用tensorflow实现SVM
环境配置
win10
Python 3.6
tensorflow1.15
scipy
matplotlib (运行时可能会遇到module tkinter的问题)
sklearn 一个基于Python的第三方模块。sklearn库集成了一些常用的机器学习方法。
代码实现
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph() sess = tf.Session()
Session是tensorflow中的一个执行OP和计算tensor的一个类。
补充:
- 张量(tensor):TensorFlow程序使用tensor数据结构来代表所有的数据,计算图中,操作间传递的数据都是tensor,你可以把TensorFlow tensor看做一个n维的数组或者列表。
- 变量(Variable):常用于定义模型中的参数,是通过不断训练得到的值。比如权重和偏置。
- 占位符(placeholder):输入变量的载体。也可以理解成定义函数时的参数。
- 图中的节点操作(op):一个op获得0个或者多个Tensor,执行计算,产生0个或者多个Tensor。op是描述张量中的运算关系,是网络中真正结构。
# Load the data
# 加载iris数据集并为每类分离目标值。
# 因为我们想绘制结果图,所以只使用花萼长度和花瓣宽度两个特征。
# 为了便于绘图,也会分离x值和y值
# iris.data = [(Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width)]
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x_vals = np.array([[x[0], x[3]] for x in iris.data])
y_vals1 = np.array([1 if y==0 else -1 for y in iris.target])
y_vals2 = np.array([1 if y==1 else -1 for y in iris.target])
y_vals3 = np.array([1 if y==2 else -1 for y in iris.target])
y_vals = np.array([y_vals1, y_vals2, y_vals3])
#取前两项作为图的横纵坐标
class1_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==0]
class1_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==0]
class2_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==1]
class2_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==1]
class3_x = [x[0] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==2]
class3_y = [x[1] for i,x in enumerate(x_vals) if iris.target[i]==2]
datasets是sklearn中的 一个包,提供了一些经典的数据集以作模型的运算。
特征存储在iris.data中,标签存储在iris.target中
# Declare batch size
# 变量的最高维度
batch_size = 50 # Initialize placeholders
# 数据集的维度在变化,从单类目标分类到三类目标分类。
# 我们将利用矩阵传播和reshape技术一次性计算所有的三类SVM。
# 注意,由于一次性计算所有分类,
# y_target占位符的维度是[3,None],模型变量b初始化大小为[3,batch_size]
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[3, None], dtype=tf.float32)
prediction_grid = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 2], dtype=tf.float32) # Create variables for svm
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[3,batch_size])) # Gaussian (RBF) kernel 核函数只依赖x_data
gamma = tf.constant(-10.0)
#dist = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1)
#dist = tf.reshape(dist, [-1,1])
sq_dists = tf.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(x_data))) my_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(sq_dists)))
tf.placeholder()--占位符相当于预先分配
reduce()--减小矩阵维数,求和
reshape--重新构造矩阵
注:
multiply--实现元素相乘,相同位置的元素相乘
matmul--实现矩阵相乘
Python 矩阵传播--Python为优化矩阵计算的一系列方法
高斯核函数
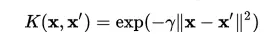
# Declare function to do reshape/batch multiplication
# 最大的变化是批量矩阵乘法。
# 最终的结果是三维矩阵,并且需要传播矩阵乘法。
# 所以数据矩阵和目标矩阵需要预处理,比如xT·x操作需额外增加一个维度。
# 这里创建一个函数来扩展矩阵维度,然后进行矩阵转置,
# 接着调用TensorFlow的tf.batch_matmul()函数
# 转置后的矩阵与原矩阵相乘(增维可能是为了消除参数项中的常数项)
def reshape_matmul(mat):
v1 = tf.expand_dims(mat, 1)
v2 = tf.reshape(v1, [3, batch_size, 1])
return(tf.matmul(v2, v1)) # Compute SVM Model 计算对偶损失函数
first_term = tf.reduce_sum(b)
b_vec_cross = tf.matmul(tf.transpose(b), b)
y_target_cross = reshape_matmul(y_target) second_term = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(my_kernel, tf.multiply(b_vec_cross, y_target_cross)),[1,2])
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.negative(tf.subtract(first_term, second_term)))
# Gaussian (RBF) prediction kernel
# 现在创建预测核函数。
# 要当心reduce_sum()函数,这里我们并不想聚合三个SVM预测,
# 所以需要通过第二个参数告诉TensorFlow求和哪几个
rA = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_data), 1),[-1,1])
rB = tf.reshape(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(prediction_grid), 1),[-1,1])
pred_sq_dist = tf.add(tf.subtract(rA, tf.multiply(2., tf.matmul(x_data, tf.transpose(prediction_grid)))), tf.transpose(rB))
pred_kernel = tf.exp(tf.multiply(gamma, tf.abs(pred_sq_dist))) # 实现预测核函数后,我们创建预测函数。
# 与二类不同的是,不再对模型输出进行sign()运算。
# 因为这里实现的是一对多方法,所以预测值是分类器有最大返回值的类别。
# 使用TensorFlow的内建函数argmax()来实现该功能
prediction_output = tf.matmul(tf.multiply(y_target,b), pred_kernel)
prediction = tf.arg_max(prediction_output-tf.expand_dims(tf.reduce_mean(prediction_output,1), 1), 0)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(prediction, tf.argmax(y_target,0)), tf.float32)) # Declare optimizer
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss) # Initialize variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# Save graph
write_log = tf.summary.FileWriter('./log',tf.get_default_graph()) # Training loop
loss_vec = []
batch_accuracy = []
for i in range(100):
#取随机数训练模型
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), size=batch_size)
rand_x = x_vals[rand_index]
rand_y = y_vals[:,rand_index]
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
loss_vec.append(temp_loss) acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x,
y_target: rand_y,
prediction_grid:rand_x})
batch_accuracy.append(acc_temp) if (i+1)%25==0:
print('Step #' + str(i+1))
print('Loss = ' + str(temp_loss)) # 创建数据点的预测网格,运行预测函数
x_min, x_max = x_vals[:, 0].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = x_vals[:, 1].min() - 1, x_vals[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))
grid_points = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
grid_predictions = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x,
y_target: rand_y,
prediction_grid: grid_points})
grid_predictions = grid_predictions.reshape(xx.shape)
# 测试random.choice程序
import numpy as np
x=np.array([[0,1],[1,2],[2,3]])
randx=np.random.choice(len(x), size=3)
print(x)
#print('\n')
print(randx)
print(x[randx])
#print(x[:,randx])
print(len(x))


用tensorflow实现SVM的更多相关文章
- SVM原理以及Tensorflow 实现SVM分类(附代码)
1.1. SVM介绍 1.2. 工作原理 1.2.1. 几何间隔和函数间隔 1.2.2. 最大化间隔 - 1.2.2.0.0.1. \(L( {x}^*)\)对$ {x}^*$求导为0 - 1.2.2 ...
- 用 TensorFlow 实现 SVM 分类问题
这篇文章解释了底部链接的代码. 问题描述  如上图所示,有一些点位于单位正方形内,并做好了标记.要求找到一条线,作为分类的标准.这些点的数据在 inearly_separable_data.csv ...
- tensorflow实现svm多分类 iris 3分类——本质上在使用梯度下降法求解线性回归(loss是定制的而已)
# Multi-class (Nonlinear) SVM Example # # This function wll illustrate how to # implement the gaussi ...
- tensorflow实现svm iris二分类——本质上在使用梯度下降法求解线性回归(loss是定制的而已)
iris二分类 # Linear Support Vector Machine: Soft Margin # ---------------------------------- # # This f ...
- 卷积神经网络提取特征并用于SVM
模式识别课程的一次作业.其目标是对UCI的手写数字数据集进行识别,样本数量大约是1600个.图片大小为16x16.要求必须使用SVM作为二分类的分类器. 本文重点是如何使用卷积神经网络(CNN)来提取 ...
- Tensorflow tflearn 编写RCNN
两周多的努力总算写出了RCNN的代码,这段代码非常有意思,并且还顺带复习了几个Tensorflow应用方面的知识点,故特此总结下,带大家分享下经验.理论方面,RCNN的理论教程颇多,这里我不在做详尽说 ...
- 学习笔记TF052:卷积网络,神经网络发展,AlexNet的TensorFlow实现
卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network,CNN),权值共享(weight sharing)网络结构降低模型复杂度,减少权值数量,是语音分析.图像识别热点.无须人工特征提 ...
- TensorFlow 实战之实现卷积神经网络
本文根据最近学习TensorFlow书籍网络文章的情况,特将一些学习心得做了总结,详情如下.如有不当之处,请各位大拿多多指点,在此谢过. 一.相关性概念 1.卷积神经网络(ConvolutionNeu ...
- 从感知机到 SVM,再到深度学习(三)
这篇博文详细分析了前馈神经网络的内容,它对应的函数,优化过程等等. 在上一篇博文中已经完整讲述了 SVM 的思想和原理.讲到了想用一个高度非线性的曲线作为拟合曲线.比如这个曲线可以是: ...
随机推荐
- FMZ发明者量化平台回测机制说明
原文连接:https://www.fmz.com/digest-topic/4009 大部分策略在实盘之前都需要回测进行验证,FMZ支持部分品种数字货币现货.期货和永续合约,以及商品期货所有品种.但发 ...
- sql注入01
1.SLQ:操作数据 数据库结构 create/drop database create/alter/drop table 数据库内容 insert values语句 insert into tabl ...
- javascript一些实用的方法
判断数据类型 function isType(type) { return function(obj) { return {}.toString.call(obj) == "[object ...
- jQuery UI Widget(1.8.1)工作原理
/*! * jQuery UI Widget 1.8.1 * * Copyright (c) 2010 AUTHORS.txt (http://jqueryui.com/about) * Dual l ...
- mybatis+mysql insert添加数据后返回数据主键id
1.根据useGeneratedKeys获取返回值,部分数据库不支持 修改mybatis xml <insert id="insertUser" useGeneratedKe ...
- 自己动手写一个服务网关-java
自己动手写一个服务网关 原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/bigben0123/p/9252444.html 引言 什么是网关?为什么需要使用网关? 如图所示,在不使用网关的情 ...
- 大数据学习笔记【一】:Hadoop-3.1.2完全分布式环境搭建(Windows 10)
一.前言 Hadoop原理架构本人就不在此赘述了,可以自行百度,本文仅介绍Hadoop-3.1.2完全分布式环境搭建(本人使用三个虚拟机搭建). 首先,步骤: ① 准备安装包和工具: hadoop-3 ...
- # 双值Hash
双值Hash 简单介绍 Hash的应用:Hash其实就像一个加密过程,很多加密算法都会用到Hash,像GitHub中生成的token值也是Hash的结果. Hash冲突:简单来说就是不同的数映射到了同 ...
- 使用rsync工具构建php项目管理平台
对于phper来说部署项目和更新项目是很方便的,只要直接将写好的项目覆盖到项目的根目录就可以啦.但是平时项目开发的时候肯定不是只部署一个环境,一般是三套环境(开发环境.测试环境.生产环境),我们每次在 ...
- MySQL反应慢排查思路
数据库异常假死排查需要数据(当时问题的时间,前后时间在2个小时的数据就行) 1.MySQL相关配置 整体可以借助于pt-mysql-summary生成(percona-tools工具) 2.操作系统方 ...
