spring的嵌套事务
转自http://www.iteye.com/topic/35907
在所有使用 spring 的应用中, 声明式事务管理可能是使用率最高的功能了, 但是, 从我观察到的情况看, 绝大多数人并不能深刻理解事务声明中不同事务传播属性配置的的含义, 让我们来看一下 TransactionDefinition 接口中的定义:
/**
* Support a current transaction, create a new one if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p>This is typically the default setting of a transaction definition.
*/
int PROPAGATION_REQUIRED = 0; /**
* Support a current transaction, execute non-transactionally if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p>Note: For transaction managers with transaction synchronization,
* PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS is slightly different from no transaction at all,
* as it defines a transaction scopp that synchronization will apply for.
* As a consequence, the same resources (JDBC Connection, Hibernate Session, etc)
* will be shared for the entire specified scope. Note that this depends on
* the actual synchronization configuration of the transaction manager.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#setTransactionSynchronization
*/
int PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS = 1; /**
* Support a current transaction, throw an exception if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
*/
int PROPAGATION_MANDATORY = 2; /**
* Create a new transaction, suspend the current transaction if one exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p>Note: Actual transaction suspension will not work on out-of-the-box
* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to JtaTransactionManager,
* which requires the <code>javax.transaction.TransactionManager</code> to be
* made available it to it (which is server-specific in standard J2EE).
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager
*/
int PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW = 3; /**
* Execute non-transactionally, suspend the current transaction if one exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p>Note: Actual transaction suspension will not work on out-of-the-box
* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to JtaTransactionManager,
* which requires the <code>javax.transaction.TransactionManager</code> to be
* made available it to it (which is server-specific in standard J2EE).
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager
*/
int PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED = 4; /**
* Execute non-transactionally, throw an exception if a transaction exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
*/
int PROPAGATION_NEVER = 5; /**
* Execute within a nested transaction if a current transaction exists,
* behave like PROPAGATION_REQUIRED else. There is no analogous feature in EJB.
* <p>Note: Actual creation of a nested transaction will only work on specific
* transaction managers. Out of the box, this only applies to the JDBC
* DataSourceTransactionManager when working on a JDBC 3.0 driver.
* Some JTA providers might support nested transactions as well.
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
*/
int PROPAGATION_NESTED = 6;
我们可以看到, 在 spring 中一共定义了六种事务传播属性, 如果你觉得看起来不够直观, 那么我来转贴一个满大街都有的翻译 :
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRED -- 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。这是最常见的选择。
- PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS -- 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。
- PROPAGATION_MANDATORY -- 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。
- PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW -- 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。
- PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED -- 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。
- PROPAGATION_NEVER -- 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。
- PROPAGATION_NESTED -- 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则进行与PROPAGATION_REQUIRED类似的操作。
- 前六个策略类似于EJB CMT,第七个(PROPAGATION_NESTED)是Spring所提供的一个特殊变量。
- 它要求事务管理器或者使用JDBC 3.0 Savepoint API提供嵌套事务行为(如Spring的DataSourceTransactionManager)
在我所见过的误解中, 最常见的是下面这种:
假如有两个业务接口 ServiceA 和 ServiceB, 其中 ServiceA 中有一个方法实现如下 /**
* 事务属性配置为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
*/
void methodA() {
// 调用 ServiceB 的方法
ServiceB.methodB();
} 那么如果 ServiceB 的 methodB 如果配置了事务, 就必须配置为 PROPAGATION_NESTED?
这种想法可能害了不少人, 认为 Service 之间应该避免互相调用, 其实根本不用担心这点,PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 已经说得很明白, 如果当前线程中已经存在事务, 方法调用会加入此事务, 果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务, 所以 ServiceB#methodB() 的事务只要遵循最普通的规则配置为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 即可, 如果 ServiceB#methodB (我们称之为内部事务, 为下文打下基础) 抛了异常, 那么 ServiceA#methodA(我们称之为外部事务) 如果没有特殊配置此异常时事务提交 (即 +MyCheckedException的用法), 那么整个事务是一定要 rollback 的, 什么 Service 只能调 Dao 之类的言论纯属无稽之谈, spring 只负责配置了事务属性方法的拦截, 它怎么知道你这个方法是在 Service 还是 Dao 里 ?
最容易弄混淆的其实是 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 和 PROPAGATION_NESTED, 那么这两种方式又有何区别呢? 翻译一下 Juergen Hoeller 的话 :
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 启动一个新的, 不依赖于环境的 "内部" 事务. 这个事务将被完全 commited 或 rolled back 而不依赖于外部事务, 它拥有自己的隔离范围, 自己的锁, 等等. 当内部事务开始执行时, 外部事务将被挂起, 内务事务结束时, 外部事务将继续执行.
另一方面, PROPAGATION_NESTED 开始一个 "嵌套的" 事务, 它是已经存在事务的一个真正的子事务. 潜套事务开始执行时, 它将取得一个 savepoint. 如果这个嵌套事务失败, 我们将回滚到此 savepoint. 潜套事务是外部事务的一部分, 只有外部事务结束后它才会被提交.
由此可见, PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 和 PROPAGATION_NESTED 的最大区别在于, PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 完全是一个新的事务, 而 PROPAGATION_NESTED 则是外部事务的子事务, 如果外部事务 commit, 潜套事务也会被 commit, 这个规则同样适用于 roll back.
那么外部事务如何利用嵌套事务的 savepoint 特性呢, 我们用代码来说话 :
ServiceA {
/**
* 事务属性配置为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
*/
void methodA() {
ServiceB.methodB();
}
}
ServiceB {
/**
* 事务属性配置为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW
*/
void methodB() {
}
}
这种情况下, 因为 ServiceB#methodB 的事务属性为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW, 所以两者不会发生任何关系, ServiceA#methodA 和 ServiceB#methodB 不会因为对方的执行情况而影响事务的结果, 因为它们根本就是两个事务, 在 ServiceB#methodB 执行时 ServiceA#methodA 的事务已经挂起了 (关于事务挂起的内容已经超出了本文的讨论范围, 有时间我会再写一些挂起的文章) .
那么 PROPAGATION_NESTED 又是怎么回事呢? 继续看代码
ServiceA {
/**
* 事务属性配置为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
*/
void methodA() {
ServiceB.methodB();
}
}
ServiceB {
/**
* 事务属性配置为 PROPAGATION_NESTED
*/
void methodB() {
}
}
现在的情况就变得比较复杂了, ServiceB#methodB 的事务属性被配置为 PROPAGATION_NESTED, 此时两者之间又将如何协作呢? 从 Juergen Hoeller 的原话中我们可以找到答案, ServiceB#methodB 如果 rollback, 那么内部事务(即 ServiceB#methodB) 将回滚到它执行前的 SavePoint(注意, 这是本文中第一次提到它, 嵌套事务中最核心的概念), 而外部事务(即 ServiceA#methodA) 可以有以下两种处理方式:
1. 改写 ServiceA 如下
ServiceA {
/**
* 事务属性配置为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
*/
void methodA() {
try {
ServiceB.methodB();
} catch (SomeException) {
// 执行其他业务, 如 ServiceC.methodC();
}
}
}
这种方式也是潜套事务最有价值的地方, 它起到了分支执行的效果, 如果 ServiceB.methodB 失败, 那么执行 ServiceC.methodC(), 而 ServiceB.methodB 已经回滚到它执行之前的 SavePoint, 所以不会产生脏数据(相当于此方法从未执行过), 这种特性可以用在某些特殊的业务中, 而 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 和 PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 都没有办法做到这一点. (题外话 : 看到这种代码, 似乎似曾相识, 想起了 prototype.js 中的 Try 函数 )
2. 代码不做任何修改, 那么如果内部事务(即 ServiceB#methodB) rollback, 那么首先 ServiceB.methodB 回滚到它执行之前的 SavePoint(在任何情况下都会如此), 外部事务(即 ServiceA#methodA) 将根据具体的配置决定自己是 commit 还是 rollback (+MyCheckedException).
上面大致讲述了潜套事务的使用场景, 下面我们来看如何在 spring 中使用 PROPAGATION_NESTED, 首先来看 AbstractPlatformTransactionManager :
/**
* Create a TransactionStatus for an existing transaction.
*/
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException { ... 省略 if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
}
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
// Create savepoint within existing Spring-managed transaction,
// through the SavepointManager API implemented by TransactionStatus.
// Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization.
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
newTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
}
else {
// Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls.
// Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here
// in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction.
doBegin(transaction, definition);
boolean newSynchronization = (this.transactionSynchronization != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
return newTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
}
}
}
一目了然
1. 我们要设置 transactionManager 的 nestedTransactionAllowed 属性为 true, 注意, 此属性默认为 false!!!
再看 AbstractTransactionStatus#createAndHoldSavepoint() 方法
/**
* Create a savepoint and hold it for the transaction.
* @throws org.springframework.transaction.NestedTransactionNotSupportedException
* if the underlying transaction does not support savepoints
*/
public void createAndHoldSavepoint() throws TransactionException {
setSavepoint(getSavepointManager().createSavepoint());
}
可以看到 Savepoint 是 SavepointManager.createSavepoint 实现的, 再看 SavepointManager 的层次结构, 发现 其 Template 实现是 JdbcTransactionObjectSupport, 常用的 DatasourceTransactionManager, HibernateTransactionManager 中的 TransactonObject 都是它的子类 :
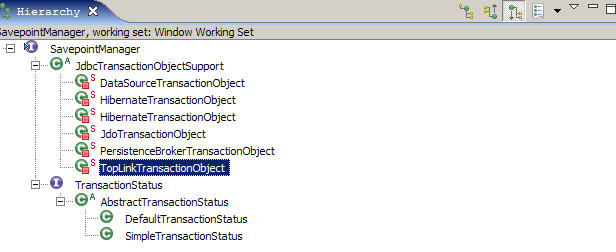
JdbcTransactionObjectSupport 告诉我们必须要满足两个条件才能 createSavepoint :
1. java.sql.Savepoint 必须存在, 即 jdk 版本要 1.4+
2. Connection.getMetaData().supportsSavepoints() 必须为 true, 即 jdbc drive 必须支持 JDBC 3.0
确保以上条件都满足后, 你就可以尝试使用 PROPAGATION_NESTED 了.
spring的嵌套事务的更多相关文章
- 一次Spring Transactional嵌套事务使用不同的rollbackFor的分析
起因: 项目期间由于一次异常回滚问题,发现自己在事务知识方面知识的遗漏,趁着这次机会,做了几次rollbackFor的测试. 测试: 现在有两个事务,事务oute包含事务Inner.事务A回滚规则 ...
- Spring:Spring嵌套事务方式
Spring遇到嵌套事务时,怎么实现 实验时却遇到一个奇怪的问题: 1.当ServiceA.a()方法调用ServiceB.b()方法时,内层事务提交和回滚,都不受外层事务提交或回滚的影响. 2.当S ...
- spring知识大全(4)
5 Spring对事务的支持 一.AOP事务的含义: 事务当作一个切面,动态地织入到目标对象,形成一个代理对象. 二.Spring的事务机制 Spring支持声明式事务. Spring使用事务服务代理 ...
- (转)添加PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 事务没有产生作用
最近在做事务添加时 发现自己的事务没有新建,上网查到 仅用作收藏. 其二 注意 事务的注解 应该在 内层的事务上面 一.描述 Spring遇到嵌套事务时,当被嵌套的事务被定义为" ...
- 添加PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 事务没有产生作用
最近在做事务添加时 发现自己的事务没有新建,上网查到 仅用作收藏. 其二 注意 事务的注解 应该在 内层的事务上面 一.描述Spring遇到嵌套事务时,当被嵌套的事务被定义为“PROPAG ...
- SpringBoot整合MongoDB,在多数据源下实现事务回滚。
项目中用到了MongoDB,准备用来存储业务数据,前提是要实现事务,保证数据一致性,MongoDB从4.0开始支持事务,提供了面向复制集的多文档事务特性.能满足在多个操作,文档,集合,数据库之间的事务 ...
- 脱离 Spring 实现复杂嵌套事务,之一(必要的概念)
事务传播行为种类 Spring在TransactionDefinition接口中规定了7种类型的事务传播行为, 它们规定了事务方法和事务方法发生嵌套调用时事务如何进行传播: 表1事务传播行为类型 事务 ...
- 关于Spring 事务管理传播属性的配置及作用-嵌套事务
先了解事务的7种传播属性: PROPAGATION_REQUIRED -- 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务.这是最常见的选择. PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS -- 支持当前 ...
- 事务之六:spring 嵌套事务
一.基本概念 事务的隔离级别,事务传播行为见<事务之二:spring事务(事务管理方式,事务5隔离级别,7个事务传播行为,spring事务回滚条件) > 二. 嵌套事务示例 2.1.Pro ...
随机推荐
- 记一次paramiko远程连接遇到的坑
背景:工作中遇到了一个问题,需要用到windows向windows连接(文件传发)以及,linux向windows连接(文件传发)的需求. 自然而然会考虑到用paramiko,然而paramiko我用 ...
- c++/c关于函数指针
顺便提一句:指针也是一种变量类型 和 int double 这些类型是一个级别 不同的是它的值是地址 #include "stdafx.h"#include<stdlib.h ...
- loadrunner中的ie浏览器无法使用
我的loadrunner是12.55版本的,windows10系统 在我们学习loadrunner的过程中,会出现下面一个问题: 在录制脚本时,loadrunner中的ie浏览器无法使用处于飘红状态. ...
- 一文速览Vue全栈
一文速览Vue全栈 原创: 新哥Lewis 天道酬勤Lewis 7月7日 Vue 是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架.与其它大型框架不同的是,Vue 被设计为可以自底向上逐层应用,专注于声明式渲染视图 ...
- Hibernate的执行流程
Hibernate框架的工作流程 1.通过Configuration().configure();读取并解析hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件 2.由hibernate.cfg.xml中的&l ...
- Windows下的bat原来可以为我们做很多
用了windows系统这么多年了,对bat也不是很了解.最近研究了一下bat的用法.这里就大概列举一下自己的用法 参考网址 基本命令 echo echo我们可以理解成程序中的输出,和我们Java的Sy ...
- 如何在GitHub上上传自己本地的项目?(很适合新手使用哦!)
这是我看了一些大佬们的博客后,尝试了几次,终于成功了上传项目,所以想做一下总结,以便以后查看,同时想分享给才接触GitHub的新手们,希望能够有所帮助~ 条条大路通罗马,上传的方法肯定不止一种,等我学 ...
- [HNOI2009]双递增序列(动态规划,序列dp)
感觉这个题还蛮难想的. 首先状态特别难想.设\(dp[i][j]\)表示前i个数,2序列的长度为j的情况下,2序列的最后一个数的最小值. 其中1序列为上一个数所在的序列,2序列为另外一个序列. 这样设 ...
- SpringBoot中快速实现邮箱发送
前言 在许多企业级项目中,需要用到邮件发送的功能,如: 注册用户时需要邮箱发送验证 用户生日时发送邮件通知祝贺 发送邮件给用户等 创建工程导入依赖 <!-- 邮箱发送依赖 --> < ...
- 一句道破所有的springmvc(面试必备)
springmvc流程 : URL--------前端控制器DispatcherServlet---------HandlerMapping处理器映射器-------调用HandlerAdapter处 ...
