Spring学习总结(三)——Spring实现AOP的多种方式
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的横向多模块统一控制的一种技术。AOP是OOP的补充,是Spring框架中的一个重要内容。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。AOP可以分为静态织入与动态织入,静态织入即在编译前将需织入内容写入目标模块中,这样成本非常高。动态织入则不需要改变目标模块。Spring框架实现了AOP,使用注解配置完成AOP比使用XML配置要更加方便与直观。上一篇随笔中已经详细讲了代理模式。
一、基于XML配置的Spring AOP
在讲注解实现AOP功能前先用前面学习过的使用xml配置Spring AOP功能,这样是为了对比以便更好的理解。
1.1、新建一个Maven项目,添加引用,项目的pom.xml文件如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.zhangguo</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring052</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging> <name>Spring052</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring.version>4.3.0.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<version>4.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
1.2、创建要被代理的Math类,代码如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01; /**
* 被代理的目标类
*/
public class Math{
//加
public int add(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1+n2;
System.out.println(n1+"+"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
} //减
public int sub(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1-n2;
System.out.println(n1+"-"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
} //乘
public int mut(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1*n2;
System.out.println(n1+"X"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
} //除
public int div(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1/n2;
System.out.println(n1+"/"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
}
}
1.3、编辑AOP中需要使用到的通知类Advices.java代码如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; /**
* 通知类,横切逻辑
*
*/
public class Advices { public void before(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------前置通知----------");
System.out.println(jp.getSignature().getName());
} public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}
}
1.4、配置容器初始化时需要的XML文件,aop01.xml文件内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 被代理对象 -->
<bean id="math" class="com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01.Math"></bean> <!-- 通知 -->
<bean id="advices" class="com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01.Advices"></bean> <!-- aop配置 -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!--切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="advices">
<!-- 切点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01.Math.*(..))" id="pointcut1"/>
<!--连接通知方法与切点 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config> </beans>
1.5、测试代码Test.java如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop01.xml");
Math math = ctx.getBean("math", Math.class);
int n1 = 100, n2 = 5;
math.add(n1, n2);
math.sub(n1, n2);
math.mut(n1, n2);
math.div(n1, n2);
} }
运行结果:

二、使用注解配置AOP
2.1、在上一个示例中修改被代理的类Math,为了实现IOC扫描在Math类上注解了@Service并命名bean为math。相当于上一个示例中在xml配置文件中增加了一个bean,<!-- 被代理对象 --><bean id="math" class="com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01.Math"></bean>,Math类的代码如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop02; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /**
* 被代理的目标类
*/
@Service("math")
public class Math{
//加
public int add(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1+n2;
System.out.println(n1+"+"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
} //减
public int sub(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1-n2;
System.out.println(n1+"-"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
} //乘
public int mut(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1*n2;
System.out.println(n1+"X"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
} //除
public int div(int n1,int n2){
int result=n1/n2;
System.out.println(n1+"/"+n2+"="+result);
return result;
}
}
2.2、修改通知类Advices,代码中有3个注解,@Component表示该类的实例会被Spring IOC容器管理;@Aspect表示声明一个切面;@Before表示before为前置通知,通过参数execution声明一个切点,Advices.java代码如下所示:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop02; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 通知类,横切逻辑
*
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class Advices {
@Before("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop02.Math.*(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------前置通知----------");
System.out.println(jp.getSignature().getName());
} @After("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop02.Math.*(..))")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}
}
上面的代码与下面的配置基本等同
<!-- 通知 -->
<bean id="advices" class="com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01.Advices"></bean> <!-- aop配置 -->
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<!--切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="advices">
<!-- 切点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop01.Math.*(..))" id="pointcut1"/>
<!--连接通知方法与切点 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
2.3、新增配置文件aop02.xml,在配置IOC的基础上增加了aop:aspectj-autoproxy节点,Spring框架会自动为与AspectJ切面配置的Bean创建代理,proxy-target-class="true"属性表示被代理的目标对象是一个类,而非实现了接口的类,主要是为了选择不同的代理方式。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop02">
</context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
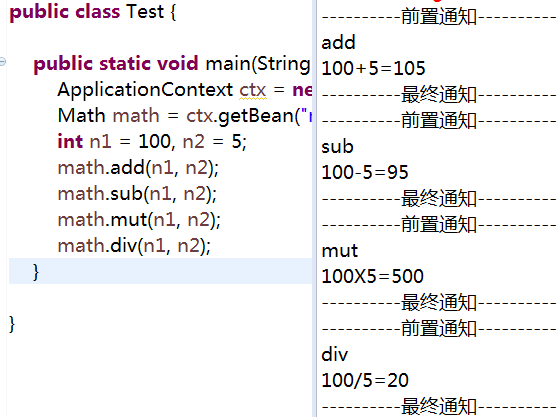
2.4、测试运行代码Test.java如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop02; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop02.xml");
Math math = ctx.getBean("math", Math.class);
int n1 = 100, n2 = 5;
math.add(n1, n2);
math.sub(n1, n2);
math.mut(n1, n2);
math.div(n1, n2);
} }
运行结果:
三、AspectJ切点函数
切点函数可以定位到准确的横切逻辑位置,在前面的示例中我们只使用过execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop02.Math.*(..)),execution就是一个切点函数,但该函数只什么方法一级,如果我们要织入的范围是类或某个注解则execution就不那么好用了,其实一共有9个切点函数,有不同的针对性。
@AspectJ使用AspectJ专门的切点表达式描述切面,Spring所支持的AspectJ表达式可分为四类:
方法切点函数:通过描述目标类方法信息定义连接点。
方法参数切点函数:通过描述目标类方法入参信息定义连接点。
目标类切点函数:通过描述目标类类型信息定义连接点。
代理类切点函数:通过描述代理类信息定义连接点。
常见的AspectJ表达式函数:
execution():满足匹配模式字符串的所有目标类方法的连接点
@annotation():任何标注了指定注解的目标方法链接点
args():目标类方法运行时参数的类型指定连接点
@args():目标类方法参数中是否有指定特定注解的连接点
within():匹配指定的包的所有连接点
target():匹配指定目标类的所有方法
@within():匹配目标对象拥有指定注解的类的所有方法
@target():匹配当前目标对象类型的执行方法,其中目标对象持有指定的注解
this():匹配当前AOP代理对象类型的所有执行方法
最常用的是:execution(<修饰符模式>?<返回类型模式><方法名模式>(<参数模式>)<异常模式>?)切点函数,可以满足多数需求。
为了展示各切点函数的功能现在新增一个类StrUtil,类如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("strUtil")
public class StrUtil {
public void show(){
System.out.println("Hello StrUtil!");
}
}
测试代码如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop03.xml");
IMath math = ctx.getBean("math", Math.class);
int n1 = 100, n2 = 5;
math.add(n1, n2);
math.sub(n1, n2);
math.mut(n1, n2);
math.div(n1, n2); StrUtil strUtil=ctx.getBean("strUtil",StrUtil.class);
strUtil.show();
} }
3.1、切点函数execution,通知与切面的定义如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 通知类,横切逻辑
*
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class Advices {
@Before("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03.Math.*(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------前置通知----------");
System.out.println(jp.getSignature().getName());
} //execution切点函数
//com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03包下所有类的所有方法被切入
@After("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03.*.*(..))")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}
}
运行结果如下:

execution(<修饰符模式>?<返回类型模式><方法名模式>(<参数模式>)<异常模式>?)
3.2、切点函数within
//within切点函数
//com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03包下所有类的所有方法被切入
@After("within(com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03.*)")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}

3.3、this切点函数
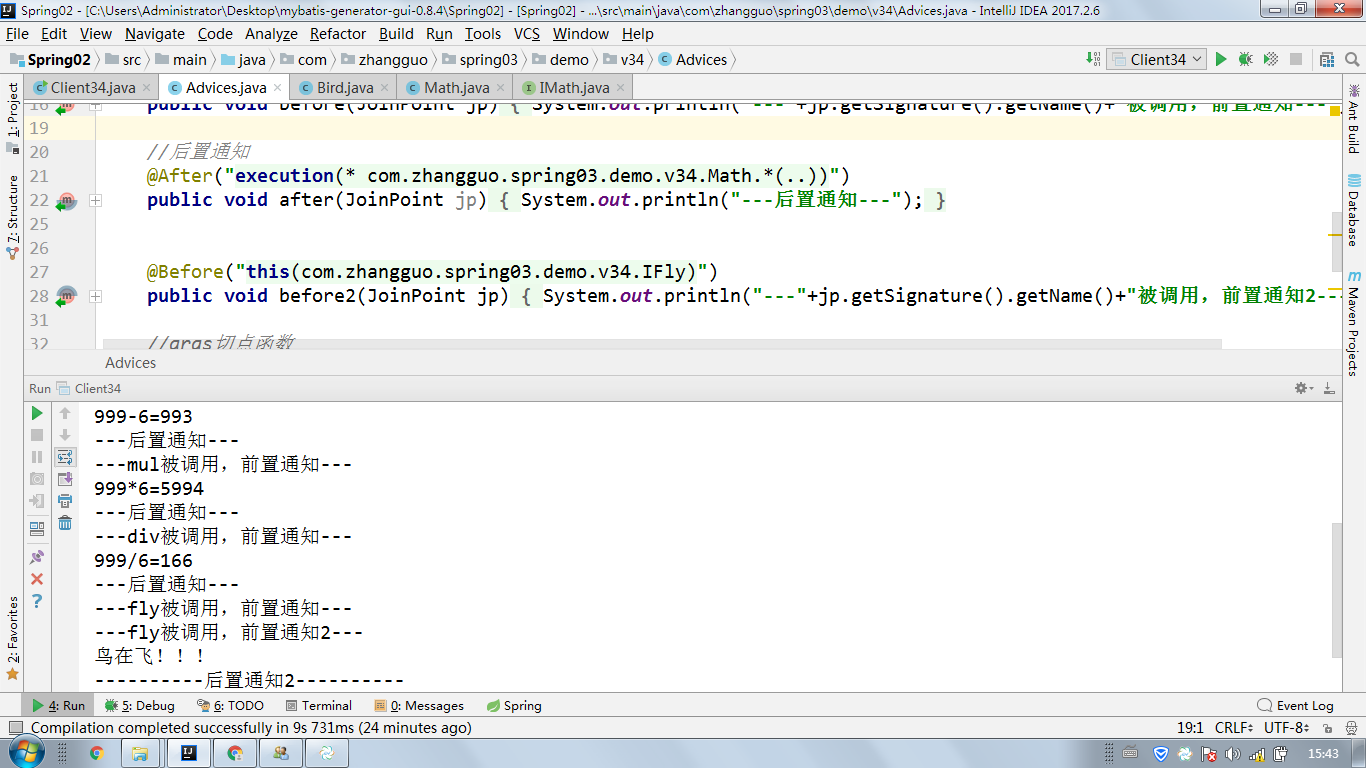
//this切点函数
//实现了IMath接口的代理对象的任意连接点
@After("this(com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03.IMath)")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}

3.4、args切点函数
//args切点函数
//要求方法有两个int类型的参考才会被织入横切逻辑
@After("args(int,int)")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}

如果参数类型不是基本数据类型则需要包名。
3.5、@annotation切点函数
先自定义一个可以注解在方法上的注解
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyAnno {
}
//@annotation切点函数
//要求方法必须被注解com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03.MyAnno才会被织入横切逻辑
@After("@annotation(com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03.MyAnno)")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop03;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("strUtil")
public class StrUtil {
@MyAnno
public void show(){
System.out.println("Hello StrUtil!");
}
}
运行结果:

其它带@的切点函数都是针对注解的
四、AspectJ通知注解
AspectJ通知注解共有6个,常用5个,引介少用一些。
先解决定义切点复用的问题,如下代码所示,切点函数的内容完全一样:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 通知类,横切逻辑
*
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class Advices {
@Before("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04.Math.*(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------前置通知----------");
System.out.println(jp.getSignature().getName());
} @After("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04.Math.*(..))")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}
}
可以先定义一个切点然后复用,如下所示:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 通知类,横切逻辑
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class Advices {
//切点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04.Math.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){
} @Before("pointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------前置通知----------");
System.out.println(jp.getSignature().getName());
} @After("pointcut()")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
}
}
修改Advices.java文件,增加各种通知类型如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /**
* 通知类,横切逻辑
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class Advices {
//切点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04.Math.a*(..))")
public void pointcut(){
} //前置通知
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println(jp.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("----------前置通知----------");
} //最终通知
@After("pointcut()")
public void after(JoinPoint jp){
System.out.println("----------最终通知----------");
} //环绕通知
@Around("execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04.Math.s*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println(pjp.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("----------环绕前置----------");
Object result=pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("----------环绕后置----------");
return result;
} //返回结果通知
@AfterReturning(pointcut="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04.Math.m*(..))",returning="result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint jp,Object result){
System.out.println(jp.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("结果是:"+result);
System.out.println("----------返回结果----------");
} //异常后通知
@AfterThrowing(pointcut="execution(* com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop04.Math.d*(..))",throwing="exp")
public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint jp,Exception exp){
System.out.println(jp.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("异常消息:"+exp.getMessage());
System.out.println("----------异常通知----------");
}
}
运行结果:

五、零配置实现Spring IoC与AOP
为了实现零配置在原有示例的基础上我们新增一个类User,如下所示:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop05;
public class User {
public void show(){
System.out.println("一个用户对象");
}
}
该类并未注解,容器不会自动管理。因为没有xml配置文件,则使用一个作为配置信息,ApplicationCfg.java文件如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop05; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; @Configuration //用于表示当前类为容器的配置类,类似<beans/>
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop05") //扫描的范围,相当于xml配置的结点<context:component-scan/>
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass=true) //自动代理,相当于<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
public class ApplicationCfg {
//在配置中声明一个bean,相当于<bean id=getUser class="com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop05.User"/>
@Bean
public User getUser(){
return new User();
}
}
该类的每一部分内容基本都与xml 配置有一对一的关系,请看注释,这样做要比写xml方便,但不便发布后修改。测试代码如下:
package com.zhangguo.Spring052.aop05; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过类初始化容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ApplicationCfg.class);
Math math = ctx.getBean("math", Math.class);
int n1 = 100, n2 = 0;
math.add(n1, n2);
math.sub(n1, n2);
math.mut(n1, n2);
try {
math.div(n1, n2);
} catch (Exception e) {
} User user=ctx.getBean("getUser",User.class);
user.show();
} }
advices.java 同上,没有任何变化,运行结果如下:

六、示例下载
七、视频
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av16071354/
Spring学习总结(三)——Spring实现AOP的多种方式的更多相关文章
- spring 学习(三):aop 学习
spring 学习(三):aop 学习 aop 概念 1 aop:面向切面(方面)编程,扩展功能不修改源代码实现 2 AOP采取横向抽取机制,取代了传统纵向继承体系重复性代码 3 aop底层使用动态代 ...
- MyEclipse Spring 学习总结三 SpringMVC
MyEclipse Spring 学习总结三 SpringMVC 一.SpringMVC原理 1.Springmvc 框架介绍 1)Spring 框架停工了构建Web应用程序的全功能MVC模块.Spr ...
- Spring学习1:Spring基本特性
http://longliqiang88.github.io/2015/08/14/Spring%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A01%EF%BC%9ASpring%E5%9F%BA%E6%9C%AC ...
- 【Spring学习笔记-MVC-3】SpringMVC返回Json数据-方式1
<Spring学习笔记-MVC>系列文章,讲解返回json数据的文章共有3篇,分别为: [Spring学习笔记-MVC-3]SpringMVC返回Json数据-方式1:http://www ...
- 【Spring学习笔记-MVC-4】SpringMVC返回Json数据-方式2
<Spring学习笔记-MVC>系列文章,讲解返回json数据的文章共有3篇,分别为: [Spring学习笔记-MVC-3]SpringMVC返回Json数据-方式1:http://www ...
- 深入浅出学习Spring框架(三):AOP 详解
AOP的英文解释——AOPAspect Oriented Programming面向切面编程.主要目的是通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态统一添加功能的一种技术. 在反 ...
- Spring学习4-面向切面(AOP)之Spring接口方式
一.初识AOP 关于AOP的学习可以参看帮助文档:spring-3.2.0.M2\docs\reference\html目录下index.html的相关章节 1.AOP:Aspect ...
- Spring学习总结(2)- AOP
一,什么是AOP AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术.AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中 ...
- Spring学习(三)——Spring中的依赖注入的方式
[前面的话] Spring对我太重要了,做个关于web相关的项目都要使用Spring,每次去看Spring相关的知识,总是感觉一知半解,没有很好的系统去学习一下,现在抽点时间学习一下Spring.不知 ...
- Spring学习8-Spring事务管理(AOP/声明式式事务管理)
一.基础知识普及 声明式事务的事务属性: 一:传播行为 二:隔离级别 三:只读提示 四:事务超时间隔 五:异常:指定除去RuntimeException其他回滚异常. 传播行为: 所谓事务的传播行为 ...
随机推荐
- PHP多文件上传(二维数组$_FILES('文件域的名称'),move_uploaded_file(‘临时文件名’,‘新的文件名’))
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- document.write 摘抄
页面载入过程中用实时脚本创建页面内容,以及用延时脚本创建本窗口或新窗口的内容.该方法需要一个字符串参数,它是写到窗口或框架中的HTML内容.这些字符串参数可以是变量或值为字符串的表达式,写入的内容常常 ...
- Centos普通用户提权至ROOT
1.利用/bin/ping的漏洞普通用户提权.(rws中的s) [root@localhost ~]# ls -l /bin/ping -rwsr-xr-x. root root 9月 /bin/pi ...
- jQuery Ready 与 Window onload 的区别(转)
“我们都知道,很多时候,在页面加载完后都需要做一些相应的初始化动作.例如,运行某些js特效,设置表单等等.怎么知道页面加载完了呢?一 般情况下都是设置body标签的onload监听window的loa ...
- SSTable 介绍(二)
作者:Jack47 上一篇SSTable 介绍(一)介绍了SSTable的适用场景和leveldb中SSTable的设计.本篇介绍SSTable文件的结构组成. SSTable的特点 首先明确一下上文 ...
- JavaScript思维导图—字符串函数
JavaScript思维导图-来自@王子墨http://julying.com/blog/the-features-of-javascript-language-summary-maps/
- [Unity3D入门]分享一个自制的入门级游戏项目"坦克狙击手"
[Unity3D入门]分享一个自制的入门级游戏项目"坦克狙击手" 我在学Unity3D,TankSniper(坦克狙击手)这个项目是用来练手的.游戏玩法来自这里(http://ww ...
- 人机大战之AlphaGo的硬件配置和算法研究
AlphaGo的硬件配置 最近AlphaGo与李世石的比赛如火如荼,关于第四盘李世石神之一手不在我们的讨论范围之内.我们重点讨论下AlphaGo的硬件配置: AlphaGo有多个版本,其中最强的是分布 ...
- java 堆栈分析2
有了mat.同时我们发现Java有提供jvisualvm, jvisualvm是一个不错的工具: heap dump . thread dump. cpu/mem profile 无所不能. 不过观察 ...
- Docker容器入门
为什么要看docker 从去年起就或多或少的接受了docker的熏陶,主要还是Infoq在去年有很多关于docker的实践视频讲座,记得有一篇是<Docker在雪球的技术实践>,当时听的也 ...
