Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之拦截器与选择器
Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之拦截器与选择器
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
本篇博客只是配置的是Flume主流的Interceptors,想要了解更详细的配置信息请参考官网:http://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html#flume-interceptors。
想必大家都知道Flume的组件有Source,channel和sink。其实在Flume还有一些更深层的东西,比如你知道soucre是如何将数据传送给channel的吗?那你有知道channel又是如何将数据发送给sink的吗?对于一个Agent来说,它只能有一个source,但是它可以有多个channel和sink,如下图:
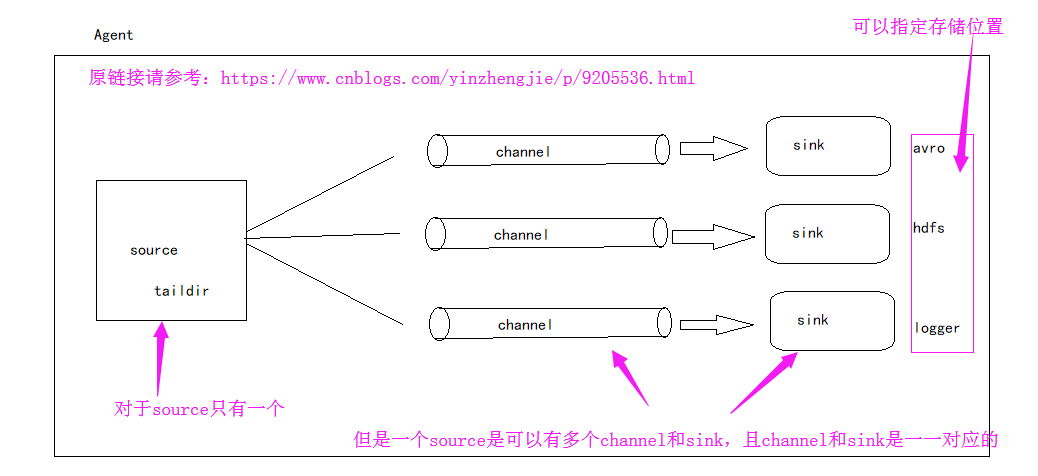
接下来就跟着我一起了了解一下更深层次的知识吧。接下来我们就一起探讨一下source是如何将数据发送到channel中的,以及sink是处理数据的。
一.Source端源码查看
1>.获取一行数据,使用其构建Event

2>.使用processEvent处理数据
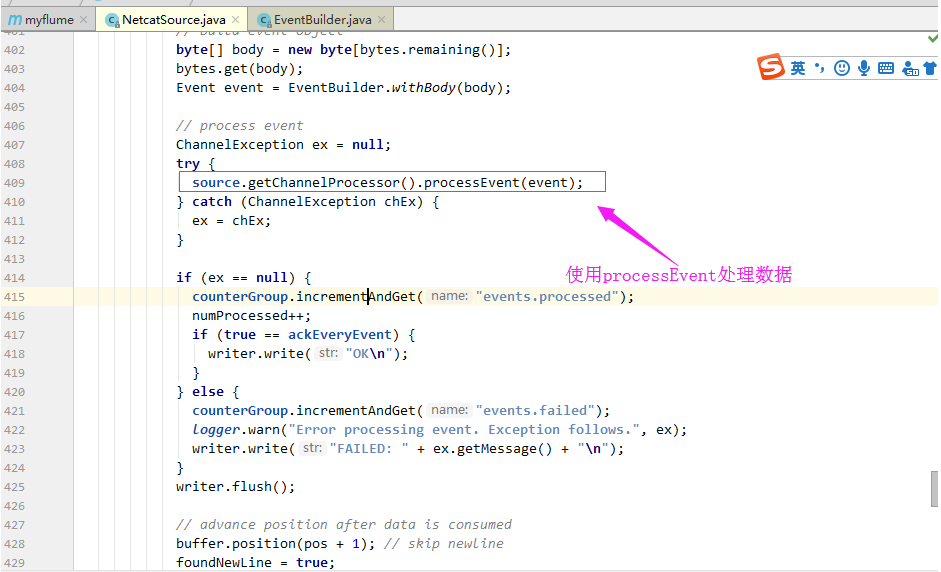
3>.在处理过程中,event需要通过拦截器链,相当于过滤数据
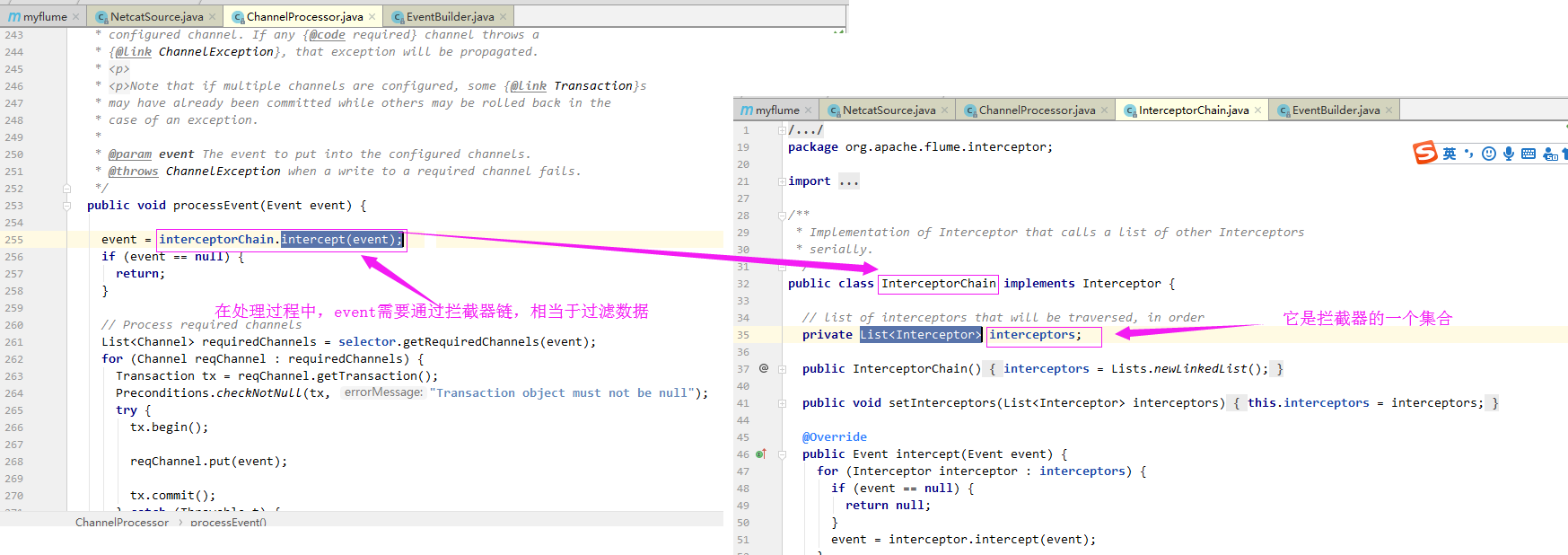
4>.在拦截器链中,通过迭代所有拦截器,对数据进行多次处理(例如:host拦截器,是对event进行添加头部操作)
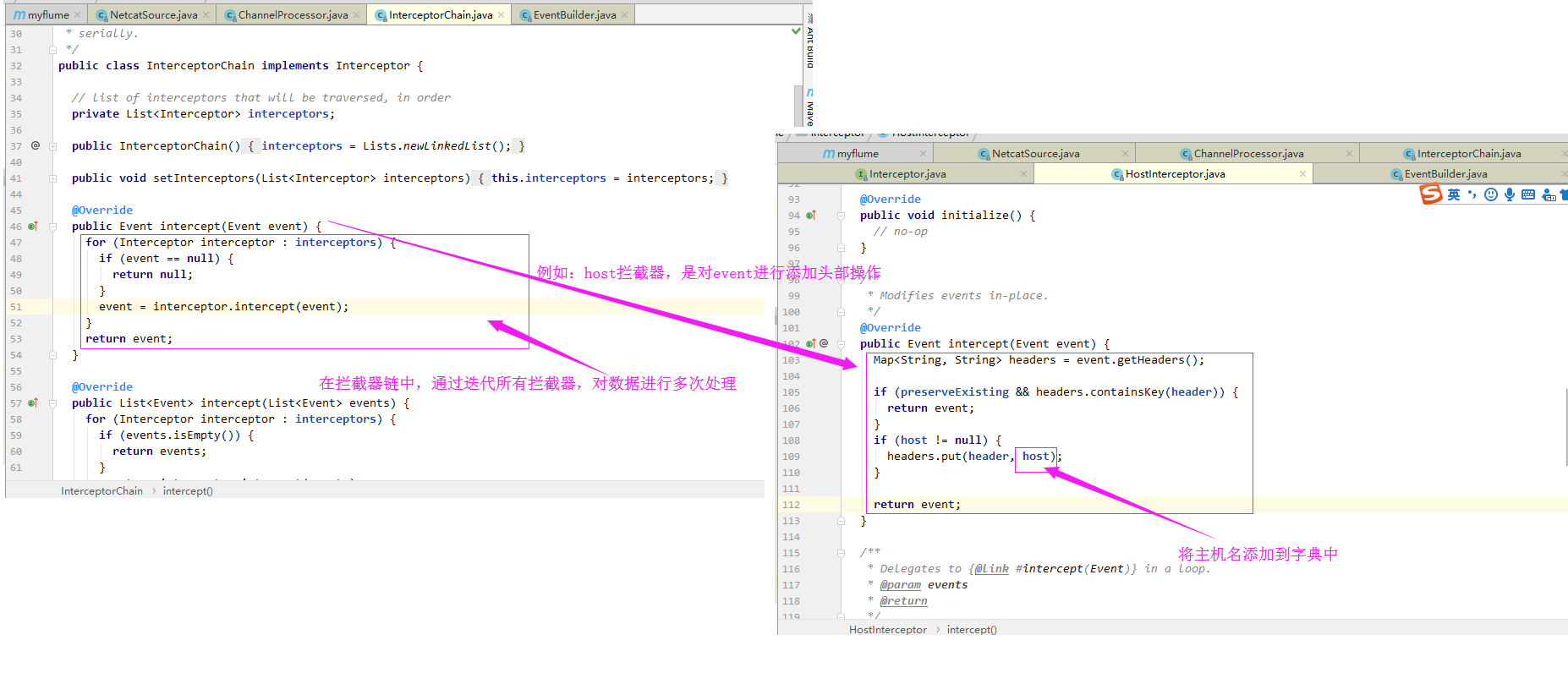
5>.通过拦截器处理后的event,再次进入到通道挑选器
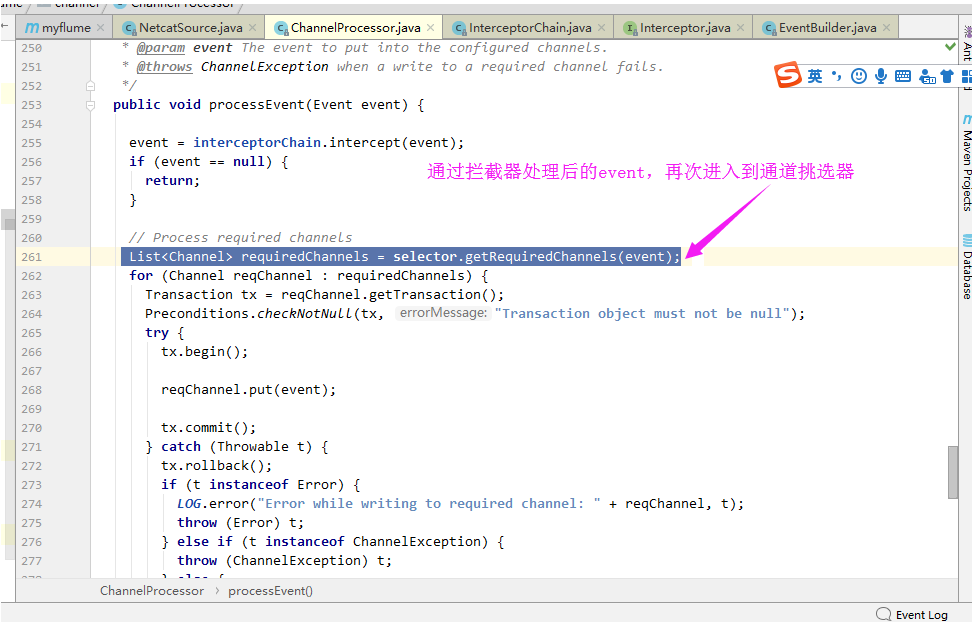
6>.迭代所有channel,将数据放进channel中

通过上面的源码解析,看下面这张图应该就不是什么难事了吧:
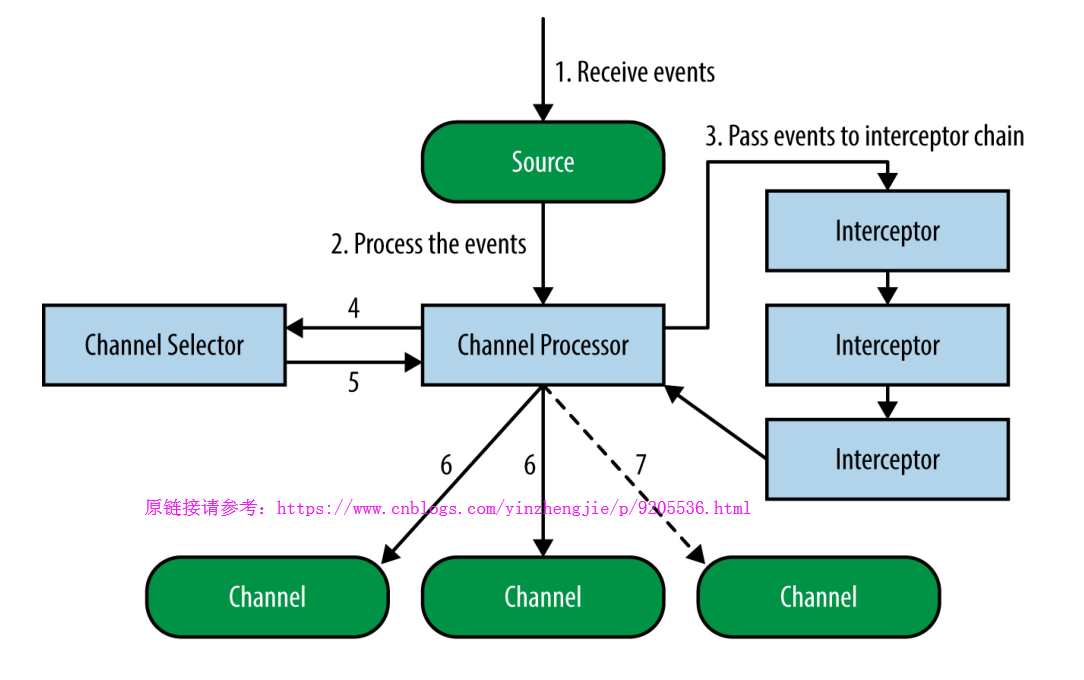
这个时候,你是否绝对第一张图画得并不自信呢?这个时候我们可以把第一张图的Source端流程画得更详细一点,如下:
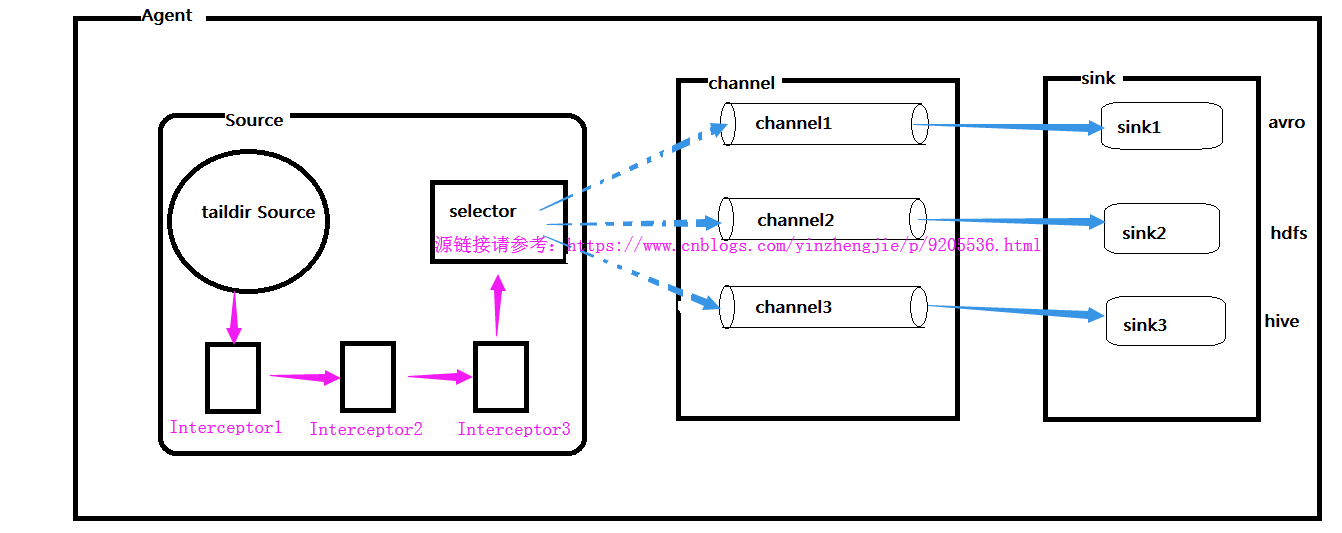
二.拦截器(Interceptors)
1>.Interceptors 功能
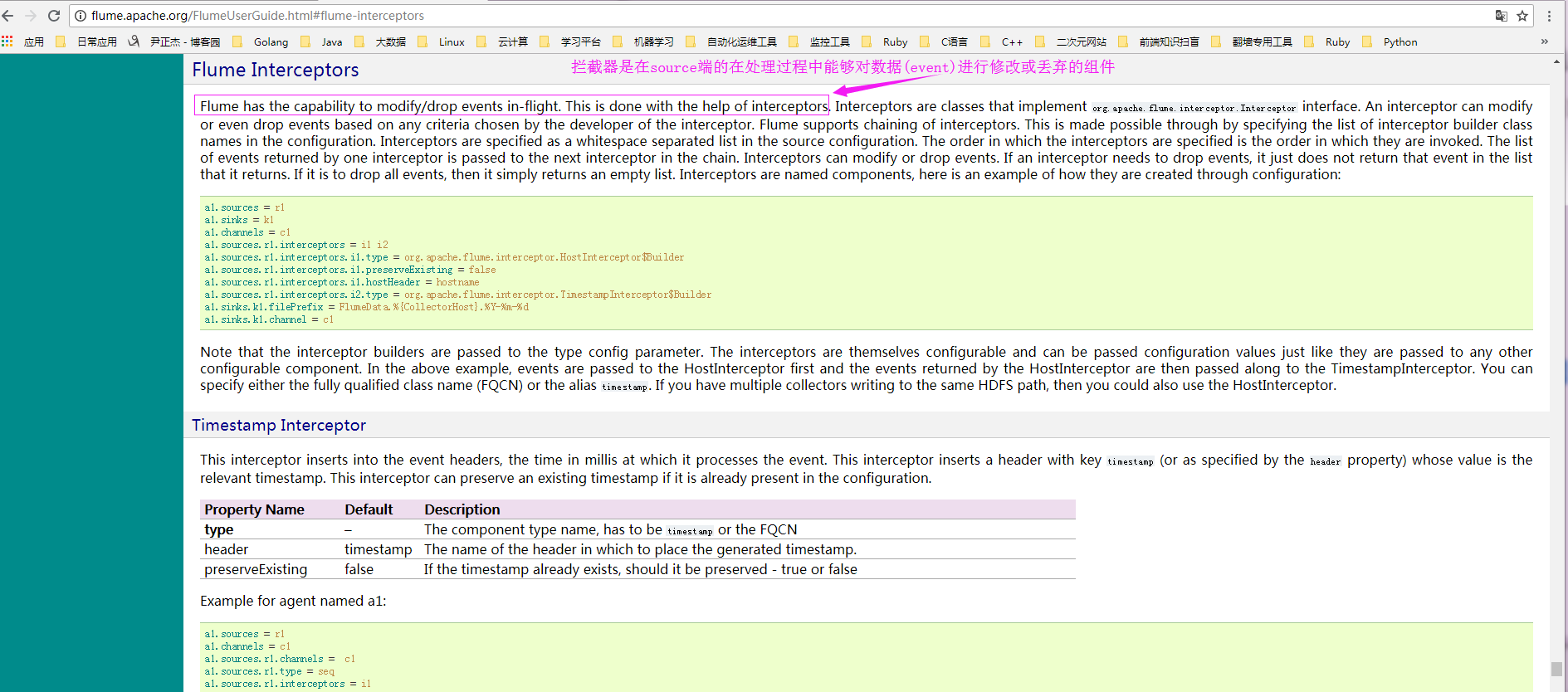
答:拦截器是在source端的在处理过程中能够对数据(event)进行修改或丢弃的组件。
2>.官方文档
3>.host interceptor(将发送的event添加主机名的header)配置案例
a>.实际配置参数:
[yinzhengjie@s101 ~]$ more /soft/flume/conf/yinzhengjie_hostInterceptor.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = # 指定添加拦截器
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = org.apache.flume.interceptor.HostInterceptor$Builder
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.preserveExisting = false
# 指定header的key
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.hostHeader = hostname
# 指定header的value为主机ip
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.useIP = true # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity =
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
[yinzhengjie@s101 ~]$
b>启动agent进程:
c>.source端产生数据(启动nc):
d>.检查sink端数据(检查定义好的目录"/home/yinzhengjie/log2")
4>.static interceptor(静态拦截器,手动指定key-value)配置案例
a>.实际配置参数:
[yinzhengjie@s101 ~]$ more /soft/flume/conf/yinzhengjie_staticInterceptor.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = # 指定添加拦截器
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = static
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.key = name
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.value = yinzhengjie # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity =
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
[yinzhengjie@s101 ~]$
b>启动agent进程:
c>.source端产生数据(启动nc):
d>.检查sink端数据(检查定义好的目录"/home/yinzhengjie/log2")
5>.timestamp interceptor(将发送的event添加时间戳的header)配置案例
a>.实际配置参数:
[yinzhengjie@s101 ~]$ more /soft/flume/conf/yinzhengjie_timestampInterceptor.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = # 指定添加拦截器
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = timestamp # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity =
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
[yinzhengjie@s101 ~]$
b>启动agent进程:
c>.source端产生数据(启动nc):
d>.检查sink端数据(检查定义好的目录"/home/yinzhengjie/log2")
6>.interceptor chain(连接器链)配置案例
a>.实际配置参数:
[yinzhengjie@s101 ~]$ more /soft/flume/conf/yinzhengjie_chainInterceptor.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = # 指定添加拦截器
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 i2 i3
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = org.apache.flume.interceptor.HostInterceptor$Builder
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.preserveExisting = false
# 指定header的key
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.hostHeader = hostname
# 指定header的value为主机ip
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.useIP = true # 添加i2拦截器
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i2.type = timestamp # 添加i3拦截器
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i3.type = remove_header
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i3.withName = timestamp # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity =
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 [yinzhengjie@s101 ~]$
b>启动agent进程:
c>.source端产生数据(启动nc):
d>.检查sink端数据(检查定义好的目录"/home/yinzhengjie/log2")
Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之拦截器与选择器的更多相关文章
- Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之自定义拦截器(interceptor)
Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之自定义拦截器(interceptor) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客只是举例了一个自定义拦截器的方法,测试字节传输速 ...
- Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之自定义Sink
Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之自定义Sink 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客主要介绍sink相关的API使用两个小案例,想要了解更多关于API的小技 ...
- Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之sink处理器
Hadoop生态圈-Flume的组件之sink处理器 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一. 二.
- Hadoop生态圈-Flume的主流source源配置
Hadoop生态圈-Flume的主流source源配置 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客只是配置的是Flume主流的Source,想要了解更详细的配置信息请参 ...
- Hadoop生态圈-flume日志收集工具完全分布式部署
Hadoop生态圈-flume日志收集工具完全分布式部署 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 目前为止,Hadoop的一个主流应用就是对于大规模web日志的分析和处理 ...
- 基于ambari搭建hadoop生态圈大数据组件
Ambari介绍1Apache Ambari是一种基于Web的工具,支持Apache Hadoop集群的供应.管理和监控.Ambari已支持大多数Hadoop组件,包括HDFS.MapReduce.H ...
- Hadoop生态圈-Flume的主流Channel源配置
Hadoop生态圈-Flume的主流Channel源配置 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一. 二. 三.
- Hadoop生态圈-Flume的主流Sinks源配置
Hadoop生态圈-Flume的主流Sinks源配置 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客只是配置的是Flume主流的Sinks,想要了解更详细的配置信息请参考官 ...
- Flume 拦截器(interceptor)详解
flume 拦截器(interceptor)1.flume拦截器介绍拦截器是简单的插件式组件,设置在source和channel之间.source接收到的事件event,在写入channel之前,拦截 ...
随机推荐
- 上google的方法
最近Google又被墙了....哎,纠结..... 说实话,咱都是良民,爱党爱国,真心不想干啥,只想查点资料的,输入google都上不去了. 方法: 1. FQ.很麻烦,有时候改来改去也容易出错,速度 ...
- [CF1009G]Allowed Letters[贪心+霍尔定理]
题意 给你一个长为 \(n\) 的串,字符集为 \(a,b,c,d,e,f\) .你可以将整个串打乱之后重新放置,但是某些位置上有一些限制:必须放某个字符集的字符.问字典序最小的串,如果无解输出 &q ...
- [转]JVM系列三:JVM参数设置、分析
不管是YGC还是Full GC,GC过程中都会对导致程序运行中中断,正确的选择不同的GC策略,调整JVM.GC的参数,可以极大的减少由于GC工作,而导致的程序运行中断方面的问题,进而适当的提高Java ...
- HTML5 标签实例
html 5 学习1.<p></p> #段落元素定义2.<h1></h1> #标题 h1代表大号的字体.依此变小3.<br /> #实例 代 ...
- Outlook2013修改数据文件默认存放目录
转载 当使用outlook 2013新建Email账户的时候,其数据文件(.ost文件)总是被保存在C盘默认目录“C:\Users\用户名\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Outloo ...
- EntityFramework Core 2.x (ef core) 在迁移中自动生成数据库表和列说明
在项目开发中有没有用过拼音首字母做列名或者接手这样的项目? 看见xmspsqb(项目审批申请表)这种表名时是否有一种无法抑制的想肛了取名的老兄的冲动? 更坑爹的是这种数据库没有文档(或者文档老旧不堪早 ...
- Ubuntu环境如何上传项目到GitHub网站?
http://blog.csdn.net/ajianyingxiaoqinghan/article/details/70544159
- Java设计模式之单例模式(七种写法)
Java设计模式之单例模式(七种写法) 第一种,懒汉式,lazy初始化,线程不安全,多线程中无法工作: public class Singleton { private static Singleto ...
- HBase集成(准备篇)
HBase与Hadoop各版本对照表:http://hbase.apache.org/book.html#configuration Hadoop 2.7.1+ 对应HBase 1.2.X,1.3.X ...
- 第十一周(11.24-12.01)----final评论II
1. Nice 项目:约跑软件 这款app非常实用.从性能上讲,这款软件基于Android开发.使用者只要注册就能实用,操作简便.在功能上,这款软件不仅为两个有意愿同时跑步的人牵线,为跑步的人提供跑 ...
