机器学习: Tensor Flow +CNN 做笑脸识别
Tensor Flow 是一个采用数据流图(data flow graphs),用于数值计算的开源软件库。节点(Nodes)在图中表示数学操作,图中的线(edges)则表示在节点间相互联系的多维数据数组,即张量(tensor)。
这是谷歌开源的一个强大的做深度学习的软件库,提供了C++ 和 Python 接口,下面给出用Tensor Flow 建立CNN 网络做笑脸识别的一个简单用例。
我们用到的数据库是GENKI4K,这个数据库有4000张图像,首先做人脸检测与剪切,将图像resize到 64×64 的大小,然后用一个 CNN 网络做识别。
网络的基本结构如下:
input -> conv 1 -> pool 1 -> conv 2 -> pool 2 -> conv 3 -> pool 3 -> fc 1 -> out
input -> 64×64
conv 1 -> filter size: 5×5, output: 60×60
pool 1 -> filter size: 2×2, output: 30×30
conv 2 -> filter size: 7×7, output: 24×24
pool 2 -> filter size: 2×2, output: 12×12
conv 3 -> filter size: 5×5, output: 8×8
pool 3 -> filter size: 2×2, output: 4×4
fc 1 -> hidden nodes: 100, output: 1×100
out -> 1×2
import string, os, sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.io
import random
import tensorflow as tf
# set the folder path
dir_name = 'GENKI4K/Feature_Data'
# set the file path
files = os.listdir(dir_name)
for f in files:
print (dir_name + os.sep + f)
file_path = dir_name + os.sep + files[10]
# get the data
dic_mat = scipy.io.loadmat(file_path)
data_mat = dic_mat['Face_64']
file_path2 = dir_name + os.sep + files[15]
dic_label = scipy.io.loadmat(file_path2)
label_mat = dic_label['Label']
file_path3 = dir_name + os.sep+files[16]
# get the label
label = label_mat.ravel()
label_y = np.zeros((4000, 2))
label_y[:, 0] = label
label_y[:, 1] = 1-label
T_ind=random.sample(range(0, 4000), 4000)
# Parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
batch_size = 40
batch_num=4000/batch_size
train_epoch=100
# Network Parameters
n_input = 4096 # data input (img shape: 64*64)
n_classes = 2 # total classes (smile & non-smile)
dropout = 0.5 # Dropout, probability to keep units
# tf Graph input
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_classes])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) #dropout (keep probability)
# Create some wrappers for simplicity
def conv2d(x, W, b, strides=1):
# Conv2D wrapper, with bias and relu activation
x = tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, strides, strides, 1], padding='VALID')
x = tf.nn.bias_add(x, b)
return tf.nn.relu(x)
def maxpool2d(x, k=2):
# MaxPool2D wrapper
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, k, k, 1], strides=[1, k, k, 1],
padding='VALID')
# Create model
def conv_net(x, weights, biases, dropout):
# Reshape input picture
x = tf.reshape(x, shape=[-1, 64, 64, 1])
# Convolution Layer
conv1 = conv2d(x, weights['wc1'], biases['bc1'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
conv1 = maxpool2d(conv1, k=2)
# Convolution Layer
conv2 = conv2d(conv1, weights['wc2'], biases['bc2'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
conv2 = maxpool2d(conv2, k=2)
# Convolution Layer
conv3 = conv2d(conv2, weights['wc3'], biases['bc3'])
# Max Pooling (down-sampling)
conv3 = maxpool2d(conv3, k=2)
# Fully connected layer
# Reshape conv2 output to fit fully connected layer input
fc1 = tf.reshape(conv3, [-1, weights['wd1'].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
fc1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['wd1']), biases['bd1'])
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(fc1)
# Apply Dropout
# fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1, dropout)
# Output, class prediction
out = tf.add(tf.matmul(fc1, weights['out']), biases['out'])
return out
# Store layers weight & bias
weights = {
# 5x5 conv, 1 input, 16 outputs
'wc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 1, 16])),
# 7x7 conv, 16 inputs, 8 outputs
'wc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7, 7, 16, 8])),
# 5x5 conv, 8 inputs, 16 outputs
'wc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5, 5, 8, 16])),
# fully connected, 7*7*64 inputs, 1024 outputs
'wd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([4*4*16, 100])),
# 1024 inputs, 10 outputs (class prediction)
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([100, n_classes]))
}
biases = {
'bc1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([16])),
'bc2': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([8])),
'bc3': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([16])),
'bd1': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([100])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
}
# Construct model
pred = conv_net(x, weights, biases, keep_prob)
# Define loss and optimizer
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred, y))
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# Evaluate model
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
# Initializing the variables
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(0, train_epoch):
for batch in range (0, batch_num):
arr_3 = T_ind[batch * batch_size:(batch + 1) * batch_size]
batch_x = data_mat[arr_3, :]
batch_y = label_y[arr_3, :]
# Run optimization op (backprop)
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y,
keep_prob: dropout})
# Calculate loss and accuracy
loss, acc = sess.run([cost, accuracy], feed_dict={x: data_mat,
y: label_y,
keep_prob: 1.})
print("Epoch: " + str(epoch) + ", Loss= " + \
"{:.3f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " + \
"{:.3f}".format(acc))
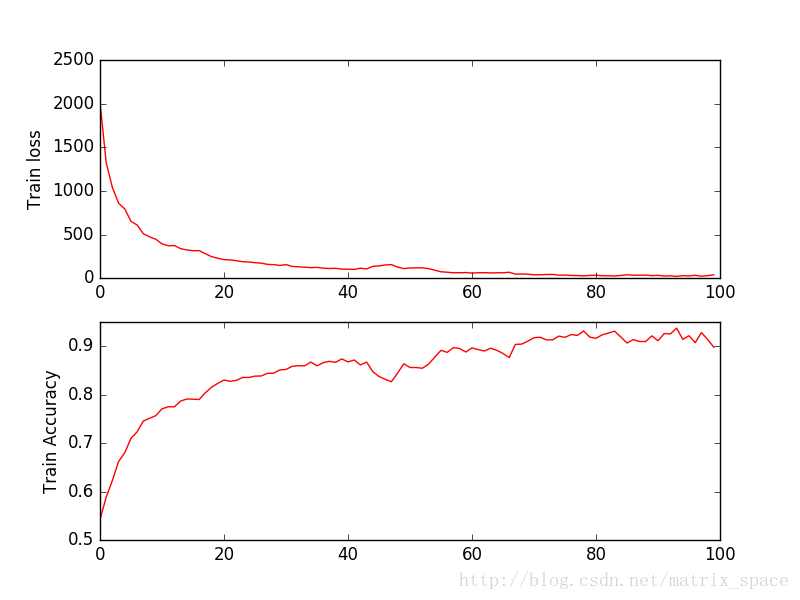
100个训练周期的结果:
机器学习: Tensor Flow +CNN 做笑脸识别的更多相关文章
- 机器学习: Tensor Flow with CNN 做表情识别
我们利用 TensorFlow 构造 CNN 做表情识别,我们用的是FER-2013 这个数据库, 这个数据库一共有 35887 张人脸图像,这里只是做一个简单到仿真实验,为了计算方便,我们用其中到 ...
- 机器学习:scikit-learn 做笑脸识别 (SVM, KNN, Logisitc regression)
scikit-learn 是 Python 非常强大的一个做机器学习的包,今天介绍scikit-learn 里几个常用的分类器 SVM, KNN 和 logistic regression,用来做笑脸 ...
- 使用CNN做数字识别和人脸识别
上次写的一层神经网络也都贴这里了. 我有点困,我先睡觉,完了我再修改 这个代码写法不太符合工业代码的规范,仅仅是用来学习的的.还望各位见谅 import sys,ossys.path.append(o ...
- 机器学习: TensorFlow with MLP 笑脸识别
Tensor Flow 是一个采用数据流图(data flow graphs),用于数值计算的开源软件库.节点(Nodes)在图中表示数学操作,图中的线(edges)则表示在节点间相互联系的多维数据数 ...
- AI从入门到放弃:CNN的导火索,用MLP做图像分类识别?
欢迎大家前往腾讯云+社区,获取更多腾讯海量技术实践干货哦~ 作者:郑善友 腾讯MIG后台开发工程师 导语:在没有CNN以及更先进的神经网络的时代,朴素的想法是用多层感知机(MLP)做图片分类的识别:但 ...
- UWP通过机器学习加载ONNX进行表情识别
首先我们先来说说这个ONNX ONNX是一种针对机器学习所设计的开放式的文件格式,用于存储训练好的模型.它使得不同的人工智能框架(如Pytorch, MXNet)可以采用相同格式存储模型数据并交互. ...
- swift通过摄像头读取每一帧的图片,并且做识别做人脸识别
最近帮别人做一个项目,主要是使用摄像头做人脸识别 github地址:https://github.com/qugang/AVCaptureVideoTemplate 要使用IOS的摄像头,需要使用AV ...
- CNN做序列标注问题(tensorflow)
一.搭建简单的CNN做序列标注代码 import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt TIME_ST ...
- ubuntu 安装(install) pwntcha[一个做"验证码识别"的开源程序]
一.安装 1. sudo apt-get install libsdl1.2-dev libsdl1.2debian sudo apt-get install libsdl1.2-dev(比较大,10 ...
随机推荐
- CSDN日报20170406 ——《代码非常烂,所以离职。》
[程序人生]代码非常烂.所以离职? 作者:stormzhang 我在面试的时候一般会问这么一个问题:你为什么离职? 当中有不少同学会提到这么一个原因.现在的项目代码太烂了,前人留下了非常多坑,我实在忍 ...
- 结合Wireshark捕获分组深入理解TCP/IP协议栈之TCP协议(TCP报文格式+三次握手实例)
摘要: 本文简单介绍了TCP面向连接理论知识,详细讲述了TCP报文各个字段含义,并从Wireshark俘获分组中选取TCP连接建立相关报文段进行分析. 一.概述 TCP是面向连接的可靠 ...
- 【z08】乌龟棋
描述 小明过生日的时候,爸爸送给他一副乌龟棋当作礼物. 乌龟棋的棋盘是一行N个格子,每个格子上一个分数(非负整数).棋盘第1格是唯一的起点,第N格是终点,游戏要求玩家控制一个乌龟棋子从起点出发走到终点 ...
- Oracle学习(六):子查询
1.知识点:能够对比以下的录屏进行阅读 SQL> --子查询所要解决的问题:问题不能一步求解 SQL> --查询工资比SCOTT高的员工信息 SQL> --(1)使用普通方法 SQL ...
- swift学习第十三天:类的构造函数
类的构造函数 构造函数的介绍 构造函数类似于OC中的初始化方法:init方法 默认情况下载创建一个类时,必然会调用一个构造函数 即便是没有编写任何构造函数,编译器也会提供一个默认的构造函数. 如果是继 ...
- Node.js v10.1.0 Documentation
Modules Stable 在 Node.js 模块系统中,每个文件都会被当做一个独立的模块.假设有一个名为 foo.js: const circle = require('./circle.js' ...
- 那些移动端web踩过的坑
原文链接:https://geniuspeng.github.io/2017/08/24/mobile-issues/ 扔了N久,还是捡回来了.好好弄一下吧.刚工作的时候挺忙的,后来不那么忙了,但是变 ...
- PHP+Aax实现异步验证
利用Ajax技术来检测用户名是否存在的原理流程图: 最终结果截图: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional/ ...
- 【C++竞赛 H】The sum problem
Time Limit: 1s Memory Limit: 32MB 问题描述 Given a sequence 1,2,3,-,N, your job is to calculate the numb ...
- 利用C#与AE调用GP工具
转自原文 利用C#与AE调用GP工具 第一,首先要明确自己需要调用arctoolbox里面的什么工具,实现什么样的功能. 第三,编写command或tool工具,编写自己要的功能工具. 1)首先创建一 ...