be in generic key-value format before uploading |
| Bulk Upload | Bulk upload is not challenging here | ES possess some buffer limit. But that could be extended after analyzing the failure happened at which point. |
| Setup | 1.Setting up Hadoop in a production environment is easy and extendable.
2. Setting up Hadoop clusters is smoother than ES. |
1.Setting up ES involves proactive estimation of the volume of data. Moreover, initial setup requires hit and trial method as well. Many setting needs to be changed when data volume increases. For example Shard per index must be set up in the initial creation of an index. If that needs a tweak that cannot be done. You will have to create a fresh one.
2.Setting up ElasticSearch cluster is more error-prone. |
| Analytics Usage | Hadoop with HBase doesn’t have that such advanced searching and analytical search capabilities like ES | Analytics is more advanced and search queries are matured in ES |
| Supported Programming languages | Hadoop doesn’t have a variety of programming languages supporting it. | ES has many Ruby, Lua, Go etc., which are not there in Hadoop |
| Preferred Use | For Batch Processing | Real-time queries and result |
| Reliability | Hadoop is reliable from testing environment till production environment | ES is reliable in a small and medium-sized environment. This doesn’t fit in a production environment, where lot many data centers and clusters exist. |
Conclusion – Hadoop vs Elasticsearch
At the end, it actually depends on the data type, volume, and use case, one is working on. If simple searching and web analytics is the focus, then Elasticsearch is better to go with. Whereas if there is an extensive demand of scaling, a volume of data and compatibility with third-party tools, Hadoop instance is the answer to it. However, Hadoop integration with ES opens a new world for heavy and big applications. Leveraging full power from Hadoop and Elasticsearch can give a good platform to enrich maximum value out of big data.
Recommended Articles:
This has been a guide to Hadoop vs Elasticsearch, their Meaning, Head to Head Comparison, Key Differences, Comparision Table, and Conclusion. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
Hadoop vs Elasticsearch – Which one is More Useful的更多相关文章
- 基于Nutch+Hadoop+Hbase+ElasticSearch的网络爬虫及搜索引擎
基于Nutch+Hadoop+Hbase+ElasticSearch的网络爬虫及搜索引擎 网络爬虫架构在Nutch+Hadoop之上,是一个典型的分布式离线批量处理架构,有非常优异的吞吐量和抓取性能并 ...
- 一个大数据方案:基于Nutch+Hadoop+Hbase+ElasticSearch的网络爬虫及搜索引擎
网络爬虫架构在Nutch+Hadoop之上,是一个典型的分布式离线批量处理架构,有非常优异的吞吐量和抓取性能并提供了大量的配置定制选项.由于网络爬虫只负责网络资源的抓取,所以,需要一个分布式搜索引擎, ...
- 【架构】基于Nutch+Hadoop+Hbase+ElasticSearch的网络爬虫及搜索引擎
网络爬虫架构在Nutch+Hadoop之上,是一个典型的分布式离线批量处理架构,有非常优异的吞吐量和抓取性能并提供了大量的配置定制选项.由于网络爬虫只负责网络资源的抓取,所以,需要一个分布式搜索引擎, ...
- 记一次netty的Hadoop和elasticsearch冲突jar包
在一个项目中同时使用hbase和elasticsearch出现netty的jar包冲突的问题 事件: 在同一maven项目中使用hbase的同时又用了es 程序运行后出错 java.lang.NoSu ...
- es第十篇:Elasticsearch for Apache Hadoop
es for apache hadoop(elasticsearch-hadoop.jar)允许hadoop作业(mapreduce.hive.pig.cascading.spark)与es交互. A ...
- Elasticsearch集成Hadoop最佳实践.pdf(内含目录)
Elasticsearch服务器开发(第2版) 介绍: ElasticSearch是一个开源的分布式搜索引擎,具有高可靠性,支持非常多的企业级搜索用例.ElasticsearchHadoop作为一个完 ...
- 使用Hive或Impala执行SQL语句,对存储在Elasticsearch中的数据操作
http://www.cnblogs.com/wgp13x/p/4934521.html 内容一样,样式好的版本. 使用Hive或Impala执行SQL语句,对存储在Elasticsearch中的数据 ...
- 用 Mahout 和 Elasticsearch 实现推荐系统
原文地址 本文内容 软件 步骤 控制相关性 总结 参考资料 本文介绍如何用带 Apache Mahout 的 MapR Sandbox for Hadoop 和 Elasticsearch 搭建推荐引 ...
- elasticsearch插件大全
Elasticsearch扩展性非常好,有很多官方和第三方开发的插件,下面以分词.同步.数据传输.脚本支持.站点.其它这几个类别进行划分. 分词插件 Combo Analysis Plugin (作者 ...
随机推荐
- NPOI Excel同一个单元格 多种字体
public static void CreateFont() { IWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); workbook.CreateSheet(&quo ...
- 如何在git中上传图片
首先在git仓库上创建一个文件夹,之后点击 Upload files 上传本地的图片 上传完之后复制存放图片的git网址 之后在新建一个.md的子文件 新建完成之后在该md文件中写入如下代码: 