tf-图像预处理
tensorflow 中自带了很多图像处理的方法,基本都在 tf.image 模块中,虽然不如 opencv 强大,但也比较常用,这里做个记录。
图像编解码
1. 用 tf 的方法读取图片后,都需要进行编解码,才能在 tf 中继续处理;
2. tf 提供了各种类型图像的编解码:decode_gif,decode_png,decode_jepg,decode_image,encode_png 等待,用法类似
tf.image.decode_png(contents, channels=0, dtype=_dtypes.uint8, name=None):channels 指定通道数
大体处理过程是:读取--解码--转换成 np --喂给 sess
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pylab as plt image = tf.gfile.FastGFile('pic/t4.png', 'rb').read()
print(type(image)) # <class 'bytes'> 格式显然不对,需要解码 image = tf.image.decode_png(image) # 这里暂时没有指定channels
print(type(image)) # <class 'tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Tensor'> 解码完是 tensor,不能直接作为 sess.run 的输入 tf.InteractiveSession() image = image.eval()
print(type(image)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> 转换成 np print(image.shape) # (620, 723, 4) 默认4个通道,不符合 tensorflow 的处理要求,在 decode_png 中可指定通道数为3,这里就变成3个通道了 print(image) # 0-255 int plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
数据类型转换
很多图像的像素默认是int类型(如上例),但在 tf 中 float 更容易处理,而且 tf 很多函数输出默认是 float,在 imshow 时会发生错误。
tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype, saturate=False, name=None)
import matplotlib as mpl
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pylab as plt mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['FangSong'] # 图片上显示中文 image = tf.gfile.FastGFile('pic/t4.png', 'rb').read()
image = tf.image.decode_png(image) tf.InteractiveSession() image1 = image.eval()
print(image1) # 默认 0-255 int
# [[[255 247 245 255]
# [255 248 245 255] ### 经过 tf 函数图像处理后,无法imshow,因为输出变成 0-255 float,imshow 只接受 0-1 float 和 0-255 int
image2 = tf.image.resize_images(image, [300, 300], method=0).eval()
print(image2)
# [[[255. 247. 245. 255. ]
# [254. 248.41 245. 255. ] ### 需要进行 数据类型转换,可以指定转换类型
image3 = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype=tf.float32) # 这里指定转成 0-1 float
print(image3) # Tensor("convert_image:0", shape=(?, ?, ?), dtype=float32) image4 = tf.image.resize_images(image3, [300, 300], method=0).eval()
print(image4)
# [[[1. 0.9686275 0.9607844 1. ]
# [0.9960785 0.9741569 0.9607844 1. ] # imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers).
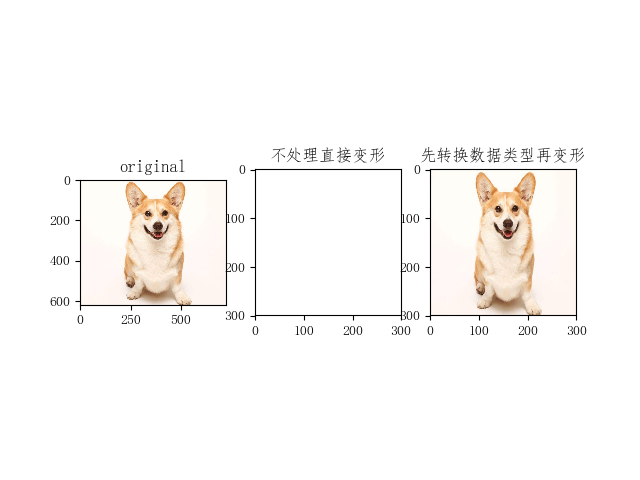
plt.subplot(131); plt.imshow(image1); plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(132); plt.imshow(image2); plt.title('不处理直接变形')
plt.subplot(133); plt.imshow(image4); plt.title('先转换数据类型再变形')
plt.show()
输出
图像翻转
包括上下翻转、左右翻转、90度翻转,随机翻转,函数见代码
tf.image.random_flip_left_right:随机左右翻转,概率为0.5
tf.image.random_flip_up_down:随机上下翻转,概率为0.5
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # 读取图像数据
img = tf.gfile.FastGFile('./pic/t4.png', 'rb').read() # 默认读取是二进制,故必须进行解码
img_data = tf.image.decode_png(img) # 将图像上下翻转
flipped0 = tf.image.flip_up_down(img_data)
flipped0 = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(flipped0, dtype=tf.float32) # 本例中此句可有可无 # 将图像左右翻转
flipped1 = tf.image.flip_left_right(img_data)
flipped1 = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(flipped1, dtype=tf.uint8) # 通过交换第一维和第二维来转置图像
flipped2 = tf.image.transpose_image(img_data) # 也就是转90度,翻转是转180度 img_ori = img_data.eval()
print(img_ori.shape) # (620, 723, 4) 4通道
print(img_ori) # 0-255 int
plt.subplot(221); plt.imshow(img_ori); plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(222); plt.imshow(flipped0.eval()); plt.title('flip_up_down')
plt.subplot(223); plt.imshow(flipped1.eval()); plt.title('flip_left_right')
plt.subplot(224); plt.imshow(flipped2.eval()); plt.title('transpose_image')
plt.show()
输出

尺寸变换
tf.image.resize_images:输出为 float
resize_images(images,
size,
method=ResizeMethod.BILINEAR,
align_corners=False,
preserve_aspect_ratio=False)
methold 取值 决定 图像大小调整算法
0 - 双线性插值法(Bilinear interprolation)
1 - 最临近插值法 (Nearest neighbor interprolation)
2 - 双三次插值法 (Bicubic interprolation)
3 - 面积插值法 (Area interprolation)
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pylab as plt image = tf.gfile.FastGFile('pic/t4.png', 'rb').read()
image = tf.image.decode_png(image, channels=3) # 注意这里需要设定3通道,默认4通道
image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype=tf.float32) # 这里变换是为了 imshow,转换成 0-1 float image_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, None, 3]) image_new_biliner = tf.image.resize_images(image_in, size=[300, 300], method=0) # method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.BILINEAR
image_new_near = tf.image.resize_images(image_in, size=[300, 100], method=1) # method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR
image_new_inter = tf.image.resize_images(image_in, [300, 100], method=2) # method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.BICUBIC
image_new_area = tf.image.resize_images(image_in, [500, 200], method=3) # method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.AREA with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
image = sess.run(image)
image1, image2, image3, image4 = sess.run([image_new_biliner, image_new_near, image_new_inter, image_new_area],
feed_dict={image_in: image})
# print(image1) 输出为 0-1 float
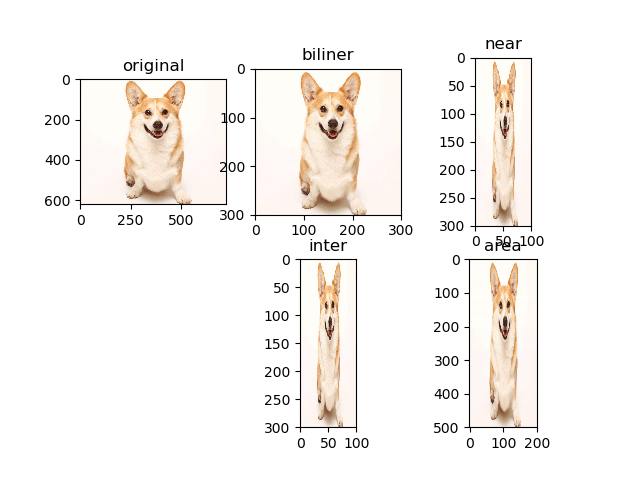
plt.subplot(231); plt.imshow(image); plt.title('original') # imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers).
plt.subplot(232); plt.imshow(image1); plt.title('biliner')
plt.subplot(233); plt.imshow(image2); plt.title('near')
plt.subplot(235); plt.imshow(image3); plt.title('inter')
plt.subplot(236); plt.imshow(image4); plt.title('area')
plt.show()
输出
图像裁剪
tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box(image, offset_height, offset_width, target_height, target_width):裁剪框裁剪
参数分别为:输入图像,裁剪起点纵坐标,裁剪起点横坐标,裁剪高度,裁剪宽度
输出为 float
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt image = tf.gfile.FastGFile('pic/t4.png', 'rb').read()
image = tf.image.decode_png(image)
image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype=tf.float32) image_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32) # 没有设定shape=[None, None, 3] image_crop1 = tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box(image_in, 100, 50, 80, 80)
image_crop2 = tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box(image_in, 100, 50, 400, 300)
image_crop3 = tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box(image_in, 0, 0, 300, 300) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) image = sess.run(image)
image1, image2, image3 = sess.run([image_crop1, image_crop2, image_crop3], feed_dict={image_in: image})
plt.subplot(221); plt.imshow(image); plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(222); plt.imshow(image1); plt.title('crop1')
plt.subplot(223); plt.imshow(image2); plt.title('crop2')
plt.subplot(224); plt.imshow(image3); plt.title('crop3')
plt.show()
输出

tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_pad(image, target_height, target_width):图像中心不变,将图像裁剪或填充至指定尺寸
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pylab as plt image = tf.gfile.FastGFile('pic/t4.png', 'rb').read()
image = tf.image.decode_png(image)
image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype=tf.float32) image_in = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32) crop = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(image_in, 400, 400)
pad = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(image_in, 1000, 1000) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) image = sess.run(image)
image1, image2 = sess.run([crop, pad], feed_dict={image_in: image})
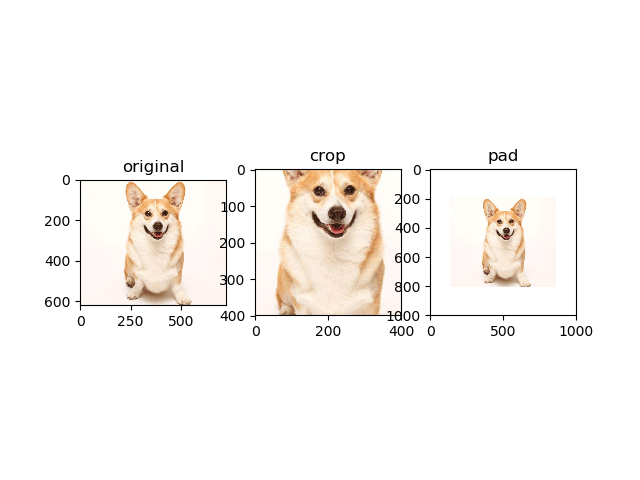
plt.subplot(131); plt.imshow(image); plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(132); plt.imshow(image1); plt.title('crop')
plt.subplot(133); plt.imshow(image2); plt.title('pad')
plt.show()
输出
tf.image.central_crop(image, central_fraction):以图像中心为依据,按一定比例裁剪图像
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf img = tf.gfile.FastGFile('pic/t4.png', 'rb').read() with tf.Session() as sess:
img_data = tf.image.decode_png(img) # 函数tf.image.central_crop可以通过比例调整图像的大小
resized1 = tf.image.central_crop(img_data, 0.6)
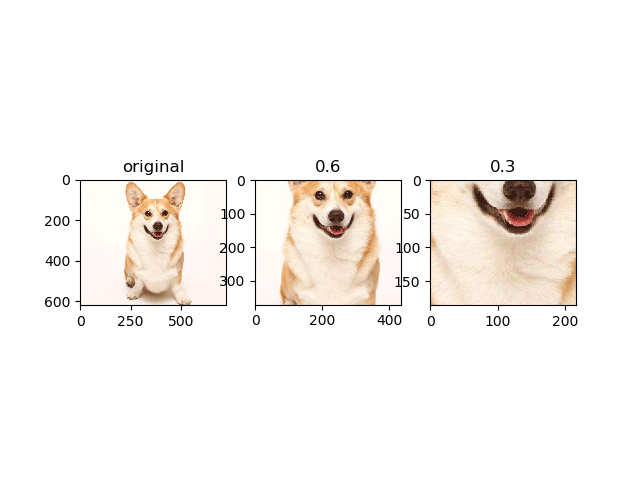
resized2 = tf.image.central_crop(img_data, 0.3) plt.subplot(131); plt.imshow(img_data.eval()); plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(132); plt.imshow(resized1.eval()); plt.title('0.6')
plt.subplot(133); plt.imshow(resized2.eval()); plt.title('0.3')
plt.show()
输出
色彩变换
包括调整亮度、对比度、色相、饱和度、规范化,函数见代码
在指定范围内随机调整图像的 亮度/对比度/色相/饱和度
tf.image.random_brightness(img_data,max_delta)
tf.image.random_contrast(img_data, lower, upper)
tf.image.random_hue(img_data, max_delta)
tf.image.random_saturation(img_data, lower, upper)
随机调整这些属性,使训练得到的模型尽可能小的受到无关因素的影响.
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['FangSong'] # 图片上显示中文 # 读取图像数据
img = tf.gfile.FastGFile('pic/t4.png', 'rb').read() with tf.Session() as sess:
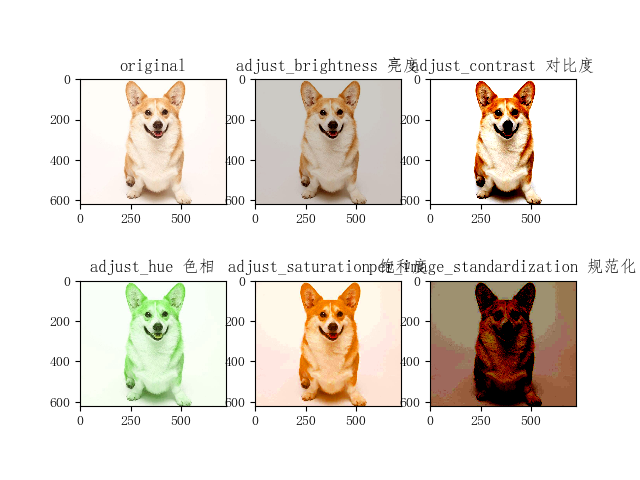
img_data = tf.image.decode_png(img, channels=3) adjusted0 = tf.image.adjust_brightness(img_data, -0.2) # 将图像的亮度-0.2
adjusted1 = tf.image.adjust_contrast(img_data, +3) # 将图像的对比度+3
adjusted2 = tf.image.adjust_hue(img_data, 0.2) # 将图像的色相+0.2
adjusted3 = tf.image.adjust_saturation(img_data, 3) # 将图像的饱和度+3
adjusted4 = tf.image.per_image_standardization(img_data) # 将图像线性缩放为零均值和单位范数 plt.subplot(231), plt.imshow(img_data.eval()), plt.title('original')
plt.subplot(232), plt.imshow(adjusted0.eval()), plt.title('adjust_brightness 亮度')
plt.subplot(233), plt.imshow(adjusted1.eval()), plt.title('adjust_contrast 对比度')
plt.subplot(234), plt.imshow(adjusted2.eval()), plt.title('adjust_hue 色相')
plt.subplot(235), plt.imshow(adjusted3.eval()), plt.title('adjust_saturation 饱和度')
plt.subplot(236), plt.imshow(adjusted4.eval()), plt.title('per_image_standardization 规范化') plt.show()
输出
图像增强
随机图像变换经常用于图像增强
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import random source_file = "./pic/" #原始文件地址
target_file = "./pic2/" #修改后的文件地址
num = 50 #产生图片次数 if not os.path.exists(target_file): #如果不存在target_file,则创造一个
os.makedirs(target_file) file_list = os.listdir(source_file) #读取原始文件的路径 with tf.Session() as sess:
for i in range(num):
# 每次随机选一张
a = random.randint(0, len(file_list)-1) #随机数字区间
image_raw_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(source_file+file_list[a],"rb").read() # 读取图片
print("正在处理:",file_list[a]) image_data = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_raw_data) # 增强方式
image_data = tf.image.random_crop(image_data, [100, 100, 3]) #随机裁剪
filpped_le_re = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image_data) #随机左右翻转
filpped_up_down = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(image_data) #随机上下翻转
adjust = tf.image.random_brightness(filpped_up_down,0.4) #随机调整亮度
adjust = tf.image.random_contrast(adjust, lower=0.2, upper=1.8) #随机调整图像对比度 image_data = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(adjust,dtype=tf.uint8) encode_data = tf.image.encode_jpeg(image_data) with tf.gfile.GFile(target_file+str(i)+"_enhance"+".jpeg","wb") as f:
f.write(encode_data.eval()) print("图像增强完毕")
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/xierhacker/article/details/72385422
https://blog.csdn.net/akadiao/article/details/78541763
https://www.cnblogs.com/Smnustudy/p/10704959.html#top
tf-图像预处理的更多相关文章
- 『TensorFlow』第九弹_图像预处理_不爱红妆爱武装
部分代码单独测试: 这里实践了图像大小调整的代码,值得注意的是格式问题: 输入输出图像时一定要使用uint8编码, 但是数据处理过程中TF会自动把编码方式调整为float32,所以输入时没问题,输出时 ...
- TensorFlow图像预处理完整样例
参考书 <TensorFlow:实战Google深度学习框架>(第2版) 以下TensorFlow程序完成了从图像片段截取,到图像大小调整再到图像翻转及色彩调整的整个图像预处理过程. #! ...
- 图像预处理第9步:存为.bmp文件
//图像预处理第9步:将最终标准化后的字符图像分为单个单个的HDIB保存,并存为.bmp文件 void CChildView::OnImgprcToDibAndSave() { unsigned ch ...
- 基于OpenCV的火焰检测(一)——图像预处理
博主最近在做一个基于OpenCV的火焰检测的项目,不仅可以检测图片中的火焰,还可以检测视频中的火焰,最后在视频检测的基础上推广到摄像头实时检测.在做这个项目的时候,博主参考了很多相关的文献,用了很多种 ...
- python+opencv 图像预处理
一 python 生成随机字符串序列+ 写入到图片上 from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont import numpy as np import rando ...
- Caffe2 图像预处理(Image Pre-Processing)[6]
学习如何使得图像符合预训练模型的需求,或者用其他数据集的图像来测试自己的模型. - 调整大小 - 缩放 - HWC和CHW,数据通道交换 - RGB和BGR,颜色通道的交换 - Caffe2的图像预处 ...
- [opencv]图像预处理方案及方式
像识别中,图像质量的好坏直接影响识别算法的设计与效果精度,那么除了能在算法上的优化外,预处理技术在整个项目中占有很重要的因素,然而人们往往忽略这一点. 图像预处理,将每一个文字图像分检出来交给识别模块 ...
- Matlab 图像预处理
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%降采样 clear all im={}; %创建字典保存读取的图片 dis=dir('F:\kaggle_data_zip\Sample\*.jpeg');%% ...
- TensorFlow图像预处理-函数
更多的基本的API请参看TensorFlow中文社区:http://www.tensorfly.cn/tfdoc/api_docs/python/array_ops.html 下面是实验的代码,可以参 ...
- pytorch中检测分割模型中图像预处理探究
Object Detection and Classification using R-CNNs 目标检测:数据增强(Numpy+Pytorch) - 主要探究检测分割模型数据增强操作有哪些? - 检 ...
随机推荐
- #4 div1E Parentheses 括号匹配
E - Parentheses Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:131072KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Subm ...
- NOI数论姿势瞎总结(Pi也没有)
Miller-Rabin素数检测 费马小定理:没人不会吧. 二次探测:如果\(n\)是质数,\(x^2 \equiv 1\ (\mod n)\)的解只有\(x \equiv 1\)或\(x \equi ...
- 在spring官网上下载历史版本的spring插件,springsource-tool-suite
目前spring官网(https://spring.io/tools3/sts/all)上可下载的spring插件只有: ECLIPSE ARCHIVE SIZE 4.9.0 springsource ...
- JS框架_(JQuery.js)图片相册掀开切换效果
百度云盘 传送门 密码:y0dk 图片掀开切换效果: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN&quo ...
- C++入门经典-例5.12-动态内存的销毁
1:当申请一块堆内存后,系统不会再程序执行时一句情况自动销毁它.若想释放该内存,则需要使用delete关键字.下面的代码中,可以看出堆和栈的不同.代码如下: // 5.12.cpp : 定义控制台应用 ...
- LeetCode328----奇偶链表
给定一个单链表,把所有的奇数节点和偶数节点分别排在一起.请注意,这里的奇数节点和偶数节点指的是节点编号的奇偶性,而不是节点的值的奇偶性. 请尝试使用原地算法完成.你的算法的空间复杂度应为 O(1),时 ...
- python开发环境的搭建,以及pycharm的安装
先到python 官网下载python. 下载好了之后,直接运行exe文件,进行安装(在安装程序运行后的第一个form上,点击next的时候,在next的左侧有一排文字和一个复选框,那个是添加环境变量 ...
- gcc编译错误
使用boost的时候遇到一个链接错误 undefined reference to `boost::system::detail::generic_category_instance 出现这个问题的有 ...
- java面试要点
基础篇 基本功 面向对象的特征 final, finally, finalize 的区别 int 和 Integer 有什么区别 重载和重写的区别 抽象类和接口有什么区别 说说反射的用途及实现 说说自 ...
- leetcode 148排序链表
优先队列容器,使用小顶堆排序:timeO(nlogn) spaceO(n) /** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * ...
