Spring框架 aop操作的注解方法 基于aspectj的自动注解aop方法 抽取相同的value="execution(public void cn.itcast.f_aspect.CRUD.*())"
首先是在xml配置文件中配置好对象,然后开启aop的注解方法——即<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
xml代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 开启注解扫描——对象和属性 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.swift"></context:component-scan> <bean id="book" class="com.swift.Book"></bean>
<bean id="adviceBook" class="com.swift.AdviceBook"></bean> <!-- 开启aop注解方法 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> <!-- 这是xml 配置文件中aop操作的方法留下对比
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.swift.Book.*())" id="pointcut1"/>
<aop:aspect ref="adviceBook">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:after-returning method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config> -->
</beans>
上面有原来xml配置aop的方法,这时已经不用了,用作参考
被增强的类及方法,代码如下:
package com.swift;
public class Book {
public String fun() {
System.out.println("This is Book's fun()..............");
return "This is Book's fun()..............";
}
}
用于增强的类及方法,代码如下:
package com.swift; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; @Aspect
public class AdviceBook {
@Before(value="execution(* com.swift.Book.*(..))")
public String before() {
System.out.println("This is AdviceBook's before()...............");
return "This is AdviceBook's before()...............";
}
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.swift.Book.*(..))")
public String after() {
System.out.println("This is AdviceBook's after()...............");
return "This is AdviceBook's after()...............";
}
@Around(value="execution(* com.swift.Book.*(..))")
public String around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable { System.out.println("This is AdviceBook's front()..............."); proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("This is AdviceBook's end()...............");
return "This is AdviceBook's around()...............";
} }
类的上边用@Aspect表示切面
方法前用@Before(value="表达式") 其中表达式与之前配置方法相同
最后测试类,代码如下:
package com.swift; import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.swift.Book;
@WebServlet("/test")
public class ServleTest extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public ServleTest() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.getWriter().append("Served at: ").append(request.getContextPath());
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml");
Book book=(Book)context.getBean("book");
//这个返回值,反复试验得出最后浏览上只输出This is AdviceBook's around().
response.getWriter().append(book.fun());
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(request, response);
} }
其实就一句
response.getWriter().append(book.fun());
网页上返回值为around()中返回值,console控制台得到前后包围所有增强的输出。
如下图:

=============================================================================================
重新整理上边内容
package cn.itcast.f_aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; @Aspect
public class Myadvice { @Before(value="execution(public void cn.itcast.f_aspect.CRUD.*())")
public void before() {
System.out.println("之前-->开启事务");
}
@Around(value="execution(public void cn.itcast.f_aspect.CRUD.*())")
public void round(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
System.out.println("之前-->开启事务");
try {
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("没有异常,之后-->提交事务");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("出现异常,之后--回滚事务");
}finally {
System.out.println("有无异常都执行,之后-->关闭事务");
} }
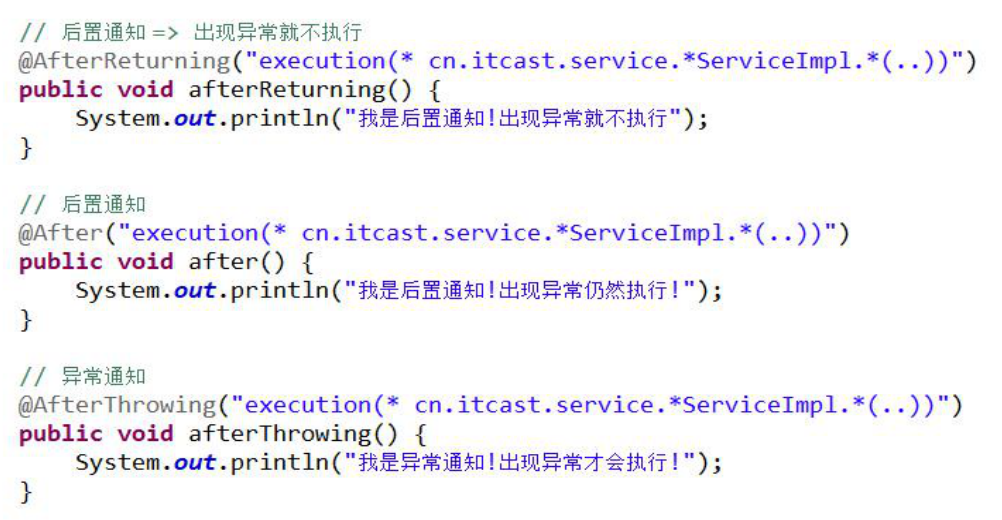
@AfterReturning(value="execution(public void cn.itcast.f_aspect.CRUD.*())")
public void afterReturning() {
System.out.println("没有异常,之后-->提交事务");
}
@After(value="execution(public void cn.itcast.f_aspect.CRUD.*())")
public void after() {
System.out.println("有无异常都执行,之后-->关闭事务");
}
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(public void cn.itcast.f_aspect.CRUD.*())")
public void afterThrowing() {
System.out.println("出现异常,之后--回滚事务");
}
}
发现每句中的内容一样,如何抽取 value="execution(public void cn.itcast.f_aspect.CRUD.*())"
Spring框架 aop操作的注解方法 基于aspectj的自动注解aop方法 抽取相同的value="execution(public void cn.itcast.f_aspect.CRUD.*())"的更多相关文章
- (spring-第19回【AOP基础篇】)基于AspectJ和Schema的AOP
基于AspectJ就是基于@AspectJ注解,基于Schema就是全部依靠配置文件.那么首先要了解Java注解. Java注解初探 在JDK5.0中,我们可以自定义标签,并通过Java语言的反射机制 ...
- IDEA02 利用Maven创建Web项目、为Web应用添加Spring框架支持、bean的创建于获取、利用注解配置Bean、自动装配Bean、MVC配置
1 环境版本说明 Jdk : 1.8 Maven : 3.5 IDEA : 专业版 2017.2 2 环境准备 2.1 Maven安装及其配置 2.2 Tomcat安装及其配置 3 详细步骤 3.1 ...
- 07 Spring框架 依赖注入(四)基于注解的依赖注入
前面几节我们都在使用xml进行依赖的注入,但是在实际的开发中我们往往偏爱于使用注解进行依赖注入,因为这样更符合我们人的思维,并且更加快捷,本节就来讲述Spring基于注解的依赖注入: 信息注入注解 @ ...
- 关于aop的两种方式-基于注解和基于aspectj
spring的aop确实好用,能够在不影响业务功能的情况下,实现一些低耦合的功能. 而aop又有两种常用的实现方式,一种是用aspectj表达式去匹配,实现全局的配置,表达式还可以使用与或非符号去连接 ...
- Spring @Bean注解 (基于java的容器注解)
基于java的容器注解,意思就是使用Java代码以及一些注解,就可以取代spring 的 xml配置文件. 1-@Configuration & @Bean的配合 @Configuration ...
- Spring框架零基础学习(一):IOC|DI、AOP
文章目录 一.IDEA创建Spring项目 二.Spring: IOC和DI 三.Spring: AOP 参考链接: HOW2J.CN:Spring idea创建一个spring项目 一.IDEA创建 ...
- Spring框架中的Quartz定时任务使用笔记(通过@Scheduled注解的方式实现)
1.修改spring的xml配置信息 applicationContext.xml 三个部分内容 1.xmlns添加:xmlns:task="http://www.springframewo ...
- Spring学习十一----------Bean的配置之基于Java的容器注解@Bean
© 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处 @Bean -@Bean标识一个用于配置和初始化一个由SpringIOC容器管理的新对象的方法,类似于XML配置文件的<bean/> -可 ...
- Spring课程 Spring入门篇 4-8 Spring bean装配之基于java的容器注解说明--基于泛型的自动装配
1 解析 1.1 什么是泛型? 1.2 泛型有什么作用? 1.3 泛型装配样式? 2 代码演练 2.1 泛型应用 1 解析 1.1 什么是泛型? Java泛型设计原则:只要在编译时期没有出现警告,那么 ...
随机推荐
- Google Play应用商店的下载路径(转载)
转自:http://blog.yanwen.org/archives/1660.html 其实,好久之前就想知道google play中下载的应用到哪里去了.之前用的MIUI系统里面,google p ...
- ARM汇编中ldr伪指令和ldr指令(转载)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/ce123_zhouwei/article/details/7182756 ARM是RISC结构,数据从内存到CPU之间的移动只能通过L/S指令来完成, ...
- gdb调试带参数的程序 (转载)
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/rosesmall/archive/2012/04/10/2440514.html 一般来说GDB主要调试的是C/C++的程序.要调试C/C++的程 ...
- $.ajax与$.post、$.get的一点区别
后台代码: [HttpPost] public string DoLogin(string username,string password) { return "success" ...
- 一个坑爹的Swift报错原因分析与解决方案
有时候在实际开发中,完全没有任何问题.但是一到实机测试,就会直接卡机 let count = scoreStorage.count return scoreStorage[Int(arc4rand ...
- 6.while循环正向反向打印一句话
message = "伤情最是晚凉天,憔悴厮人不堪言."' count=0 num=-1 while count<len(message): print(message[co ...
- (四)SpringBoot如何定义消息转换器
一:添加fastjson依赖 <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastj ...
- php 获得上周数据
$lastMondy = date('Y-m-d', strtotime('-2 sunday +1 days', time()));$lastSundy = date('Y-m-d', strtot ...
- 3分钟入门微信小程序直播
效果预览 开发环境搭建 安装微信开发者工具 相对于以前微信以前的产品来说.小程序在发布之初就面向开发者开放微信开发者工具.使开发者更加方便的开发和调试小程序.我们从官网下载安装.官网下载地址.现在 ...
- Java反编译工具-JD-GUI
Java是跨平台的,JD-GUI提供了多个系统的支持,但是不建议直接安装,最快的方式推荐直接下载JAR包,然后用java -jar进行运行. 就现在的版本是1.4.0,停留在2015年,估计近期会更新 ...
