UVA 1394 And Then There Was One / Gym 101415A And Then There Was One / UVAlive 3882 And Then There Was One / POJ 3517 And Then There Was One / Aizu 1275 And Then There Was One (动态规划,思维题)
UVA 1394 And Then There Was One / Gym 101415A And Then There Was One / UVAlive 3882 And Then There Was One / POJ 3517 And Then There Was One / Aizu 1275 And Then There Was One (动态规划,思维题)
Description
Let’s play a stone removing game.
Initially, n stones are arranged on a circle and numbered 1, …, n clockwise (Figure 1). You are also given two numbers k and m. From this state, remove stones one by one following the rules explained below, until only one remains. In step 1, remove stone m. In step 2, locate the k-th next stone clockwise from m and remove it. In subsequent steps, start from the slot of the stone removed in the last step, make k hops clockwise on the remaining stones and remove the one you reach. In other words, skip (k − 1) remaining stones clockwise and remove the next one. Repeat this until only one stone is left and answer its number. For example, the answer for the case n = 8, k = 5, m = 3 is 1, as shown in Figure 1.
Initial state: Eight stones are arranged on a circle.
Step 1: Stone 3 is removed since m = 3.
Step 2: You start from the slot that was occupied by stone 3. You skip four stones 4, 5, 6 and 7 (since k = 5), and remove the next one, which is 8.
Step 3: You skip stones 1, 2, 4 and 5, and thus remove 6. Note that you only count stones that are still on the circle and ignore those already removed. Stone 3 is ignored in this case.
Steps 4–7: You continue until only one stone is left. Notice that in later steps when only a few stones remain, the same stone may be skipped multiple times. For example, stones 1 and 4 are skipped twice in step 7.
Final State: Finally, only one stone, 1, is on the circle. This is the final state, so the answer is 1.
Input
The input consists of multiple datasets each of which is formatted as follows.
n k m
The last dataset is followed by a line containing three zeros. Numbers in a line are separated by a single space. A dataset satisfies the following conditions.
2 ≤ n ≤ 10000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 10000, 1 ≤ m ≤ n
The number of datasets is less than 100.
Output
For each dataset, output a line containing the stone number left in the final state. No extra characters such as spaces should appear in the output.
Sample Input
8 5 3
100 9999 98
10000 10000 10000
0 0 0
Sample Output
1
93
2019
Http
UVA:https://vjudge.net/problem/UVA-1394
Gym:https://vjudge.net/problem/Gym-101415A
UVAlive:https://vjudge.net/problem/UVALive-3882
POJ:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-3517
Aizu:https://vjudge.net/problem/Aizu-1275
Source
动态规划,思维
题目大意
约瑟夫问题的变式。先指定第m个人必须死,然后每隔k个人死一个。求最后那个死的人的编号是什么。
解决思路
首先不考虑第一个必须死的人是m的情况。我们把n个人编号为[0,n-1]。那么第一轮出局的就是编号为k-1的人,剩下的人的编号是\([0,k-2]\cup[k,n-1]\)。
然后我们从编号为k的人开始,循环一圈给所有人重新分配编号
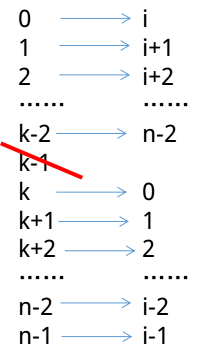
然后我们就可以发现原来n个人的题目就变成了n-1的规模。运用这种方法,我们就可以推到n=1的情况,而此时,F[1]=0。
那么,既然现在知道n=1的结果,那么我们考虑从1开始正着推出n。我们设F[i]表示i个人中最后存活的人的编号。现在我们知道F[i-1],怎么推出F[i]呢?
其实这个问题就是问如何用存活者在i-1个人中的编号求出存活者在i个人中的编号。我们知道,从原问题推到子问题其实是把所有人的编号-k,那么从子问题推到原问题就是把人的编号+k,但要注意,此时+k可能会大于当前人的规模i,所以要对i取膜。
综上,动态转移的方程就是
\]
当然这个式子还可以化简。因为F[i]的状态只与F[i-1]有关,所以我们可以直接用一个变量f代替整个F数组
\]
最后再来考虑第一个死的人必须是m的情况,而我们第一个人是k,所以相当于我们要补上m-k的一个差量,所以最后的答案是f+m-k。另外需要注意的是,因为我们在递推的时候为了方便从0开始编号的,所以还要加上1,也就是f+m-k+1,再对n取膜。同时,如果取膜后结果是0或负数,要加上n变成正数。
代码不长,但要想到很难。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int inf=2147483647;
int main()
{
int n,k,m;
while (scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&k,&m)!=EOF)
{
if ((n==0)&&(m==0)&&(k==0))
break;
int f=0;//初始值
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++)//动态转移
f=(f+k)%i;
f=(f+m-k+1)%n;//把开始是m的情况考虑进去
if (f<=0)//取膜后有可能变成负数或0,此时要将其变成正数
f=f+n;
printf("%d\n",f);
}
return 0;
}
UVA 1394 And Then There Was One / Gym 101415A And Then There Was One / UVAlive 3882 And Then There Was One / POJ 3517 And Then There Was One / Aizu 1275 And Then There Was One (动态规划,思维题)的更多相关文章
- poj 2229 一道动态规划思维题
http://poj.org/problem?id=2229 先把题目连接发上.题目的意思就是: 把n拆分为2的幂相加的形式,问有多少种拆分方法. 看了大佬的完全背包代码很久都没懂,就照着网上的写了动 ...
- UVA.699 The Falling Leaves (二叉树 思维题)
UVA.699 The Falling Leaves (二叉树 思维题) 题意分析 理解题意花了好半天,其实就是求建完树后再一条竖线上的所有节点的权值之和,如果按照普通的建树然后在计算的方法,是不方便 ...
- UVA.679 Dropping Balls (二叉树 思维题)
UVA.679 Dropping Balls (二叉树 思维题) 题意分析 给出深度为D的完全二叉树,按照以下规则,求第I个小球下落在那个叶子节点. 1. 默认所有节点的开关均处于关闭状态. 2. 若 ...
- UVA.11384 Help is needed for Dexter (思维题)
UVA.11384 Help is needed for Dexter (思维题) 题意分析 同样水题一道,这回思路对了. 给出数字n,面对一个1,2,3,4--n的数字序列,你可以对他们的部分或者全 ...
- UVA.11636 Hello World! (思维题)
UVA.11636 Hello World! (思维题) 题意分析 这题挺水的,还是错了几发. QWQ. 有一个同学打了一行hello world,现在他想打n行hello world,请问最少复制粘 ...
- UVA.11464 Even Parity (思维题 开关问题)
UVA.11464 Even Parity (思维题 开关问题) 题目大意 给出一个n*n的01方格,现在要求将其中的一些0转换为1,使得每个方格的上下左右格子的数字和为偶数(如果存在的话),求使得最 ...
- UVA.10881 Piotr's Ants (思维题)
UVA.10881 Piotr's Ants (思维题) 题意分析 有一根长度为L cm的木棍,上有n只蚂蚁,蚂蚁要么向左爬,要么向右,速度均为1cm/s,若2只蚂蚁相撞,则蚂蚁同时调头.求解第T秒时 ...
- UVA.11300 Spreading the Wealth (思维题 中位数模型)
UVA.11300 Spreading the Wealth (思维题) 题意分析 现给出n个人,每个人手中有a[i]个数的金币,每个人能给其左右相邻的人金币,现在要求你安排传递金币的方案,使得每个人 ...
- 思维题 Gym 100553A Alter Board
题目传送门 /* 题意:一个n×m的矩形,相邻的颜色不同,黑或白.问最少的翻转次数,每次翻转可指定任意一个子矩形 思维题:最少要把偶数行和列翻转,也就是n/2+m/2次 */ #include < ...
随机推荐
- PowerBI开发 第十五篇:DAX 表达式(时间+过滤+关系)
DAX表达式中包含时间关系(Time Intelligence)相关的函数,用于对日期维度进行累加.同比和环比等分析.PowerBI能够创建关系,通过过滤器来对影响计算的上下文. 一,时间关系 DAX ...
- C#编写WINNT服务,随便解决安卓开发遇到的5037被众多程序无节操占用的问题
需求分析: 最近重新开始学习安卓开发,好久不用的ADT集成开发环境频繁遇到不能在仿真机和真机上调试的问题,也就是本人另一篇博文描述的ADB(Android Debug Bridge)监控的5037被金 ...
- 从源码的角度再看 React JS 中的 setState
在这一篇文章中,我们从源码的角度再次理解下 setState 的更新机制,供深入研究学习之用. 在上一篇手记「深入理解 React JS 中的 setState」中,我们简单地理解了 React 中 ...
- 常用rsync命令操作梳理
作为一个运维工程师,经常可能会面对几十台.几百台甚至上千台服务器,除了批量操作外,环境同步.数据同步也是必不可少的技能.说到“同步”,不得不提的利器就是rsync.rsync不但可以在本机进行文件同步 ...
- snmpd.conf 配置
开启snmp后,一些指标获取不到,需要配置snmpd.conf文件,如下图所示 参考文章:http://blog.csdn.net/flyingfalcon/article/details/47831 ...
- Finished yeah!
终于到了最后的博客阶段,这时候才知道博客此时此刻是多么的惬意,它成了书写心声的自由平台!耗时一天完成这作业说起来也是蛮辛苦的,编译器需要新装,IDE需要熟悉,当然最主要的是之前浅入浅出的C++功底在此 ...
- "Linux内核分析"第七周
可执行程序的装载 张文俊+原创作品转载请注明出处+<Linux内核分析>MOOC课程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000029000 一.预 ...
- warning C4996: 'strcpy': This function or variable may be unsafe.
mkdir 写成 _mkdir strcpy 写成为 strcpy_s 或是在项目处右击-->属性-->C/C++-->预处理器-->在预处理器定义后添加";_CR ...
- Python学习笔记 -- 第四章
高阶函数 变量可以指向函数 f=abs f(-10) 10 变量f指向abs函数,直接调用abs()函数和调用f()完全相同 传入参数 变量可以指向函数,函数的参数可以接收另一个函数的参数,这种函数成 ...
- pandas获取groupby分组里最大值所在的行,获取第一个等操作
pandas获取groupby分组里最大值所在的行 10/May 2016 python pandas pandas获取groupby分组里最大值所在的行 如下面这个DataFrame,按照Mt分组, ...
