why’s kafka so fast
As we all know that Kafka is very fast, much faster than most of its competitors. So what’s the reason here?
Avoid Random Disk Access
Kafka writes everything onto the disk in order and consumers fetch data in order too. So disk access always works sequentially instead of randomly. For traditional hard disks(HDD), sequential access is much faster than random access. Here is a comparison:
| hardware | sequential writes | random writes |
|---|---|---|
| 6 * 7200rpm SATA RAID-5 | 300MB/s | 50KB/s |
Kafka Writes Everything Onto The Disk Instead of Memory
Yes, you read that right. Kafka writes everything onto the disk instead of memory. But wait a moment, isn’t memory supposed to be faster than disks? Typically it’s the case, for Random Disk Access. But for sequential access, the difference is much smaller. Here is a comparison taken from https://queue.acm.org/detail.cfm?id=1563874.

As you can see, it’s not that different. But still, sequential memory access is faster than Sequential Disk Access, why not choose memory? Because Kafka runs on top of JVM, which gives us two disadvantages.
1.The memory overhead of objects is very high, often doubling the size of the data stored(or even higher).
2.Garbage Collection happens every now and then, so creating objects in memory is very expensive as in-heap data increases because we will need more time to collect unused data(which is garbage).
So writing to file systems may be better than writing to memory. Even better, we can utilize MMAP(memory mapped files) to make it faster.
Memory Mapped Files(MMAP)
Basically, MMAP(Memory Mapped Files) can map the file contents from the disk into memory. And when we write something into the mapped memory, the OS will flush the change onto the disk sometime later. So everything is faster because we are using memory actually, but in an indirect way. So here comes the question. Why would we use MMAP to write data onto disks, which later will be mapped into memory? It seems to be a roundabout route. Why not just write data into memory directly? As we have learned previously, Kafka runs on top of JVM, if we wrote data into memory directly, the memory overhead would be high and GC would happen frequently. So we use MMAP here to avoid the issue.
Zero Copy
Suppose that we are fetching data from the memory and sending them to the Internet. What is happening in the process is usually twofold.
1.To fetch data from the memory, we need to copy those data from the Kernel Context into the Application Context.
2.To send those data to the Internet, we need to copy the data from the Application Context into the Kernel Context.
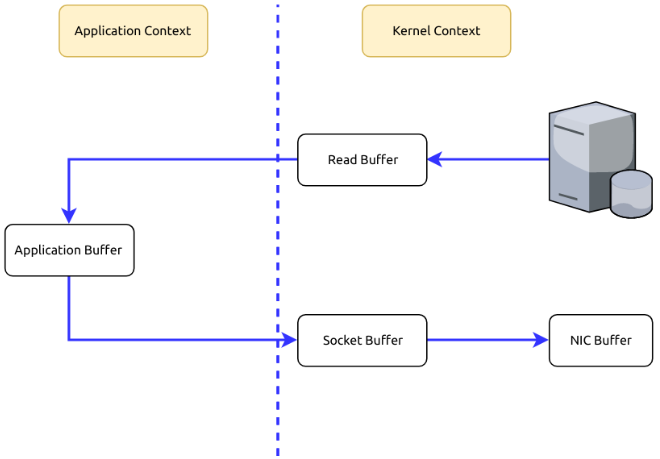
As you can see, it’s redundant to copy data between the Kernel Context and the Application Context. Can we avoid it? Yes, using Zero Copy we can copy data directly from the Kernel Context to the Kernel Context.

Batch Data
Kafka only sends data when batch.size is reached instead of one by one. Assuming the bandwidth is 10MB/s, sending 10MB data in one go is much faster than sending 10000 messages one by one(assuming each message takes 100 bytes).
"I would be fine and made no troubles."
why’s kafka so fast的更多相关文章
- Apache Kafka for Item Setup
At Walmart.com in the U.S. and at Walmart's 11 other websites around the world, we provide seamless ...
- Apache Kafka - Schema Registry
关于我们为什么需要Schema Registry? 参考, https://www.confluent.io/blog/how-i-learned-to-stop-worrying-and-love- ...
- Understanding, Operating and Monitoring Apache Kafka
Apache Kafka is an attractive service because it's conceptually simple and powerful. It's easy to un ...
- Build an ETL Pipeline With Kafka Connect via JDBC Connectors
This article is an in-depth tutorial for using Kafka to move data from PostgreSQL to Hadoop HDFS via ...
- How to choose the number of topics/partitions in a Kafka cluster?
This is a common question asked by many Kafka users. The goal of this post is to explain a few impor ...
- kafka producer源码
producer接口: /** * Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more * contributor l ...
- Flume-ng+Kafka+storm的学习笔记
Flume-ng Flume是一个分布式.可靠.和高可用的海量日志采集.聚合和传输的系统. Flume的文档可以看http://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html ...
- Apache Kafka: Next Generation Distributed Messaging System---reference
Introduction Apache Kafka is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system. It was originally dev ...
- Exploring Message Brokers: RabbitMQ, Kafka, ActiveMQ, and Kestrel--reference
[This article was originally written by Yves Trudeau.] http://java.dzone.com/articles/exploring-mess ...
随机推荐
- SpringCloud的阿里巴巴相关开源组件
Sentinel 阿里巴巴开源产品,把流量作为切入点,从流量控制.熔断降级.系统负载保护等多个维度保护服务的稳定性. Nacos 阿里巴巴开源产品,一个更易于构建云原生应用的动态服务发现.配置管理和服 ...
- Git上传到码云及其常见问题详解
1.git init 初始化 2.git remote origin add https://gitee.com/su_yong_qing/SyqSystem.git 这里注意把链接替换为自己的仓库 ...
- ios路线
http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20150303/11218.html
- PMP备考-第一章-引论
项目 项目是为创造独特的产品,服务和成果而进行的临时性工作.在规定的范围,进度,成本,和质量要求之下完成项目可交付成果. 项目与运用 项目 :临时性,独特性,渐进明细 运营 :持续的,相似性,标准化 ...
- leetcode - 括号字符串是否有效
括号字符串是否有效 给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效. 有效字符串需满足: 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合. 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合. ...
- 利用Python调用pastebin.com API自动创建paste
在上一篇文章中,已经实现了模拟pastebin.com的账号登录,并且获取了api_dev_key,这一篇文章主要讲一下调用API创建paste 登录之后,进入API页面,发现网站已经提供了几个API ...
- Oracle使用命令行登录提示ERROR: ORA-01017: invalid username/password; logon denied
刚在Windows上面安装好Oracle 10g,刚开始使用PLSQLDevelop软件登录提示 not logged on ,然后使用命令行登录提示 ERROR: ORA-01017: inval ...
- Linux目录管理
Linux文件目录管理 1:目录管理 1)切换目录 # cd [ 目录名称] 2)退到上一目录 # cd .. 2:创建目录 mkdir [文件名称] mkdir -p [文件名称] 递归创建目 ...
- 201871010133 赵永军《面向对象程序设计(java)》第六、七周学习总结
201871010133 赵永军<面向对象程序设计(java)>第六.七周学习总结 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ ...
- hbase链接失败
https://blog.csdn.net/u010886217/article/details/84444046
