leveldb 学习记录(四) skiplist补与变长数字
在leveldb 学习记录(一) skiplist 已经将skiplist的插入 查找等操作流程用图示说明
这里在介绍 下skiplist的代码
里面有几个模块
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
class SkipList {......}
class Arena;(内存池模块 暂时不介绍)
struct Node;(节点 存储key 和指向其他Node的指针)
//Node 构造函数 KEY赋值
// Implementation details follow
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { } Key const key; // Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
// 访问修改器使用 包装在方法中 可以使用内存屏障
// Node指向的另一层?
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
}
//设置下层Node指向
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].Release_Store(x);
} // No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
// 读取本Node在N层的NODE指向 非内存屏蔽操作
Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
assert(n >= 0);
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
} //设置Node 在N层的Node指向 非内存屏蔽操作
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= 0);
next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
} private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
// 原子指针数组 指向其他Node 创建时候动态确认数组长度
port::AtomicPointer next_[1];
};
结构示意图如下
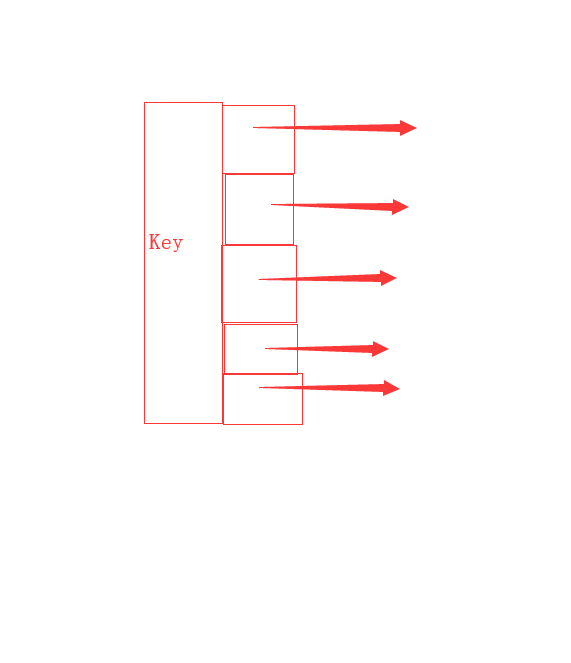
其他操作可参见系列文章一
最后附上我注释的代码
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "port/port.h"
#include "util/arena.h"
#include "util/random.h" namespace leveldb { class Arena; template<typename Key, class Comparator>
class SkipList {
private:
struct Node; public:
// Create a new SkipList object that will use "cmp" for comparing keys,
// and will allocate memory using "*arena". Objects allocated in the arena
// must remain allocated for the lifetime of the skiplist object.
explicit SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena); // Insert key into the list.
// REQUIRES: nothing that compares equal to key is currently in the list.
void Insert(const Key& key); // Returns true iff an entry that compares equal to key is in the list.
bool Contains(const Key& key) const; // Iteration over the contents of a skip list
class Iterator {
public:
// Initialize an iterator over the specified list.
// The returned iterator is not valid.
explicit Iterator(const SkipList* list); // Returns true iff the iterator is positioned at a valid node.
bool Valid() const; // Returns the key at the current position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
const Key& key() const; // Advances to the next position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
void Next(); // Advances to the previous position.
// REQUIRES: Valid()
void Prev(); // Advance to the first entry with a key >= target
void Seek(const Key& target); // Position at the first entry in list.
// Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
void SeekToFirst(); // Position at the last entry in list.
// Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
void SeekToLast(); private:
const SkipList* list_;
Node* node_;
// Intentionally copyable
}; private:
enum { kMaxHeight = }; // Immutable after construction
Comparator const compare_;
Arena* const arena_; // Arena used for allocations of nodes Node* const head_; // Modified only by Insert(). Read racily by readers, but stale
// values are ok.
port::AtomicPointer max_height_; // Height of the entire list inline int GetMaxHeight() const {
return reinterpret_cast<intptr_t>(max_height_.NoBarrier_Load());
} // Read/written only by Insert().
Random rnd_; Node* NewNode(const Key& key, int height);
int RandomHeight();
bool Equal(const Key& a, const Key& b) const { return (compare_(a, b) == ); } // Return true if key is greater than the data stored in "n"
bool KeyIsAfterNode(const Key& key, Node* n) const; // Return the earliest node that comes at or after key.
// Return NULL if there is no such node.
//
// If prev is non-NULL, fills prev[level] with pointer to previous
// node at "level" for every level in [0..max_height_-1].
Node* FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev) const; // Return the latest node with a key < key.
// Return head_ if there is no such node.
Node* FindLessThan(const Key& key) const; // Return the last node in the list.
// Return head_ if list is empty.
Node* FindLast() const; // No copying allowed
SkipList(const SkipList&);
void operator=(const SkipList&);
}; //Node 构造函数 KEY赋值
// Implementation details follow
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
struct SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node {
explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { } Key const key; // Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
// add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
// 访问修改器使用 包装在方法中 可以使用内存屏障
// Node指向的另一层?
Node* Next(int n) {
assert(n >= );
// Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
// version of the returned Node.
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
}
//设置下层Node指向
void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= );
// Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
// pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
next_[n].Release_Store(x);
} // No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
// 读取本Node在N层的NODE指向 非内存屏蔽操作
Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
assert(n >= );
return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
} //设置Node 在N层的Node指向 非内存屏蔽操作
void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
assert(n >= );
next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
} private:
// Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
// 原子指针数组 指向其他Node 创建时候动态确认数组长度
port::AtomicPointer next_[];
}; //创建一个NODE 内存池arena_分配内存 height确认该NODE的Node指向数量
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::NewNode(const Key& key, int height) {
char* mem = arena_->AllocateAligned(
sizeof(Node) + sizeof(port::AtomicPointer) * (height - ));
return new (mem) Node(key);
} //根据输入的SkipList指针构造一个 iterator
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Iterator(const SkipList* list) {
list_ = list;
node_ = NULL;
} //
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Valid() const {
return node_ != NULL;
} //返回iterator指向的Node的key
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline const Key& SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::key() const {
assert(Valid());
return node_->key;
} //获取iterator指向的下一个node 在第0层获取(Node第0层均有记录)
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Next() {
assert(Valid());
node_ = node_->Next();
} //寻找该node上一个node
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Prev() {
// Instead of using explicit "prev" links, we just search for the
// last node that falls before key.
assert(Valid());
node_ = list_->FindLessThan(node_->key);
if (node_ == list_->head_) {
node_ = NULL;
}
} //调用 FindGreaterOrEqual 查找
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Seek(const Key& target) {
node_ = list_->FindGreaterOrEqual(target, NULL);
} //重置到head Node 第0层 第一个Node
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::SeekToFirst() {
node_ = list_->head_->Next();
} //重置到last Node
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::SeekToLast() {
node_ = list_->FindLast();
if (node_ == list_->head_) {
node_ = NULL;
}
} //返回height 随机增加1
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
int SkipList<Key,Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
// Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
static const unsigned int kBranching = ;
int height = ;
while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == )) {
height++;
}
assert(height > );
assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
return height;
} //调用 cmp 比较是大小
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::KeyIsAfterNode(const Key& key, Node* n) const {
// NULL n is considered infinite
return (n != NULL) && (compare_(n->key, key) < );
} //寻找比key大或者等于的Node
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev)
const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - ;
// k在Next后面 则在本level寻找 否则 在下一层level寻找
while (true) {
Node* next = x->(level);
if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
// Keep searching in this list
x = next;
} else {
if (prev != NULL) prev[level] = x;
if (level == ) {
return next;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
}
}
} //寻找小于等于KEY的第一个NODE
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindLessThan(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - ;
while (true) {
assert(x == head_ || compare_(x->key, key) < );
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (next == NULL || compare_(next->key, key) >= ) {
if (level == ) {
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
} else {
x = next;
}
}
} //在最高层 寻找最后一个Node
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindLast()
const {
Node* x = head_;
int level = GetMaxHeight() - ;
while (true) {
Node* next = x->Next(level);
if (next == NULL) {
if (level == ) {
return x;
} else {
// Switch to next list
level--;
}
} else {
x = next;
}
}
} //构建函数 第一个head Node key是0 后继Node指针最大kMaxHeight
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
SkipList<Key,Comparator>::SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena)
: compare_(cmp),
arena_(arena),
head_(NewNode( /* any key will do */, kMaxHeight)),
max_height_(reinterpret_cast<void*>()),
rnd_(0xdeadbeef) {
for (int i = ; i < kMaxHeight; i++) {
head_->SetNext(i, NULL);
}
} //insert算法
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
// TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
// here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev); // Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
assert(x == NULL || !Equal(key, x->key)); int height = RandomHeight();
if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
prev[i] = head_;
}
//fprintf(stderr, "Change height from %d to %d\n", max_height_, height); // It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
// with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
// the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
// new level pointers from head_ (NULL), or a new value set in
// the loop below. In the former case the reader will
// immediately drop to the next level since NULL sorts after all
// keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast<void*>(height));
} x = NewNode(key, height);
for (int i = ; i < height; i++) {
// NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
// we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
}
} //寻找等于KEY 即可确认是否包含与KEY相等的Node
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Contains(const Key& key) const {
Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, NULL);
if (x != NULL && Equal(key, x->key)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
} }
varint变长数
leveldb使用了Protocol Buffers的变长字节整形编码 每个字节中使用7位来表示数字 最高位用作他处
300的编码,编码后是两个字节:
1010 1100 0000 0010
它这个例子是每个字节左边是高位,可以看到每个字节的最高位是一个标识位,从左到右第一个字节是10101100,最高位是1,说明后面还有字节需要解码,然后第二个字节是00000010,最高位是0,后面没字节了。所以这两个字节就需要解码成一个整数,再往下看。
代码 1010 1100 0000 0010
→ 010 1100 000 0010 //每个字节去掉最高位
→ 000 0010 010 1100 //字节序转换,两个字节互换位置
→ 000 0010 ++ 010 1100 //两个字节进行链接操作(不是相加)
→ 100101100 //合并后的结果,高位位0的部分截取掉
→ 256 + 32 + 8 + 4 = 300 //每个值为1的bit位乘以以2为底的幂,得出编码后的值
主要函数在
coding.h
extern void PutFixed32(std::string* dst, uint32_t value);
extern void PutFixed64(std::string* dst, uint64_t value);
extern void PutVarint32(std::string* dst, uint32_t value);
extern void PutVarint64(std::string* dst, uint64_t value);
extern void PutLengthPrefixedSlice(std::string* dst, const Slice& value);
extern bool GetVarint32(Slice* input, uint32_t* value);
extern bool GetVarint64(Slice* input, uint64_t* value);
extern bool GetLengthPrefixedSlice(Slice* input, Slice* result);
extern const char* GetVarint32Ptr(const char* p,const char* limit, uint32_t* v);
extern const char* GetVarint64Ptr(const char* p,const char* limit, uint64_t* v);
extern int VarintLength(uint64_t v);
extern void EncodeFixed32(char* dst, uint32_t value);
extern void EncodeFixed64(char* dst, uint64_t value);
extern char* EncodeVarint32(char* dst, uint32_t value);
extern char* EncodeVarint64(char* dst, uint64_t value);
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/onlytiancai/archive/2010/10/16/1853003.html
leveldb 学习记录(四) skiplist补与变长数字的更多相关文章
- leveldb 学习记录(四)Log文件
前文记录 leveldb 学习记录(一) skiplistleveldb 学习记录(二) Sliceleveldb 学习记录(三) MemTable 与 Immutable Memtablelevel ...
- leveldb 学习记录(一) skiplist
leveldb LevelDb是一个持久化存储的KV系统,并非完全将数据放置于内存中,部分数据也会存储到磁盘上. 想了解这个由谷歌大神编写的经典项目. 可以从数据结构以及数据结构的处理下手,也可以从示 ...
- leveldb 学习记录(三) MemTable 与 Immutable Memtable
前文: leveldb 学习记录(一) skiplist leveldb 学习记录(二) Slice 存储格式: leveldb数据在内存中以 Memtable存储(核心结构是skiplist 已介绍 ...
- JavaScript学习记录四
title: JavaScript学习记录四 toc: true date: 2018-09-16 20:31:22 --<JavaScript高级程序设计(第2版)>学习笔记 要多查阅M ...
- 4.VUE前端框架学习记录四:Vue组件化编码2
VUE前端框架学习记录四:Vue组件化编码2文字信息没办法描述清楚,主要看编码Demo里面,有附带完整的代码下载地址,有需要的同学到脑图里面自取.脑图地址http://naotu.baidu.com/ ...
- leveldb 学习记录(五)SSTable格式介绍
本节主要记录SSTable的结构 为下一步代码阅读打好基础,考虑到已经有大量优秀博客解析透彻 就不再编写了 这里推荐 https://blog.csdn.net/tankles/article/det ...
- leveldb 学习记录(七) SSTable构造
使用TableBuilder构造一个Table struct TableBuilder::Rep { // TableBuilder内部使用的结构,记录当前的一些状态等 Options options ...
- leveldb 学习记录(八) compact
随着运行时间的增加,memtable会慢慢 转化成 sstable. sstable会越来越多 我们就需要进行整合 compact 代码会在写入查询key值 db写入时等多出位置调用MaybeSche ...
- Linux 学习记录 四(Bash 和 Shell scirpt)
一.什么是 Shell? 狭义的shell指的是指令列方面的软件,包括基本的Linux操作窗口Bash等,广义的shell则包括 图形接口的软件,因为图形接口其实也可以操作各种驱动程序来呼叫核心进行工 ...
随机推荐
- G2 绘制混合图例 demo
G2 绘制混合图例 demo import G2 from '@antv/g2'; import DataSet from '@antv/data-set'; // G2 对数据源格式的要求,仅仅是 ...
- 浅读官方代码--ActionManager
用于管理节点的动作 { CCDirector* pDirector = CCDirector::sharedDirector(); //获得单例 pDirector->getActionMana ...
- PAT 乙级 1065 单身狗 (25 分)
1065 单身狗 (25 分) “单身狗”是中文对于单身人士的一种爱称.本题请你从上万人的大型派对中找出落单的客人,以便给予特殊关爱. 输入格式: 输入第一行给出一个正整数 N(≤ 50 000),是 ...
- Linux背背背(3)
目录 1.文件操作命令 2.文件夹操作命令 文件操作命令 创建 命令:touch 语法:#touch 文件的名字 文件名可以是一个完整的路径 如果后面的参数文件名指定了路径,则表示在指定的路 ...
- vue仿淘宝订单状态的tab切换效果
<div class="navigation"> //这里是通过循环遍历出来的数据,你需要根据index的值来判断你现在点击的是第几个tab栏导航,同时在js中写一个 ...
- vue仿淘宝结账订单
<template> <div class="container"> <div class="checkout-title"& ...
- 网页导出PDF文件
转自-----出道诗人 var downPdf = document.getElementById("exportToPdf"); downPdf.onclick = functi ...
- js 一些方法
1.js去除字符串前后的空格 function Trim(str) { return str.replace(/(^\s*)|(\s*$)/g, ""); } 2.js打乱数组的顺 ...
- mybatis xml中返回map 参看aiwanpai
<!-- 指定日期活动被创建次数查询结果数据集--> <resultMap id="countPlayTimesMap" type="HashMap&q ...
- 面向对象开发C++快速入门视频教程 C++基础加实战视频教程
课程目录: ├<C++面向对象高级开发(上)> │ ├1.C++编程简介.mp4 │ ├2.头文件与类的声明.mp4 │ ├3.构造函数.mp4 │ ├4.参数传递与返回值.mp4 │ ├ ...
