Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) A,B,C
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Okabe needs to renovate the Future Gadget Laboratory after he tried doing some crazy experiments! The lab is represented as an n by nsquare grid of integers. A good lab is defined as a lab in which every number not equal to 1 can be expressed as the sum of a number in the same row and a number in the same column. In other words, for every x, y such that 1 ≤ x, y ≤ n and ax, y ≠ 1, there should exist two indices s and t so that ax, y = ax, s + at, y, where ai, j denotes the integer in i-th row and j-th column.
Help Okabe determine whether a given lab is good!
The first line of input contains the integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 50) — the size of the lab.
The next n lines contain n space-separated integers denoting a row of the grid. The j-th integer in the i-th row is ai, j (1 ≤ ai, j ≤ 105).
Print "Yes" if the given lab is good and "No" otherwise.
You can output each letter in upper or lower case.
3
1 1 2
2 3 1
6 4 1
Yes
3
1 5 2
1 1 1
1 2 3
No
In the first sample test, the 6 in the bottom left corner is valid because it is the sum of the 2 above it and the 4 on the right. The same holds for every number not equal to 1 in this table, so the answer is "Yes".
In the second sample test, the 5 cannot be formed as the sum of an integer in the same row and an integer in the same column. Thus the answer is "No".
题意:
懒得说。
思路:
四重循环暴力;
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; int main(){
int m,i,j,k,l,a[][];
cin>>m;
for(i=;i<m;i++){
for(j=;j<m;j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
int flag = ;
for(i=;i<m;i++){
for(j=;j<m;j++){
if(a[i][j]!=){
flag = ;
for(k=;k<m;k++){
for(l=;l<m;l++){
if(a[i][k]+a[l][j]==a[i][j])
flag = ;
}
}
if(flag==){
cout<<"No"<<endl;
return ;
}
}
}
}
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
return ; }
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Okabe needs bananas for one of his experiments for some strange reason. So he decides to go to the forest and cut banana trees.
Consider the point (x, y) in the 2D plane such that x and y are integers and 0 ≤ x, y. There is a tree in such a point, and it has x + ybananas. There are no trees nor bananas in other points. Now, Okabe draws a line with equation 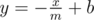 . Okabe can select a single rectangle with axis aligned sides with all points on or under the line and cut all the trees in all points that are inside or on the border of this rectangle and take their bananas. Okabe's rectangle can be degenerate; that is, it can be a line segment or even a point.
. Okabe can select a single rectangle with axis aligned sides with all points on or under the line and cut all the trees in all points that are inside or on the border of this rectangle and take their bananas. Okabe's rectangle can be degenerate; that is, it can be a line segment or even a point.
Help Okabe and find the maximum number of bananas he can get if he chooses the rectangle wisely.
Okabe is sure that the answer does not exceed 1018. You can trust him.
The first line of input contains two space-separated integers m and b (1 ≤ m ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ b ≤ 10000).
Print the maximum number of bananas Okabe can get from the trees he cuts.
1 5
30
2 3
25
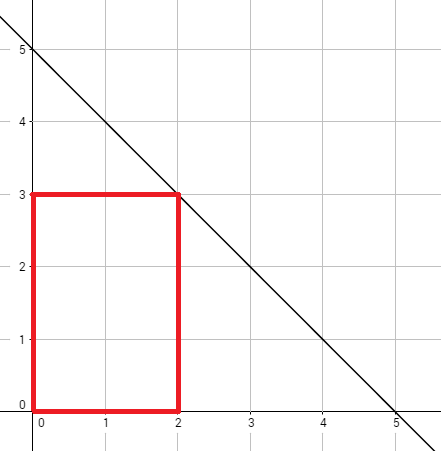
The graph above corresponds to sample test 1. The optimal rectangle is shown in red and has 30 bananas.
思路:
推公式。
实现代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
ll m,b;
ll num(ll x){
ll sum1 = ;
//cout<<"x:"<<x<<endl;
sum1 = (b-x/m)*(b-x/m+)/*(x+)+(b-x/m+)*(+x)*x/;
return sum1;
}
int main(){
ll sum=,maxx,i,j;
cin>>m>>b;
ll k = -m;
ll maxn = -;
while(k<=m*b){
k+=m;
if(num(k)>maxn){
maxn = num(k);
}
}
cout<<maxn<<endl;
return ;
}
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Okabe and Super Hacker Daru are stacking and removing boxes. There are n boxes numbered from 1 to n. Initially there are no boxes on the stack.
Okabe, being a control freak, gives Daru 2n commands: n of which are to add a box to the top of the stack, and n of which are to remove a box from the top of the stack and throw it in the trash. Okabe wants Daru to throw away the boxes in the order from 1 to n. Of course, this means that it might be impossible for Daru to perform some of Okabe's remove commands, because the required box is not on the top of the stack.
That's why Daru can decide to wait until Okabe looks away and then reorder the boxes in the stack in any way he wants. He can do it at any point of time between Okabe's commands, but he can't add or remove boxes while he does it.
Tell Daru the minimum number of times he needs to reorder the boxes so that he can successfully complete all of Okabe's commands. It is guaranteed that every box is added before it is required to be removed.
The first line of input contains the integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3·105) — the number of boxes.
Each of the next 2n lines of input starts with a string "add" or "remove". If the line starts with the "add", an integer x (1 ≤ x ≤ n) follows, indicating that Daru should add the box with number x to the top of the stack.
It is guaranteed that exactly n lines contain "add" operations, all the boxes added are distinct, and n lines contain "remove" operations. It is also guaranteed that a box is always added before it is required to be removed.
Print the minimum number of times Daru needs to reorder the boxes to successfully complete all of Okabe's commands.
3
add 1
remove
add 2
add 3
remove
remove
1
7
add 3
add 2
add 1
remove
add 4
remove
remove
remove
add 6
add 7
add 5
remove
remove
remove
2
In the first sample, Daru should reorder the boxes after adding box 3 to the stack.
In the second sample, Daru should reorder the boxes after adding box 4 and box 7 to the stack.
解题思路:
要按顺序输出1-n,那么当栈顶元素和当前要输出的相同时,直接输出就行,不同时,则需要进行排序操作,默认最优排序使栈中所有元素都可以按指定顺序输出,记一次操作,问需要几次操作。
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack<int>sta;
int main()
{
int m,i,x,ans = ;
int sum = ;
char s[];
scanf("%d",&m);
for(i=;i<m*;i++){
scanf("%s",s);
if(s[]=='a'){
scanf("%d",&x);
sta.push(x);
}
else{
ans ++;
if(sta.empty()==)
continue;
if(sta.top()!=ans){
sum++;
while(sta.empty()==){
sta.pop();}
}
else{
sta.pop();
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) A,B,C的更多相关文章
- 【Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) C】Okabe and Boxes
[题目链接]:http://codeforces.com/contest/821/problem/C [题意] 给你2*n个操作; 包括把1..n中的某一个数压入栈顶,以及把栈顶元素弹出; 保证压入和 ...
- 【Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) B】Okabe and Banana Trees
[题目链接]:http://codeforces.com/contest/821/problem/B [题意] 当(x,y)这个坐标中,x和y都为整数的时候; 这个坐标上会有x+y根香蕉; 然后给你一 ...
- 【Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) A】Okabe and Future Gadget Laboratory
[题目链接]:http://codeforces.com/contest/821/problem/A [题意] 给你一个n*n的数组; 然后问你,是不是每个位置(x,y); 都能找到一个同一行的元素q ...
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) - C
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/821/problem/C 题意:起初有一个栈,给定2*n个命令,其中n个命令是往栈加入元素,另外n个命令是从栈中取出元素.你可以 ...
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) - E
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/821/problem/E 题意:起初在(0,0),现在要求走到(k,0),问你存在多少种走法. 其中有n条线段,每条线段为(a, ...
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) - B
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/821/problem/B 题意:二维每个整点坐标(x,y)拥有的香蕉数量为x+y,现在给你一个直线方程的m和b参数,让你找一个位 ...
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) - A
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/821/problem/A 题意:给定一个n*n的矩阵. 问你这个矩阵是否满足矩阵里的元素除了1以外,其他元素都可以在该元素的行和 ...
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2)
/*************************************************************************************************** ...
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo 矩阵快速幂优化dp
E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
随机推荐
- TerraGate软件安装后,服务无法启动的解决方法
前些天有朋友问,TerraGate安装后,服务无法启动,而且启动按钮也是不可用的状态,不知道是为什么,如下图: 打开TerraGate的安装目录,发现里面缺少一些文件,如下图: *解决办法: 重新安装 ...
- Python常见十六个错误集合,你知道那些?
使用python会出现各种各样的错误,以下是Python常见的错误以及解决方法. 1.ValueError: 'Conv2d_1a_3×3' is not a valid scope name 这个是 ...
- CF908D New Year and Arbitrary Arrangement 期望、DP
题目传送门 题意:给出正整数$pa,pb,k$,最开始你有一个空串,每一次你有$\frac{pa}{pa + pb}$的概率向串最后放一个$a$,有$\frac{pb}{pa + pb}$的概率向串最 ...
- (原创)odoo解决方案---接收以及回复外部邮件
关于我的那篇"odoo邮件配置那些事儿"中提到的用户接收外部与业务无关邮件的问题,现已形成解决方案,有需要的朋友可以给发email,价格好商量,呵呵 直接贴图了 1.用户绑定 图1 ...
- kettle学习笔记——插件的安装与使用
一.概述 暂略 二.ODPS插件 https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/68911
- VS2017中 C# dll引用(C生成dll,C++生成dll)小结 - 简书
原文:VS2017中 C# dll引用(C生成dll,C++生成dll)小结 - 简书 dll引用小结 一.dll与应用程序 动态链接库(也称为DLL,即为“Dynamic Link Library” ...
- 【转】单KEY业务,数据库水平切分架构实践
本文将以“用户中心”为例,介绍“单KEY”类业务,随着数据量的逐步增大,数据库性能显著降低,数据库水平切分相关的架构实践: 如何来实施水平切分 水平切分后常见的问题 典型问题的优化思路及实践 一.用户 ...
- [Spark][Python]Spark Join 小例子
[training@localhost ~]$ hdfs dfs -cat people.json {"name":"Alice","pcode&qu ...
- JVM规范系列:总结
我们花了几天的时间来阅读<Java虚拟机规范>,了解要实现一个虚拟机应该包括什么内容.通过这么一次阅读,我们大致了解了虚拟机规范的内容. 第1章.对Java虚拟机进行了一些简单的介绍. 第 ...
- Unity3D安卓打包
Unity3D安卓打包须知: 最近在接触Unity3D,在打包安卓时,出现了一些问题,在这里写出来跟大家分享: 首先需要安装jdk和android-sdk,安装方法略 Jdk的目录结构如下: andr ...
