TensorFlow使用记录 (三): Learning Rate Scheduling
file: tensorflow/python/training/learning_rate_decay.py
神经网络中通过超参数 learning rate,来控制每次参数更新的幅度。学习率太小会降低网络优化的速度,增加训练时间;学习率太大则可能导致可能导致参数在局部最优解两侧来回振荡,网络不能收敛。
tensorflow 定义了很多的 学习率衰减方式:
指数衰减 tf.train.exponential_decay()
指数衰减是比较常用的衰减方法,学习率是跟当前的训练轮次指数相关的。
tf.train.exponential_decay(
learning_rate, # 初始学习率
global_step, # 当前训练轮次
decay_steps, # 衰减周期
decay_rate, # 衰减率系数
staircase=False, # 定义是否是阶梯型衰减,还是连续衰减,默认是 False
name=None
)
'''
decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate *
decay_rate ^ (global_step / decay_steps)
'''
示例代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
style1 = []
style2 = []
N = 200 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(N):
# 标准指数型衰减
learing_rate1 = tf.train.exponential_decay(
learning_rate=0.5, global_step=step, decay_steps=10, decay_rate=0.9, staircase=False)
# 阶梯型衰减
learing_rate2 = tf.train.exponential_decay(
learning_rate=0.5, global_step=step, decay_steps=10, decay_rate=0.9, staircase=True)
lr1 = sess.run([learing_rate1])
lr2 = sess.run([learing_rate2])
style1.append(lr1)
style2.append(lr2) step = range(N) plt.plot(step, style1, 'g-', linewidth=2, label='exponential_decay')
plt.plot(step, style2, 'r--', linewidth=1, label='exponential_decay_staircase')
plt.title('exponential_decay')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.ylabel('learing rate')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

分段常数衰减 tf.train.piecewise_constant()
tf.train.piecewise_constant_decay(
x, # 当前训练轮次
boundaries, # 学习率应用区间
values, # 学习率常数列表
name=None
)
'''
learning_rate value is `values[0]` when `x <= boundaries[0]`,
`values[1]` when `x > boundaries[0]` and `x <= boundaries[1]`, ...,
and values[-1] when `x > boundaries[-1]`.
'''
示例代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
boundaries = [10, 20, 30]
learing_rates = [0.1, 0.07, 0.025, 0.0125] style = []
N = 40 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(N):
learing_rate = tf.train.piecewise_constant(step, boundaries=boundaries, values=learing_rates)
lr = sess.run([learing_rate])
style.append(lr) step = range(N) plt.plot(step, style, 'r-', linewidth=2)
plt.title('piecewise_constant')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.ylabel('learing rate')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
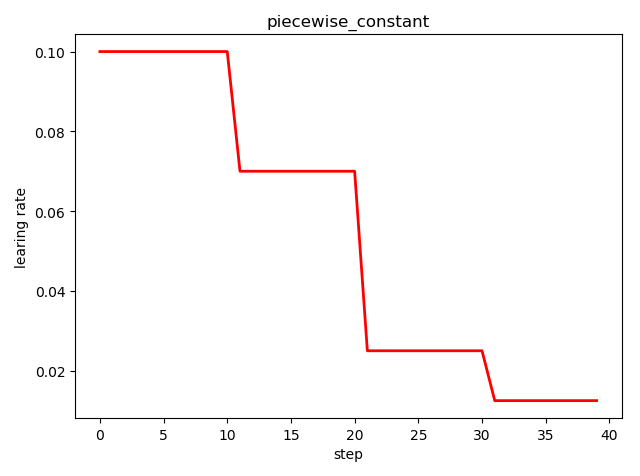
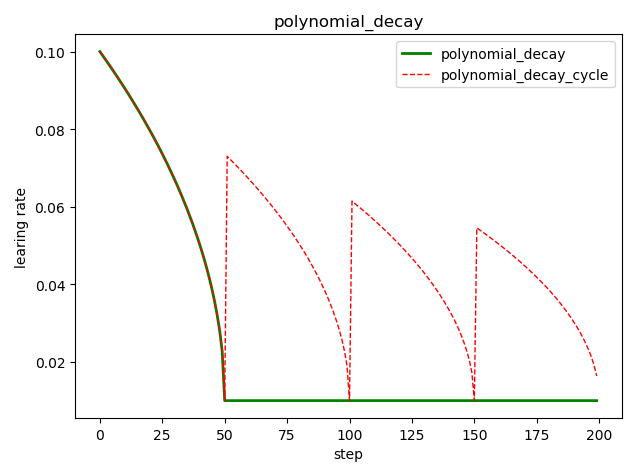
多项式衰减 tf.train.polynomial_decay()
tf.train.polynomial_decay(
learning_rate, # 初始学习率
global_step, # 当前训练轮次
decay_steps, # 大衰减周期
end_learning_rate=0.0001, # 最小的学习率
power=1.0, # 多项式的幂
cycle=False, # 学习率是否循环
name=None)
'''
global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
decayed_learning_rate = (learning_rate - end_learning_rate) *
(1 - global_step / decay_steps) ^ (power) +
end_learning_rate
'''
示例代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
style1 = []
style2 = []
N = 200 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(N):
# cycle=False
learing_rate1 = tf.train.polynomial_decay(
learning_rate=0.1, global_step=step, decay_steps=50,
end_learning_rate=0.01, power=0.5, cycle=False)
# cycle=True
learing_rate2 = tf.train.polynomial_decay(
learning_rate=0.1, global_step=step, decay_steps=50,
end_learning_rate=0.01, power=0.5, cycle=True)
lr1 = sess.run([learing_rate1])
lr2 = sess.run([learing_rate2])
style1.append(lr1)
style2.append(lr2) steps = range(N) plt.plot(steps, style1, 'g-', linewidth=2, label='polynomial_decay')
plt.plot(steps, style2, 'r--', linewidth=1, label='polynomial_decay_cycle')
plt.title('polynomial_decay')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.ylabel('learing rate')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
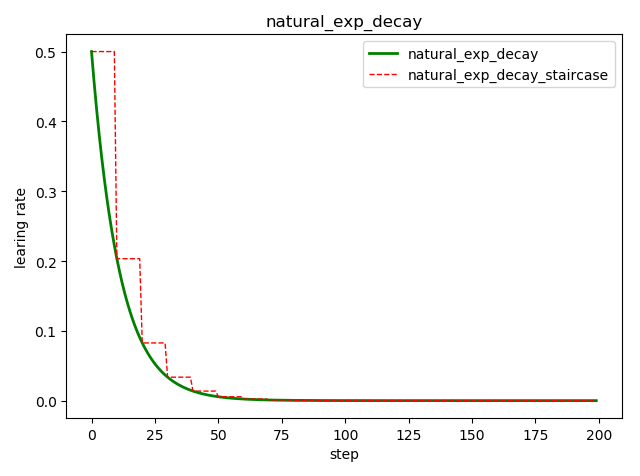
自然指数衰减 tf.train.natural_exp_decay()
tf.train.natural_exp_decay(
learning_rate, # 初始学习率
global_step, # 当前训练轮次
decay_steps, # 衰减周期
decay_rate, # 衰减率系数
staircase=False, # 定义是否是阶梯型衰减,还是连续衰减,默认是 False
name=None
)
'''
decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * exp(-decay_rate * global_step)
'''
示例代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
style1 = []
style2 = []
N = 200 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(N):
# 标准指数型衰减
learing_rate1 = tf.train.natural_exp_decay(
learning_rate=0.5, global_step=step, decay_steps=10, decay_rate=0.9, staircase=False)
# 阶梯型衰减
learing_rate2 = tf.train.natural_exp_decay(
learning_rate=0.5, global_step=step, decay_steps=10, decay_rate=0.9, staircase=True)
lr1 = sess.run([learing_rate1])
lr2 = sess.run([learing_rate2])
style1.append(lr1)
style2.append(lr2) step = range(N) plt.plot(step, style1, 'g-', linewidth=2, label='natural_exp_decay')
plt.plot(step, style2, 'r--', linewidth=1, label='natural_exp_decay_staircase')
plt.title('natural_exp_decay')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.ylabel('learing rate')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
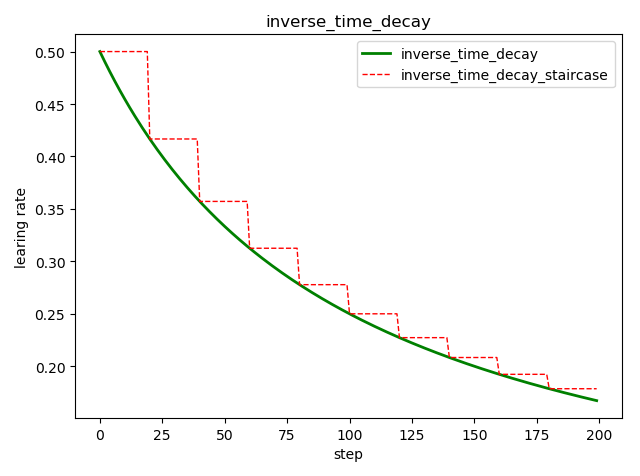
倒数衰减 tf.train.inverse_time_decay()
tf.train.inverse_time_decay(
learning_rate, # 初始学习率
global_step, # 当前训练轮次
decay_steps, # 衰减周期
decay_rate, # 衰减率系数
staircase=False, # 定义是否是阶梯型衰减,还是连续衰减,默认是 False
name=None
)
'''
decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate / (1 + decay_rate * global_step / decay_step)
'''
示例代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
style1 = []
style2 = []
N = 200 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(N):
# 标准指数型衰减
learing_rate1 = tf.train.inverse_time_decay(
learning_rate=0.5, global_step=step, decay_steps=20, decay_rate=0.2, staircase=False)
# 阶梯型衰减
learing_rate2 = tf.train.inverse_time_decay(
learning_rate=0.5, global_step=step, decay_steps=20, decay_rate=0.2, staircase=True)
lr1 = sess.run([learing_rate1])
lr2 = sess.run([learing_rate2])
style1.append(lr1)
style2.append(lr2) step = range(N) plt.plot(step, style1, 'g-', linewidth=2, label='inverse_time_decay')
plt.plot(step, style2, 'r--', linewidth=1, label='inverse_time_decay_staircase')
plt.title('inverse_time_decay')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.ylabel('learing rate')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
余弦衰减 tf.train.cosine_decay()
tf.train.cosine_decay(
learning_rate, # 初始学习率
global_step, # 当前训练轮次
decay_steps, # 衰减周期
alpha=0.0, # 最小的学习率
name=None
)
'''
global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
cosine_decay = 0.5 * (1 + cos(pi * global_step / decay_steps))
decayed = (1 - alpha) * cosine_decay + alpha
decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * decayed
'''
改进的余弦衰减方法还有:
线性余弦衰减,对应函数 tf.train.linear_cosine_decay()
噪声线性余弦衰减,对应函数 tf.train.noisy_linear_cosine_decay()
示例代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
style1 = []
style2 = []
style3 = []
N = 200 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(N):
# 余弦衰减
learing_rate1 = tf.train.cosine_decay(
learning_rate=0.1, global_step=step, decay_steps=50)
# 线性余弦衰减
learing_rate2 = tf.train.linear_cosine_decay(
learning_rate=0.1, global_step=step, decay_steps=50)
# 噪声线性余弦衰减
learing_rate3 = tf.train.noisy_linear_cosine_decay(
learning_rate=0.1, global_step=step, decay_steps=50,
initial_variance=0.01, variance_decay=0.1, num_periods=0.2, alpha=0.5, beta=0.2)
lr1 = sess.run([learing_rate1])
lr2 = sess.run([learing_rate2])
lr3 = sess.run([learing_rate3])
style1.append(lr1)
style2.append(lr2)
style3.append(lr3) step = range(N) plt.plot(step, style1, 'g-', linewidth=2, label='cosine_decay')
plt.plot(step, style2, 'r--', linewidth=1, label='linear_cosine_decay')
plt.plot(step, style3, 'b--', linewidth=1, label='linear_cosine_decay')
plt.title('cosine_decay')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.ylabel('learing rate')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

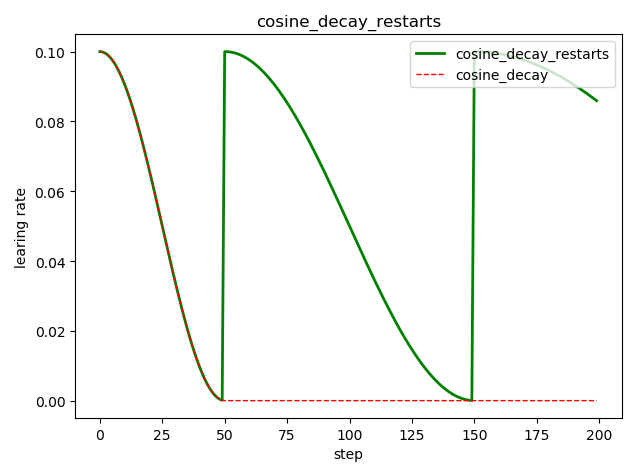
循环余弦衰减 tf.train.cosine_decay_restarts()
这是在 fast.ai 中强推的衰减方式
tf.train.cosine_decay_restarts(
learning_rate, # 初始学习率
global_step, # 当前训练轮次
first_decay_steps, # 首次衰减周期
t_mul=2.0, # 随后每次衰减周期倍数
m_mul=1.0, # 随后每次初始学习率倍数
alpha=0.0, # 最小的学习率=alpha*learning_rate
name=None
)
'''
See [Loshchilov & Hutter, ICLR2016], SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent
with Warm Restarts. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.03983
The learning rate multiplier first decays
from 1 to `alpha` for `first_decay_steps` steps. Then, a warm
restart is performed. Each new warm restart runs for `t_mul` times more steps
and with `m_mul` times smaller initial learning rate.
'''
示例代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
style1 = []
style2 = []
N = 200 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for step in range(N):
# 循环余弦衰减
learing_rate1 = tf.train.cosine_decay_restarts(
learning_rate=0.1, global_step=step, first_decay_steps=50,
)
# 余弦衰减
learing_rate2 = tf.train.cosine_decay(
learning_rate=0.1, global_step=step, decay_steps=50)
lr1 = sess.run([learing_rate1])
lr2 = sess.run([learing_rate2])
style1.append(lr1)
style2.append(lr2) step = range(N) plt.plot(step, style1, 'g-', linewidth=2, label='cosine_decay_restarts')
plt.plot(step, style2, 'r--', linewidth=1, label='cosine_decay')
plt.title('cosine_decay_restarts')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.ylabel('learing rate')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
调用例子
import tensorflow as tf def Swish(features):
return features*tf.nn.sigmoid(features) # 1. create data
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('../MNIST_data', one_hot=True) X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 784), name='X')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(None), name='y')
is_training = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, None, name='is_training') # 2. define network
he_init = tf.contrib.layers.variance_scaling_initializer()
with tf.name_scope('dnn'):
hidden1 = tf.layers.dense(X, 300, kernel_initializer=he_init, name='hidden1')
hidden1 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(hidden1, momentum=0.9)
hidden1 = tf.nn.relu(hidden1)
hidden2 = tf.layers.dense(hidden1, 100, kernel_initializer=he_init, name='hidden2')
hidden2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(hidden2, training=is_training, momentum=0.9)
hidden2 = tf.nn.relu(hidden2)
logits = tf.layers.dense(hidden2, 10, kernel_initializer=he_init, name='output')
# prob = tf.layers.dense(hidden2, 10, tf.nn.softmax, name='prob') # 3. define loss
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
# tf.losses.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy() label is not one_hot and dtype is int*
# xentropy = tf.losses.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy(labels=tf.argmax(y, axis=1), logits=logits)
# tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits() label is not one_hot and dtype is int*
# xentropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=tf.argmax(y, axis=1), logits=logits)
# loss = tf.reduce_mean(xentropy)
loss = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(onehot_labels=y, logits=logits) # label is one_hot # 4. define optimizer
learning_rate_init = 0.01
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
learning_rate = tf.train.polynomial_decay( # 多项式衰减
learning_rate=learning_rate_init, # 初始学习率
global_step=global_step, # 当前迭代次数
decay_steps=22000, # 在迭代到该次数实际,学习率衰减为 learning_rate * dacay_rate
end_learning_rate=learning_rate_init / 10, # 最小的学习率
power=0.9,
cycle=False
)
update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS) # for batch normalization
with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):
optimizer_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(
learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(
loss=loss,
var_list=tf.trainable_variables(),
global_step=global_step # 不指定的话学习率不更新
)
# ================= clip gradient
# threshold = 1.0
# optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
# grads_and_vars = optimizer.compute_gradients(loss)
# capped_gvs = [(tf.clip_by_value(grad, -threshold, threshold), var)
# for grad, var in grads_and_vars]
# optimizer_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(capped_gvs)
# ================= with tf.name_scope('eval'):
correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, tf.argmax(y, axis=1), 1) # 目标是否在前K个预测中, label's dtype is int*
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct, tf.float32)) # 5. initialize
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver() # =================
print([v.name for v in tf.trainable_variables()])
print([v.name for v in tf.global_variables()])
# ================= # 6. train & test
n_epochs = 20
n_batches = 50
batch_size = 50 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
# saver.restore(sess, './my_model_final.ckpt')
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for iteration in range(mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size):
X_batch, y_batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run([optimizer_op, learning_rate], feed_dict={X: X_batch, y: y_batch, is_training:True})
# ================= check gradient
# for grad, var in grads_and_vars:
# grad = grad.eval(feed_dict={X: X_batch, y: y_batch, is_training:True})
# var = var.eval()
# =================
learning_rate_cur = learning_rate.eval()
acc_train = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={X: X_batch, y: y_batch, is_training:False}) # 最后一个 batch 的 accuracy
acc_test = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels, is_training:False})
loss_test = loss.eval(feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels, is_training:False})
print(epoch, "Current learning rate:", learning_rate_cur, "Train accuracy:", acc_train, "Test accuracy:", acc_test, "Test loss:", loss_test)
save_path = saver.save(sess, "./my_model_final.ckpt") with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
saver.restore(sess, "./my_model_final.ckpt")
acc_test = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels, is_training:False})
loss_test = loss.eval(feed_dict={X: mnist.test.images, y: mnist.test.labels, is_training:False})
print("Test accuracy:", acc_test, ", Test loss:", loss_test)
Since AdaGrad, RMSProp, and Adam optimization automatically reduce the learning rate during training, it is not necessary to add an extra learning schedule. For other optimization algorithms, using exponential decay or performance scheduling can considerably speed up convergence.
TensorFlow使用记录 (三): Learning Rate Scheduling的更多相关文章
- 5、Tensorflow基础(三)神经元函数及优化方法
1.激活函数 激活函数(activation function)运行时激活神经网络中某一部分神经元,将激活信息向后传入下一层的神经网络.神经网络之所以能解决非线性问题(如语音.图像识别),本质上就是激 ...
- Deep Learning 32: 自己写的keras的一个callbacks函数,解决keras中不能在每个epoch实时显示学习速率learning rate的问题
一.问题: keras中不能在每个epoch实时显示学习速率learning rate,从而方便调试,实际上也是为了调试解决这个问题:Deep Learning 31: 不同版本的keras,对同样的 ...
- TensorFlow使用记录 (九): 模型保存与恢复
模型文件 tensorflow 训练保存的模型注意包含两个部分:网络结构和参数值. .meta .meta 文件以 “protocol buffer”格式保存了整个模型的结构图,模型上定义的操作等信息 ...
- TensorFlow使用记录 (六): 优化器
0. tf.train.Optimizer tensorflow 里提供了丰富的优化器,这些优化器都继承与 Optimizer 这个类.class Optimizer 有一些方法,这里简单介绍下: 0 ...
- tensorflow笔记(三)之 tensorboard的使用
tensorflow笔记(三)之 tensorboard的使用 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请指明转载地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/fydeblog/p/7429344.h ...
- mxnet设置动态学习率(learning rate)
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaotao_1/article/details/78874336 如果learning rate很大,算法会在局部最优点附近来回跳动,不会收敛: 如果l ...
- TensorFlow使用记录 (八): 梯度修剪 和 Max-Norm Regularization
梯度修剪 梯度修剪主要避免训练梯度爆炸的问题,一般来说使用了 Batch Normalization 就不必要使用梯度修剪了,但还是有必要理解下实现的 In TensorFlow, the optim ...
- TensorFlow实战第三课(可视化、加速神经网络训练)
matplotlib可视化 构件图形 用散点图描述真实数据之间的关系(plt.ion()用于连续显示) # plot the real data fig = plt.figure() ax = fig ...
- Dynamic learning rate in training - 培训中的动态学习率
I'm using keras 2.1.* and want to change the learning rate during training. I know about the schedul ...
随机推荐
- Java基础(十)
复习 静态方法与成员方法 //另一个类里的静态和成员方法 public class MyClass { //静态方法 public static void method2() { System.out ...
- 最短meeting路线(树的直径)--牛客第四场(meeting)
题意: 给你一棵树,树上有些点是有人的,问你选一个点,最短的(最远的那个人的距离)是多少. 思路: 其实就是树的直径,两遍dfs,dfs第二遍的时候遇到人就更新直径就行了,ans是/2,奇数的话+1. ...
- 02:linux常用命令
1.1 linux查看系统基本参数常用命令 1.查看磁盘 [root@linux-node1 ~]# df -hl Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on ...
- Robot Framework(一)安装笔记
参考网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yinrw/p/5837828.html因为自己安装了py,网上教程都是统一安装py2.7开始的. 所以这里总结下安装笔记:cmd命令界面进行 ...
- 树莓派USB存储设备自动挂载并通过脚本实现自动拷贝,自动播放视频,脚本自动升级等功能
需求:首先需要树莓派自动挂载USB设备,然后扫描USB指定目录下文件,将相关文件拷贝至树莓派指定目录,然后通过omxplayer循环播放新拷贝文件视频 1. 树莓派实现USB存储设备自动挂载 树莓派U ...
- docker toolbox的redis 配置主从及哨兵模式保证高可用
redis 的缓存中间件安装方法,简单举例如下: 环境: docker toolbox 一 主从模式1 搜索redis镜像 docker search redis2 拉取镜像docker pul ...
- 09 Python两种创建类的方式
第一种比较普遍的方式: class Work(): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name w = Work('well woker') 这样就简单创建了一 ...
- Delphi 键盘的编程
- deployment控制pod进行滚动更新以及回滚
更新pod镜像两种方式: 方式一:kubectl set image deployment/${deployment name} ${container name}=${image} 例: kubec ...
- 002-loganalyzer装完报错no syslog records found
1.登录mysql查看库Syslog中的表SystemEvents;是否有返回数据 # select * from Syslog.SystemEvents; #又返回数据说明rsyslog配置正确, ...
