WordCount (Python)
Github项目地址:https://github.com/w1036933220/WordCount
一、解题思路
- 把项目需求理清楚,画一个思维导图
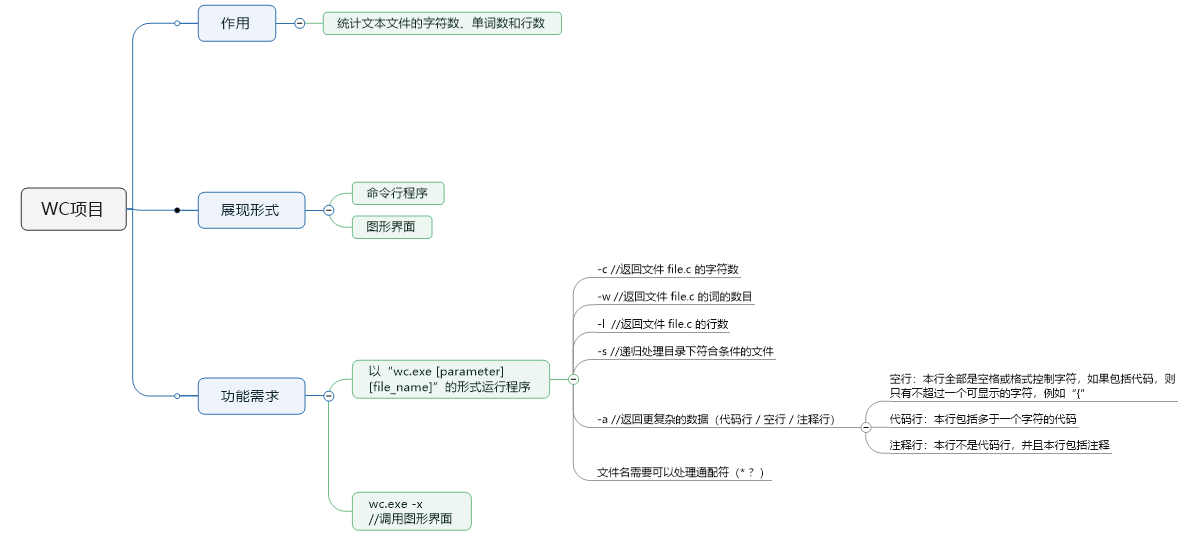
- 考虑各部分功能所需要的大概实现思路
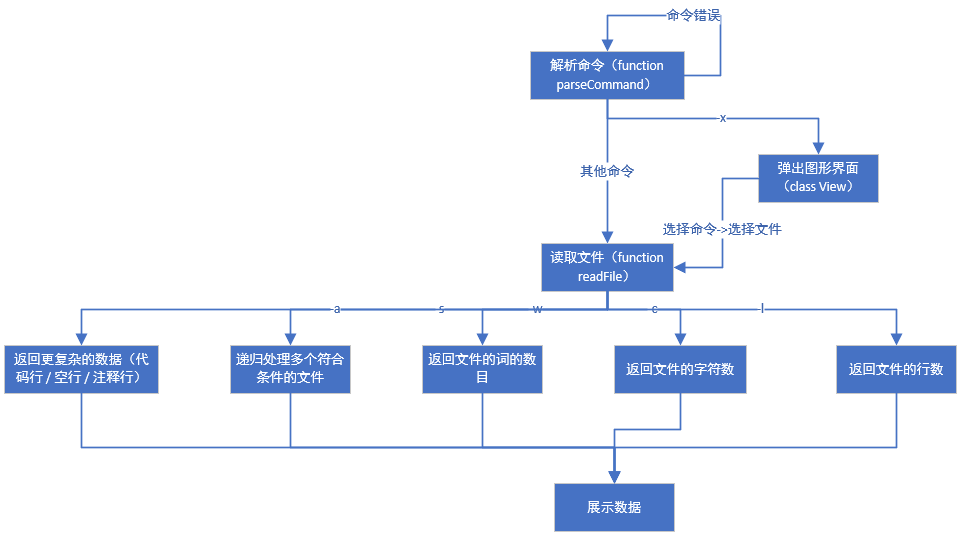
- 然后完成了计算文件属性的算法部分
- 再回头想对指令的解析问题,顺带添加了递归处理多个文件的功能
- 查python的os库文档,最后决定用os.walk读取当前文件夹内的所有文件夹和文件,替换掉输入的*和?通配符,再进行匹配
三、设计实现过程及代码说明
- main.py(入口文件)
from utils.utils import *
if __name__ == '__main__':
command = input("请输入命令(wc.exe [parameter] {file_name}):\n")
parse_command(command)
- orders.py
存放指令集,和输出各类数据的函数
from utils.count import *
from views.main_view import *
import tkinter as tk
# 输出字符数
def print_char_num(text):
print("字符数:" + str(FileProperties(text).count_char_num()))
# 输出单词数
def print_word_num(text):
print("词数:" + str(FileProperties(text).count_word_num()))
# 输出行数
def print_line_num(text):
print("行数:" + str(FileProperties(text).count_line_num()))
# 输出代码行/空行/注释行
def print_code_property(text):
file_properties = FileProperties(text)
print("空行:" + str(file_properties.count_null_line_num()))
print("注释行:" + str(file_properties.count_annotation_line_num()))
print("代码行:" + str(file_properties.count_code_line_num()))
# 调出图形界面
def draw_view():
root = MainView(tk.Tk())
def print_error():
print("指令输入错误")
# 单指令命令集
orders = {
'-c': print_char_num,
'-w': print_word_num,
"-l": print_line_num,
"-a": print_code_property,
"-s": print_error,
"-x": draw_view
}
- utils.py
放置解析指令、读取文件、模糊搜素的函数
import os
from utils.orders import *
# description:parse command
# param:order input
# return:[order, [file_list]] / FALSE
def parse_command(command):
command = command.strip().split(" ")
# 指令若为空或者起始不为wc.exe则报错
if command == [] or command[0] != "wc.exe":
print("指令输入错误")
# 打开图形界面的指令(一级指令)
if "-x" in command:
orders.get("-x")
elif len(command) > 2:
order = command[-2]
file_name = command[-1]
file_list = get_file_list(file_name)
# 递归调用的指令
if "-s" in command:
if file_list:
for file in file_list:
print(file + ":")
text = read_file(file)
orders.get(order)(text)
else:
print(file_list[0] + ":")
text = read_file(file_name)
orders.get(order)(text)
else:
print("指令输入错误")
# 读取目录下符合条件的文件名
def get_file_list(file_name):
# 最终构建的文件列表
file_list = []
# 匹配到的文件夹列表、需二次处理
dir_list = []
file_name = file_name.replace("?", "\\S").replace("*", "\\S+")
file_name += "$"
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(".", topdown=False):
for name in files:
if re.match(file_name, name):
file_list.append(os.path.join(root, name))
for name in dirs:
if re.match(file_name, name):
dir_list.append(os.path.join(os.getcwd() + os.sep, name))
# 如果文件夹非空,则继续收集
if dir_list:
for item in dir_list:
all_file = os.listdir(item)
for file in all_file:
# 文件的完整路径
file_path = item + os.sep + file
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
file_list.append(file_path)
print(file_list)
return file_list
# description:read files
# param:file_list
# return:file content
def read_file(file):
with open(file, 'r') as f:
return f.readlines()
- count.py
存放计算文件属性的类
import re
class FileProperties(object):
def __init__(self, file_text):
self.file_text = file_text
# 字符数
self.char_num = 0
# 单词数
self.word_num = 0
# 行数
self.line_num = len(file_text)
# 空行
self.null_line_num = 0
# 代码行
self.code_line_num = 0
# 注释行数
self.annotation_line_num = 0
# 计算字符数
def count_char_num(self):
for line in self.file_text:
self.char_num += len(line.strip())
return self.char_num
# 计算单词数
def count_word_num(self):
for line in self.file_text:
# 正则匹配一行中的所有单词,并计算单词数
self.word_num += len(re.findall(r'[a-zA-Z0-9]+[\-\']?[a-zA-Z]*', line))
return self.word_num
# 计算行数
def count_line_num(self):
return self.line_num
# 计算空行数
def count_null_line_num(self):
for line in self.file_text:
# 只有不超过一个可显示的字符
if len(re.findall(r'\S', line)) <= 1:
self.null_line_num += 1
return self.null_line_num
# 计算代码行
def count_code_line_num(self):
return self.line_num - self.null_line_num - self.annotation_line_num
# 计算注释行
def count_annotation_line_num(self):
flag = 0
for line in self.file_text:
line = line.strip()
# 匹配不是代码行且有//
if re.match(r'^\S?\s*?\/\/', line):
self.annotation_line_num += 1
# 匹配不是代码行且有/*
elif re.match(r'^\S?\s*?\/\*', line):
flag = 1
self.annotation_line_num += 1
if line.endswith('*/'):
flag = 0
elif flag == 1:
self.annotation_line_num += 1
elif "*/" in line:
self.annotation_line_num += 1
flag = 0
return self.annotation_line_num
- main_view.py(新增)
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import tkinter.filedialog
from utils.utils import *
from utils.count import *
class MainView(object):
def __init__(self, window):
self.window = window
self.window.title("这是船新的版本!")
self.window.geometry("540x290")
self.data_tree = ttk.Treeview(self.window, show="headings")
self.creat_view()
def creat_view(self):
# 选择文件按钮
btn = tk.Button(self.window, text="选择文件", command=self.file_choose).place(x=240, y=247)
# 文件数据显示表格
self.data_tree.place(x=8, y=8)
# 定义列
self.data_tree["columns"] = ("文件名", "字符数", "单词数", "行数", "空行数", "代码行数", "注释行数")
# 设置列属性,列不显示
self.data_tree.column("文件名", width=100)
self.data_tree.column("字符数", width=70)
self.data_tree.column("单词数", width=70)
self.data_tree.column("行数", width=70)
self.data_tree.column("空行数", width=70)
self.data_tree.column("代码行数", width=70)
self.data_tree.column("注释行数", width=70)
# 设置表头
self.data_tree.heading("文件名", text="文件名")
self.data_tree.heading("字符数", text="字符数")
self.data_tree.heading("单词数", text="单词数")
self.data_tree.heading("行数", text="行数")
self.data_tree.heading("空行数", text="空行数")
self.data_tree.heading("代码行数", text="代码行数")
self.data_tree.heading("注释行数", text="注释行数")
self.window.mainloop()
def file_choose(self):
file_list = tk.filedialog.askopenfilenames()
for index, file in enumerate(file_list):
text = read_file(file)
[char_num, word_num, line_num, null_line_num, code_line_num,
annotation_line_num] = FileProperties(text).all_count()
file = file.split("/")[-1]
self.data_tree.insert('', index, values=(file, char_num, word_num, line_num,
null_line_num, code_line_num, annotation_line_num))
五、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 10 | 8 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 8 |
| Development | 开发 | 460 | 610 + 90 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 200 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 90 | 60 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 5 | 5 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 5 | 0 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 120 | 100 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 90 | 200 + 90 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 10 | 30 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 20 | 15 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 30 | 32 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 10 | 12 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 5 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 10 | 15 |
| 合计 | 355 | 630 + 90 |
六、测试运行
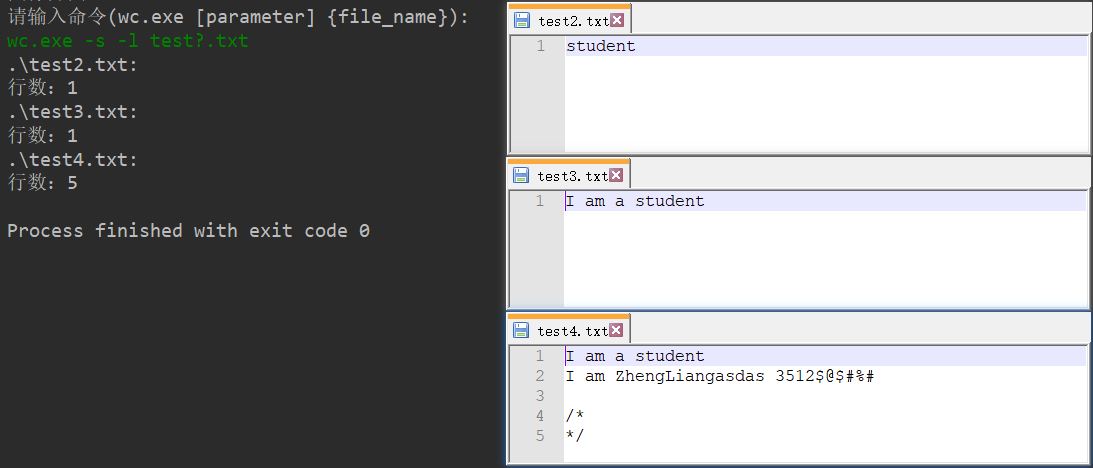

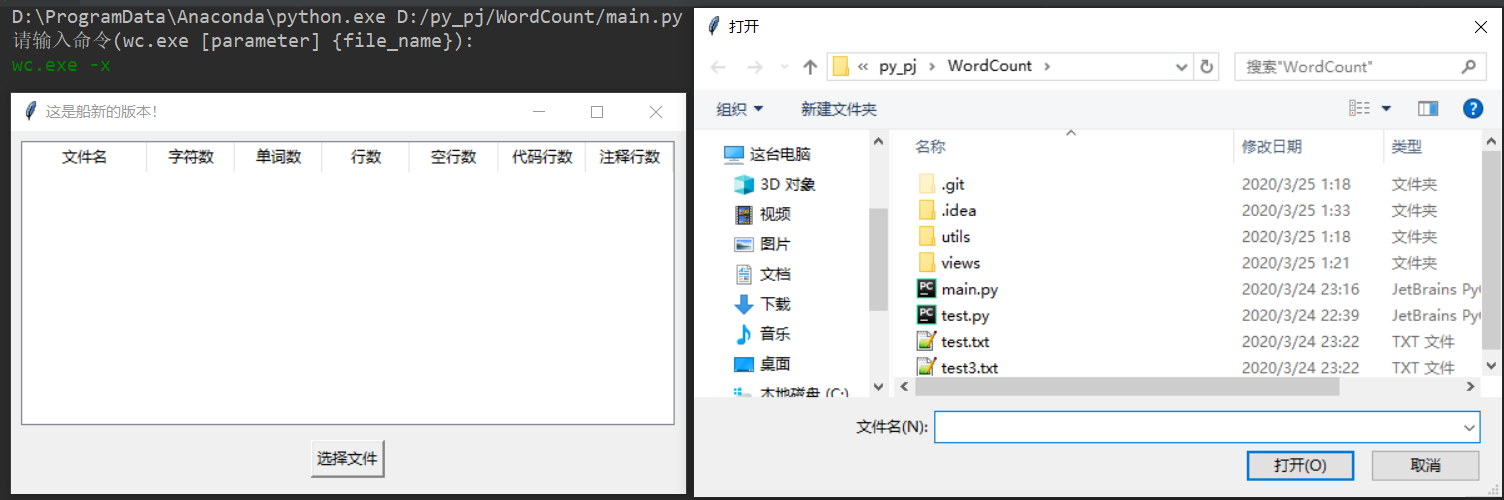
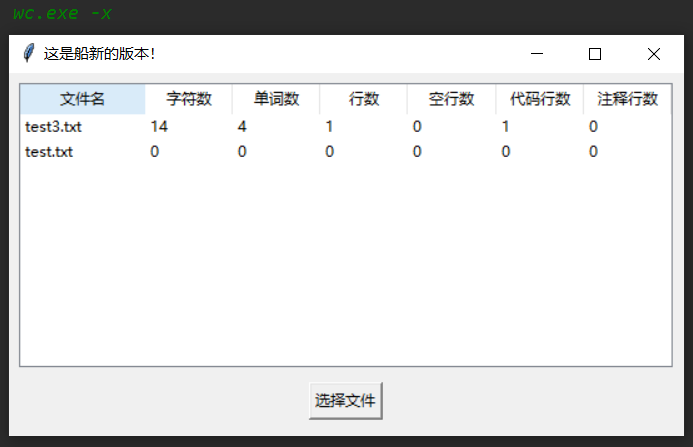
七、总结
- 太久没写python了,发现居然没有switch这个语句,百度查到了表驱动这个东西
- 用时与预计的出入有点大(过了大半年遗忘率确实高)
- 输入验证处理没有做完全
- 写的时候发现python有些问题不知道是bug还是什么
orders = {
'-c': print_char_num,
'-w': print_word_num,
"-l": print_line_num,
"-a": print_code_property,
"-s": print_error,
}
这是我的指令集,如果把他写成像js
orders = {
'-c': function () {
// 某些操作
},
}
python不管会不会用到这个指令集,都会把字典中的值执行一遍,所以只能放函数名,js就不会
WordCount (Python)的更多相关文章
- Python进阶篇四:Python文件和流
摘要: Python对于文件和流的操作与其他编程语言基本差不多,甚至语句上比其他语言更为简洁.文件和流函数针对的对象除了这两者之外还有,类文件(file-like),即python中只支持读却不支持写 ...
- Python3调用Hadoop的API
前言: 上一篇文章 我学习使用pandas进行简单的数据分析,但是各位...... Pandas处理.分析不了TB级别数据的大数据,于是再看看Hadoop. 另附上人心不足蛇吞象 对故事一的感悟: ...
- 大数据并行计算框架Spark
Spark2.1. http://dblab.xmu.edu.cn/blog/1689-2/ 0+入门:Spark的安装和使用(Python版) Spark2.1.0+入门:第一个Spark应用程序: ...
- Python初次实现MapReduce——WordCount
前言 Hadoop 本身是用 Java 开发的,所以之前的MapReduce代码小练都是由Java代码编写,但是通过Hadoop Streaming,我们可以使用任意语言来编写程序,让Hadoop 运 ...
- 利用python操作mrjob实例---wordcount
网上利用java实现mr操作实例相对较多,现将python实现mr操作实例---Wordcount分享如下: 在操作前,需要作如下准备: 1.确保linux系统里安装有python3.5,pyt ...
- Python实现MapReduce,wordcount实例,MapReduce实现两表的Join
Python实现MapReduce 下面使用mapreduce模式实现了一个简单的统计日志中单词出现次数的程序: from functools import reduce from multiproc ...
- hadoop学习笔记——用python写wordcount程序
尝试着用3台虚拟机搭建了伪分布式系统,完整的搭建步骤等熟悉了整个分布式框架之后再写,今天写一下用python写wordcount程序(MapReduce任务)的具体步骤. MapReduce任务以来H ...
- 在Hadoop上用Python实现WordCount
一.简单说明 本例中我们用Python写一个简单的运行在Hadoop上的MapReduce程序,即WordCount(读取文本文件并统计单词的词频).这里我们将要输入的单词文本input.txt和Py ...
- python在mapreduce运行Wordcount程序
首先脚本文件: mapper.py: #!/usr/bin/env python import sys for line in sys.stdin: line = line.strip() words ...
随机推荐
- Android中service的生命周期
Service作为Android四大组件 Service Activity ContentProvider BroadcastReceiver 之一,应用非常广泛,和Activity一样,Servic ...
- Antd DatePicker 语言项-显示中文月份
官网:https://ant.design/components/date-picker-cn/ 如果要显示中文,官网是这么指导的: 但是,设置后并没有生效!原因是默认的中文local文件并没有月份的 ...
- 虚拟机 NAT 网络静态ip配置记录
环境 VMware 15.5.5 build-16285975 centos7 虚拟网络编辑器配置 位置 编辑 --> 虚拟网络编辑器 示例 以下以 192.168.18.0 网段ip为例,实际 ...
- Kafka 入门(三)--为什么 Kafka 依赖 ZooKeeper?
一.ZooKeeper 简介 1.基本介绍 ZooKeeper 的官网是:https://zookeeper.apache.org/.在官网上是这么介绍 ZooKeeper 的:ZooKeeper 是 ...
- 4. JSON字符串是如何被解析的?JsonParser了解一下
公司不是你家,领导不是你妈.本文已被 https://www.yourbatman.cn 收录,里面一并有Spring技术栈.MyBatis.JVM.中间件等小而美的专栏供以免费学习.关注公众号[BA ...
- 关于if后有无else谜题
在自定义函数中 for(i=1;i<=6;i++) { if(a%i==0) return 0; else return 1; } 意思是,如果有一个除不尽就返回零,有一个除尽会立刻返回一. 如 ...
- setTimeout、clearTimeout、setInterval
setTimeout(cb, ms) setTimeout(cb, ms) 全局函数在指定的毫秒(ms)数后执行指定函数(cb).:setTimeout() 只执行一次指定函数. 返回一个代表定时器的 ...
- PHP import_request_variables() 函数
import_request_variables() 函数将 GET/POST/Cookie 变量导入到全局作用域中.该函数在最新版本的 PHP 中已经不支持.高佣联盟 www.cgewang.com ...
- PHP imageaffinematrixget - 获取矩阵
imageaffinematrixget — 获取矩阵.高佣联盟 www.cgewang.com 语法 array imageaffinematrixget ( int $type [, mixed ...
- 学习vue.js (一)
MVVM模式 MVVM是Model-View-ViewModel的简写,即模型-视图-视图模型.当View(视图层)变化时,会自动更新到ViewModel(视图模型),反之也一样,View和ViewM ...
