Morley's Theorem (计算几何基础+向量点积、叉积、旋转、夹角等+两直线的交点)
题目链接:https://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&page=show_problem&problem=2119
题面:Morleys theorem states that that the lines trisecting the angles of an arbitrary plane triangle meet at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. For example in the figure below the tri-sectors of angles A, B and C has intersected and created an equilateral triangle DEF. Of course the theorem has various generalizations, in particular if all of the trisectors are intersected one obtains four other equilateral triangles. But in the original theorem only tri-sectors nearest to BC are allowed to intersect to get point D, tri-sectors nearest to CA are allowed to intersect point E and tri-sectors nearest to AB are intersected to get point F. Trisector like BD and CE are not allowed to intersect. So ultimately we get only one equilateral triangle DEF. Now your task is to find the Cartesian coordinates of D, E and F given the coordinates of A, B, and C.
Input
First line of the input file contains an integer N (0 < N < 5001) which denotes the number of test cases to follow. Each of the next lines contain six integers XA,YA,XB,YB,XC,YC. This six integers actually indicates that the Cartesian coordinates of point A, B and C are (XA,YA),(XB,YB) and (XC,YC) respectively. You can assume that the area of triangle ABC is not equal to zero, 0 ≤ XA,YA,XB,YB,XC,YC ≤ 1000 and the points A, B and C are in counter clockwise order.
Output
For each line of input you should produce one line of output. This line contains six floating point numbers XD,YD,XE,YE,XF,YF separated by a single space. These six floating-point actually means that the Cartesian coordinates of D, E and F are (XD,YD),(XE,YE) ,(XF,YF) respectively. Errors less than 10−5 will be accepted.
Sample Input
2
1 1 2 2 1 2
0 0 100 0 50 50
Sample Output
1.316987 1.816987 1.183013 1.683013 1.366025 1.633975
56.698730 25.000000 43.301270 25.000000 50.000000 13.397460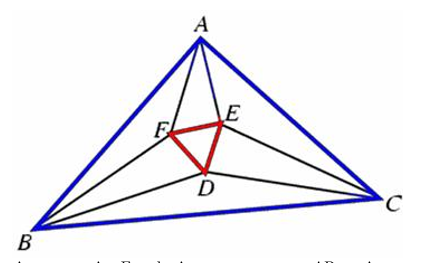
思路:本题为一道比较简单的计算几何入门题,运用了很多的计算几何知识,不过只要想通如何求DEF的话,就只需通过套用模板即可解决
代码实现如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std; struct Point{
double x,y;
Point(double x = , double y = ) : x(x), y(y) {}
}; typedef Point Vector; int t;
Point A, B, C, D, E, F; Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B){
return Vector(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y);
} Vector operator - (Vector A, Vector B){
return Vector(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y);
} Vector operator * (Vector A, double p){
return Vector(A.x * p, A.y * p);
} Vector operator / (Vector A, double p){
return Vector(A.x / p, A.y / p);
} double Dot(Vector A, Vector B){
return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y;
} double Length(Vector A){
return sqrt(Dot(A, A));
} double Angle(Vector A, Vector B){
return acos(Dot(A, B) / Length(A) / Length(B));
} Vector Rotate(Vector A, double rad){
return Vector(A.x * cos(rad) - A.y * sin(rad), A.x * sin(rad) + A.y * cos(rad));
} double Cross(Vector A, Vector B){
return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x;
} Point GetLineIntersection(Point P, Vector v, Point Q, Vector w){
Vector u = P - Q;
double t = Cross(w, u) / Cross(v, w);
return P + v * t;
} Point GetD(Point A, Point B, Point C){
Vector v1 = C - B;
double a1 = Angle((A - B), v1);
v1 = Rotate(v1, a1 / ); Vector v2 = B - C;
double a2 = Angle((A - C), v2);
v2 = Rotate(v2, -a2 / ); return GetLineIntersection(B, v1, C, v2);
} int main(){
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--){
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &A.x, &A.y, &B.x, &B.y, &C.x, &C.y);
D = GetD(A, B, C);
E = GetD(B, C, A);
F = GetD(C, A, B);
printf("%.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f\n", D.x, D.y, E.x, E.y, F.x, F.y);
}
}
Morley's Theorem (计算几何基础+向量点积、叉积、旋转、夹角等+两直线的交点)的更多相关文章
- 51nod--1265 四点共面 (计算几何基础, 点积, 叉积)
题目: 1265 四点共面 基准时间限制:1 秒 空间限制:131072 KB 分值: 0 难度:基础题 收藏 关注 给出三维空间上的四个点(点与点的位置均不相同),判断这4个点是否在同一个平面内(4 ...
- Uva 11178 Morley's Theorem 向量旋转+求直线交点
http://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=9 题意: Morlery定理是这样的:作三角形ABC每个 ...
- UVA_11178_Morley's_Theorem_(计算几何基础)
描述 https://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&category=23&pag ...
- uva 11178二维几何(点与直线、点积叉积)
Problem D Morley’s Theorem Input: Standard Input Output: Standard Output Morley’s theorem states tha ...
- AC日记——向量点积计算 openjudge 1.6 09
09:向量点积计算 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 在线性代数.计算几何中,向量点积是一种十分重要的运算. 给定两个n维向量a=(a1,a2,...,an)和b=(b ...
- UVa 11178:Morley’s Theorem(两射线交点)
Problem DMorley’s TheoremInput: Standard Input Output: Standard Output Morley’s theorem states that ...
- UVA 11178 Morley's Theorem(几何)
Morley's Theorem [题目链接]Morley's Theorem [题目类型]几何 &题解: 蓝书P259 简单的几何模拟,但要熟练的应用模板,还有注意模板的适用范围和传参不要传 ...
- SAM4E单片机之旅——24、使用DSP库求向量数量积
DSP(Digital Signal Processing,数字信号处理)中会使用大量的数学运算.Cortex-M4中,配置了一些强大的部件,以提高DSP能力.同时CMSIS提供了一个DSP库,提供了 ...
- uva11178 Morley’s Theorem(求三角形的角三分线围成三角形的点)
Morley’s Theorem Input: Standard Input Output: Standard Output Morley’s theorem states that that the ...
随机推荐
- 3dContactPointAnnotationTool开发日志(二二)
昨天是实现了显示GameObject子GameObject的选项卡功能,今天就是要让statusPanel可以控制它们的位置.旋转和缩放了. 没什么难的,对应选项卡绑定上对应的物体或子物体即可 ...
- CEntOS6.5从启动界面直接进入命令行界面
ctrl + alt + F1 ctrl + alt + F2 ctrl + alt + F3 ctrl + alt + F4 ctrl + alt + F5 ctrl + alt + F6 同时按下 ...
- WebExtensions & tabs.executeScript()
tabs.executeScript() https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Add-ons/WebExtensions/API/tabs ...
- poj 1422 Air Raid (二分匹配)
Air Raid Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 6520 Accepted: 3877 Descript ...
- P1297 [国家集训队]单选错位
题目背景 原 <网线切割>请前往P1577 题目描述 gx和lc去参加noip初赛,其中有一种题型叫单项选择题,顾名思义,只有一个选项是正确答案.试卷上共有n道单选题,第i道单选题有ai个 ...
- (一)Redis简介及安装
Redis简介 Redis 是一个开源(BSD许可)的,内存中的key-value数据结构存储系统,它可以用作数据库.缓存和消息中间件. Redis具有丰富的数据结构类型.包括字符串(string), ...
- BZOJ5338:[TJOI2018]异或——题解
https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=5338 现在有一颗以1为根节点的由n个节点组成的树,树上每个节点上都有一个权值vi. 现在有Q 次操 ...
- HDU5726:GCD——题解
题目:hdu的5726 (我原博客的东西,正好整理过来,属于st表裸题) (可以看出我当时有多么的菜--) 这道题写了一遍,然而蒟蒻的我的时间爆炸了-- 于是看了一下学长的代码(顺便在此处%一下学长) ...
- [Leetcode] Maximum depth of binary tree二叉树的最大深度
Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth. The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the long ...
- HDOJ.1342 Lotto (DFS)
Lotto [从零开始DFS(0)] 点我挑战题目 从零开始DFS HDOJ.1342 Lotto [从零开始DFS(0)] - DFS思想与框架/双重DFS HDOJ.1010 Tempter of ...
