linux内核数据结构之链表【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/p/3475643.html
1、前言
最近写代码需用到链表结构,正好公共库有关于链表的。第一眼看时,觉得有点新鲜,和我之前见到的链表结构不一样,只有前驱和后继指针,而没有数据域。后来看代码注释发现该代码来自linux内核,在linux源代码下include/Lish.h下。这个链表具备通用性,使用非常方便。只需要在结构定义一个链表结构就可以使用。
2、链表介绍
链表是非常基本的数据结构,根据链个数分为单链表、双链表,根据是否循环分为单向链表和循环链表。通常定义定义链表结构如下:
typedef struct node
{
ElemType data; //数据域
struct node *next; //指针域
}node, *list;
链表中包含数据域和指针域。链表通常包含一个头结点,不存放数据,方便链表操作。单向循环链表结构如下图所示:
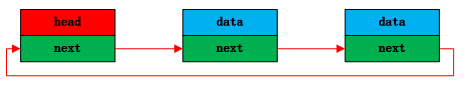
双向循环链表结构如下图所示:
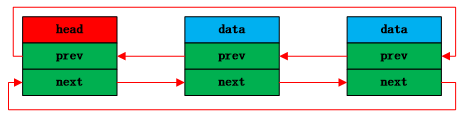
这样带数据域的链表降低了链表的通用性,不容易扩展。linux内核定义的链表结构不带数据域,只需要两个指针完成链表的操作。将链表节点加入数据结构,具备非常高的扩展性,通用性。链表结构定义如下所示:
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
链表结构如下所示:

需要用链表结构时,只需要在结构体中定义一个链表类型的数据即可。例如定义一个app_info链表,

1 typedef struct application_info
2 {
3 uint32_t app_id;
4 uint32_t up_flow;
5 uint32_t down_flow;
6 struct list_head app_info_head; //链表节点
7 }app_info;

定义一个app_info链表,app_info app_info_list;通过app_info_head进行链表操作。根据C语言指针操作,通过container_of和offsetof,可以根据app_info_head的地址找出app_info的起始地址,即一个完整ap_info结构的起始地址。可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/p/3472271.html。
3、linux内核链表实现
内核实现的是双向循环链表,提供了链表操作的基本功能。
(1)初始化链表头结点

#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}

LIST_HEAD宏创建一个链表头结点,并用LIST_HEAD_INIT宏对头结点进行赋值,使得头结点的前驱和后继指向自己。
INIT_LIST_HEAD函数对链表进行初始化,使得前驱和后继指针指针指向头结点。
(2)插入节点

1 static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
2 struct list_head *prev,
3 struct list_head *next)
4 {
5 next->prev = new;
6 new->next = next;
7 new->prev = prev;
8 prev->next = new;
9 }
10
11 static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
12 {
13 __list_add(new, head, head->next);
14 }
15
16 static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
17 {
18 __list_add(new, head->prev, head);
19 }

插入节点分为从链表头部插入list_add和链表尾部插入list_add_tail,通过调用__list_add函数进行实现,head->next指向之一个节点,head->prev指向尾部节点。
(3)删除节点

1 static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
2 {
3 next->prev = prev;
4 prev->next = next;
5 }
6
7 static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
8 {
9 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
10 entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
11 entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
12 }

从链表中删除一个节点,需要改变该节点前驱节点的后继结点和后继结点的前驱节点。最后设置该节点的前驱节点和后继结点指向LIST_POSITION1和LIST_POSITION2两个特殊值,这样设置是为了保证不在链表中的节点项不可访问,对LIST_POSITION1和LIST_POSITION2的访问都将引起页故障

/*
* These are non-NULL pointers that will result in page faults
* under normal circumstances, used to verify that nobody uses
* non-initialized list entries.
*/
#define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
#define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)

(4)移动节点

1 /**
2 * list_move - delete from one list and add as another's head
3 * @list: the entry to move
4 * @head: the head that will precede our entry
5 */
6 static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
7 {
8 __list_del(list->prev, list->next);
9 list_add(list, head);
10 }
11
12 /**
13 * list_move_tail - delete from one list and add as another's tail
14 * @list: the entry to move
15 * @head: the head that will follow our entry
16 */
17 static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
18 struct list_head *head)
19 {
20 __list_del(list->prev, list->next);
21 list_add_tail(list, head);
22 }

move将一个节点移动到头部或者尾部。
(5)判断链表

1 /**
2 * list_is_last - tests whether @list is the last entry in list @head
3 * @list: the entry to test
4 * @head: the head of the list
5 */
6 static inline int list_is_last(const struct list_head *list,
7 const struct list_head *head)
8 {
9 return list->next == head;
10 }
11
12 /**
13 * list_empty - tests whether a list is empty
14 * @head: the list to test.
15 */
16 static inline int list_empty(const struct list_head *head)
17 {
18 return head->next == head;
19 }

list_is_last函数判断节点是否为末尾节点,list_empty判断链表是否为空。
(6)遍历链表

1 /**
2 * list_entry - get the struct for this entry
3 * @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
4 * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
5 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
6 */
7 #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
8 container_of(ptr, type, member)
9
10 /**
11 * list_first_entry - get the first element from a list
12 * @ptr: the list head to take the element from.
13 * @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
14 * @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
15 *
16 * Note, that list is expected to be not empty.
17 */
18 #define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
19 list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
20
21 /**
22 * list_for_each - iterate over a list
23 * @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop cursor.
24 * @head: the head for your list.
25 */
26 #define list_for_each(pos, head) \
27 for (pos = (head)->next; prefetch(pos->next), pos != (head); \
28 pos = pos->next)

宏list_entity获取链表的结构,包括数据域。list_first_entry获取链表第一个节点,包括数据源。list_for_each宏对链表节点进行遍历。
4、测试例子
编写一个简单使用链表的程序,从而掌握链表的使用。
自定义个类似的list结构如下所示:mylist.h

1 # define POISON_POINTER_DELTA 0
2
3 #define LIST_POISON1 ((void *) 0x00100100 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
4 #define LIST_POISON2 ((void *) 0x00200200 + POISON_POINTER_DELTA)
5
6 //计算member在type中的位置
7 #define offsetof(type, member) (size_t)(&((type*)0)->member)
8 //根据member的地址获取type的起始地址
9 #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
10 const typeof(((type *)0)->member)*__mptr = (ptr); \
11 (type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); })
12
13 //链表结构
14 struct list_head
15 {
16 struct list_head *prev;
17 struct list_head *next;
18 };
19
20 static inline void init_list_head(struct list_head *list)
21 {
22 list->prev = list;
23 list->next = list;
24 }
25
26 static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
27 struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
28 {
29 prev->next = new;
30 new->prev = prev;
31 new->next = next;
32 next->prev = new;
33 }
34
35 //从头部添加
36 static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new , struct list_head *head)
37 {
38 __list_add(new, head, head->next);
39 }
40 //从尾部添加
41 static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
42 {
43 __list_add(new, head->prev, head);
44 }
45
46 static inline void __list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
47 {
48 prev->next = next;
49 next->prev = prev;
50 }
51
52 static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
53 {
54 __list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
55 entry->next = LIST_POISON1;
56 entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
57 }
58
59 static inline void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
60 {
61 __list_del(list->prev, list->next);
62 list_add(list, head);
63 }
64
65 static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
66 struct list_head *head)
67 {
68 __list_del(list->prev, list->next);
69 list_add_tail(list, head);
70 }
71 #define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
72 container_of(ptr, type, member)
73
74 #define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
75 list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
76
77 #define list_for_each(pos, head) \
78 for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)

mylist.c如下所示:

1 /**@brief 练习使用linux内核链表,功能包括:
2 * 定义链表结构,创建链表、插入节点、删除节点、移动节点、遍历节点
3 *
4 *@auther Anker @date 2013-12-15
5 **/
6 #include <stdio.h>
7 #include <inttypes.h>
8 #include <stdlib.h>
9 #include <errno.h>
10 #include "mylist.h"
11 //定义app_info链表结构
12 typedef struct application_info
13 {
14 uint32_t app_id;
15 uint32_t up_flow;
16 uint32_t down_flow;
17 struct list_head app_info_node;//链表节点
18 }app_info;
19
20
21 app_info* get_app_info(uint32_t app_id, uint32_t up_flow, uint32_t down_flow)
22 {
23 app_info *app = (app_info*)malloc(sizeof(app_info));
24 if (app == NULL)
25 {
26 fprintf(stderr, "Failed to malloc memory, errno:%u, reason:%s\n",
27 errno, strerror(errno));
28 return NULL;
29 }
30 app->app_id = app_id;
31 app->up_flow = up_flow;
32 app->down_flow = down_flow;
33 return app;
34 }
35 static void for_each_app(const struct list_head *head)
36 {
37 struct list_head *pos;
38 app_info *app;
39 //遍历链表
40 list_for_each(pos, head)
41 {
42 app = list_entry(pos, app_info, app_info_node);
43 printf("ap_id: %u\tup_flow: %u\tdown_flow: %u\n",
44 app->app_id, app->up_flow, app->down_flow);
45
46 }
47 }
48
49 void destroy_app_list(struct list_head *head)
50 {
51 struct list_head *pos = head->next;
52 struct list_head *tmp = NULL;
53 while (pos != head)
54 {
55 tmp = pos->next;
56 list_del(pos);
57 pos = tmp;
58 }
59 }
60
61
62 int main()
63 {
64 //创建一个app_info
65 app_info * app_info_list = (app_info*)malloc(sizeof(app_info));
66 app_info *app;
67 if (app_info_list == NULL)
68 {
69 fprintf(stderr, "Failed to malloc memory, errno:%u, reason:%s\n",
70 errno, strerror(errno));
71 return -1;
72 }
73 //初始化链表头部
74 struct list_head *head = &app_info_list->app_info_node;
75 init_list_head(head);
76 //插入三个app_info
77 app = get_app_info(1001, 100, 200);
78 list_add_tail(&app->app_info_node, head);
79 app = get_app_info(1002, 80, 100);
80 list_add_tail(&app->app_info_node, head);
81 app = get_app_info(1003, 90, 120);
82 list_add_tail(&app->app_info_node, head);
83 printf("After insert three app_info: \n");
84 for_each_app(head);
85 //将第一个节点移到末尾
86 printf("Move first node to tail:\n");
87 list_move_tail(head->next, head);
88 for_each_app(head);
89 //删除最后一个节点
90 printf("Delete the last node:\n");
91 list_del(head->prev);
92 for_each_app(head);
93 destroy_app_list(head);
94 free(app_info_list);
95 return 0;
96 }

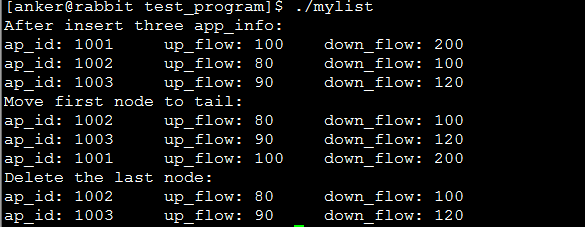
测试结果如下所示:
参考网址:
linux内核数据结构之链表【转】的更多相关文章
- linux内核数据结构之链表
linux内核数据结构之链表 1.前言 最近写代码需用到链表结构,正好公共库有关于链表的.第一眼看时,觉得有点新鲜,和我之前见到的链表结构不一样,只有前驱和后继指针,而没有数据域.后来看代码注释发现该 ...
- linux内核数据结构学习总结
目录 . 进程相关数据结构 ) struct task_struct ) struct cred ) struct pid_link ) struct pid ) struct signal_stru ...
- 拒绝造轮子!如何移植并使用Linux内核的通用链表(附完整代码实现)
在实际的工作中,我们可能会经常使用链表结构来存储数据,特别是嵌入式开发,经常会使用linux内核最经典的双向链表 list_head.本篇文章详细介绍了Linux内核的通用链表是如何实现的,对于经常使 ...
- linux内核系列(二)内核数据结构之链表
双向链表 传统链表与linu内核链表的区别图: 图一 图二 从上图中看出在传统链表中各种不同链表间没有通用性,因为各个数据域不同,而在linux内核中巧妙将链表结构内嵌到数据域结构中使得不同结构之间能 ...
- Linux 内核数据结构:Linux 双向链表
Linux 内核提供一套双向链表的实现,你可以在 include/linux/list.h 中找到.我们以双向链表着手开始介绍 Linux 内核中的数据结构 ,因为这个是在 Linux 内核中使用最为 ...
- Linux 内核数据结构:双向链表
Linux 内核提供一套双向链表的实现,你可以在 include/linux/list.h 中找到.我们以双向链表着手开始介绍 Linux 内核中的数据结构 ,因为这个是在 Linux 内核中使用最为 ...
- linux内核数据结构--进程相关
linux里面,有一个结构体task_struct,也叫“进程描述符”的数据结构,它包含了与进程相关的所有信息,它非常复杂,每一个字段都可能与一个功能相关,所以大部分细节不在我的研究范围之内,在这篇文 ...
- linux内核中的链表
1.内核中的链表 linux内核链表与众不同,他不是把将数据结构塞入链表,而是将链表节点塞入数据,在2.1内核中引入了官方链表,从此内核中所有的链表使用都采用此链表,千万不要在重复造车轮子了!链表实现 ...
- linux内核的双链表list_head、散列表hlist_head
一.双链表list_head 1.基本概念 linux内核提供的标准链表可用于将任何类型的数据结构彼此链接起来. 不是数据内嵌到链表中,而是把链表内嵌到数据对象中. 即:加入链表的数据结构必须包含一个 ...
随机推荐
- 第206天:http协议终极详解---看这一篇就够了
HTTP简介 HTTP协议是Hyper Text Transfer Protocol(超文本传输协议)的缩写,是用于从万维网(WWW:World Wide Web )服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的传送 ...
- 两种方法实现TAB菜单及文件操作
1,自定义属性的方法实现----TAB菜单操作 cursor:pointer; 鼠标的小手 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> ...
- 【BZOJ3105】新Nim游戏(线性基)
[BZOJ3105]新Nim游戏(线性基) 题面 BZOJ Description 传统的Nim游戏是这样的:有一些火柴堆,每堆都有若干根火柴(不同堆的火柴数量可以不同).两个游戏者轮流操作,每次可以 ...
- NOIP2016天天爱跑步 题解报告【lca+树上统计(桶)】
题目描述 小c同学认为跑步非常有趣,于是决定制作一款叫做<天天爱跑步>的游戏.«天天爱跑步»是一个养成类游戏,需要玩家每天按时上线,完成打卡任务. 这个游戏的地图可以看作一一棵包含 nn个 ...
- NOIP2016愤怒的小鸟 题解报告 【状压DP】
题目什么大家都清楚 题解 我们知道,三点确定一条抛物线,现在这条抛物线过原点,所以任意两只猪确定一条抛物线.通过运算的出对于两头猪(x1,y1),(x2,y2),他们所在抛物线a=(y1*x2-y2* ...
- Linux系统启动详解(二)
上节讲到了Linux启动大体流程,及grub的作用,本节主要扯扯initramfs的那些事,并且通过简单修改initramfs,将整体操作系统运行到了内存中. 3 initramfs 3. ...
- 开放接口/RESTful/Api服务的设计和安全方案
总体思路 这个涉及到两个方面问题:一个是接口访问认证问题,主要解决谁可以使用接口(用户登录验证.来路验证)一个是数据数据传输安全,主要解决接口数据被监听(HTTPS安全传输.敏感内容加密.数字签名) ...
- javascript中的位运算,
罗浮宫群里又有讨论位运算符号|了,做过一段时间php,数据库保存布尔值数据经常用到,比如100110 就表明了六个属性的是与否,极大减少了数据量..] ECMAScript 中位运算跟其他语言一样的. ...
- 【生成树,堆】【CF1095F】 Make It Connected
Description 给定 \(n\) 个点,每个点有点权,连结两个点花费的代价为两点的点权和.另外有 \(m\) 条特殊边,参数为 \(x,y,z\).意为如果你选择这条边,就可以花费 \(z\) ...
- Codeforces 585.D Lizard Era: Beginning
D. Lizard Era: Beginning time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input sta ...
