hdu-5714 拍照(二分)
题目链接:
拍照
Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others)
Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
小明位于河的边上,并且可以在河边的任意位置进行拍照,照相机的视野恰好为90度角,只能以垂直于河边的方向进行拍照。河上的船只全都可看作是平行于河边的一条线段,跟河边的距离各不相同,有的正在向左移动,有的正在向右移动,但移动速度恰好都是一样的。小明可以等待恰当的时间让尽量多的船只都走进照相机的视野里,你不需要考虑船只之间会互相遮挡视野的情况。
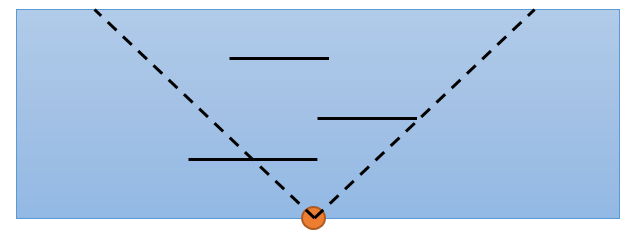
下面T组数据,对于每组数据:
第一行是一个数n(1≤n≤10^4),表示船只的数量。
接下来n行,每行四个整数
x,y,z,d(−10^6≤x<y≤10^6,1≤z≤10^4),表示船只的左端点位置、右端点位置、距离河边的距离,以及航行的方向。d为−1表示向左航行,1表示向右航行。
Case #i:
然后输出一行,仅包含一个整数,表示最多可以拍到多少完整的船只。
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//有树状数组的
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio> using namespace std;
#define Riep(n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
#define Riop(n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
#define Rjep(n) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
#define Rjop(n) for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
#define mst(ss,b) memset(ss,b,sizeof(ss));
typedef long long LL;
template<class T> void read(T&num) {
char CH; bool F=false;
for(CH=getchar();CH<''||CH>'';F= CH=='-',CH=getchar());
for(num=;CH>=''&&CH<='';num=num*+CH-'',CH=getchar());
F && (num=-num);
}
int stk[], tp;
template<class T> inline void print(T p) {
if(!p) { puts(""); return; }
while(p) stk[++ tp] = p%, p/=;
while(tp) putchar(stk[tp--] + '');
putchar('\n');
} const LL mod=1e9+;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const LL inf=1e18;
const int N=1e4+; int n,sum[][*N],a[*N],b[*N],pre[*N],nex[*N];
int num,mmax; struct node
{
int l,r,d;
}po[*N]; int findpos(int x)
{
int l=,r=mmax;
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>;
if(b[mid]<x)l=mid+;
else r=mid-;
}
return l;
} int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int x,int y,int flag)
{
while(x<=mmax)
{
sum[flag][x]+=y;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int query(int x,int flag)
{
int s=;
while(x>)
{
s+=sum[flag][x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return s;
} int main()
{
int t;
read(t);
int Case=;
while(t--)
{
mst(sum,);
int x,y,z,d,cnt=;
num=;
mmax=; read(n);
Riep(n)
{
read(x),read(y),read(z),read(d);
if(x+z<y-z)continue;
po[cnt].l=y-z;
po[cnt].r=x+z;
if(d==-)po[cnt++].d=;
else po[cnt++].d=d;
a[++num]=y-z;
a[++num]=x+z;
}
sort(a+,a+num+);
b[++mmax]=a[];
for(int i=;i<=num;i++)
{
if(a[i]!=a[i-])b[++mmax]=a[i];
} for(int i=;i<cnt;i++)
{
po[i].l=findpos(po[i].l);
po[i].r=findpos(po[i].r);
update(po[i].l,,po[i].d);
update(po[i].r+,-,po[i].d);
}
for(int i=;i<=mmax;i++)
{
pre[i]=max(query(i,),pre[i-]);
nex[i]=query(i,);
}
int ans=;
nex[mmax+]=;
for(int i=mmax;i>;i--)
{
nex[i]=max(nex[i+],nex[i]);
ans=max(ans,pre[i]+nex[i]);
}
printf("Case #%d:\n",Case++);
print(ans);
}
return ;
}
//#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio> using namespace std;
#define Riep(n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
#define Riop(n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
#define Rjep(n) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
#define Rjop(n) for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
#define mst(ss,b) memset(ss,b,sizeof(ss));
typedef long long LL;
template<class T> void read(T&num) {
char CH; bool F=false;
for(CH=getchar();CH<''||CH>'';F= CH=='-',CH=getchar());
for(num=;CH>=''&&CH<='';num=num*+CH-'',CH=getchar());
F && (num=-num);
}
int stk[], tp;
template<class T> inline void print(T p) {
if(!p) { puts(""); return; }
while(p) stk[++ tp] = p%, p/=;
while(tp) putchar(stk[tp--] + '');
putchar('\n');
} const LL mod=1e9+;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const LL inf=1e18;
const int N=1e4+; int n,sum[][*N],a[*N],b[*N],pre[*N],nex[*N],sum1[*N],sum2[*N];
int num,mmax; struct node
{
int l,r,d;
}po[*N]; int findpos(int x)
{
int l=,r=mmax;
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>;
if(b[mid]<x)l=mid+;
else r=mid-;
}
return l;
} int main()
{
int t;
read(t);
int Case=;
while(t--)
{
mst(sum,);
int x,y,z,d,cnt=;
num=;
mmax=; read(n);
Riep(n)
{
read(x),read(y),read(z),read(d);
if(x+z<y-z)continue;
po[cnt].l=y-z;
po[cnt].r=x+z;
if(d==-)po[cnt++].d=;
else po[cnt++].d=d;
a[++num]=y-z;
a[++num]=x+z;
}
sort(a+,a+num+);
b[++mmax]=a[];
for(int i=;i<=num;i++)
{
if(a[i]!=a[i-])b[++mmax]=a[i];
} for(int i=;i<cnt;i++)
{
po[i].l=findpos(po[i].l);
po[i].r=findpos(po[i].r);
sum[po[i].d][po[i].l]++;
sum[po[i].d][po[i].r+]--;
}
for(int i=;i<=mmax;i++)
{
sum1[i]=sum1[i-]+sum[][i];
sum2[i]=sum2[i-]+sum[][i];
nex[i]=sum1[i];
pre[i]=max(pre[i-],sum2[i]);
}
int ans=;
nex[mmax+]=;
for(int i=mmax;i>;i--)
{
nex[i]=max(nex[i+],nex[i]);
ans=max(ans,pre[i]+nex[i]);
}
printf("Case #%d:\n",Case++);
print(ans);
}
return ;
}
hdu-5714 拍照(二分)的更多相关文章
- HDU 5714 拍照 前缀和
拍照 题目连接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5714 Description 小明在旅游的路上看到了一条美丽的河,河上有许多船只,有的船只向左 ...
- UVA 10816 + HDU 1839 Dijstra + 二分 (待研究)
UVA 题意:两个绿洲之间是沙漠,沙漠的温度不同,告诉起点,终点,求使得从起点到终点的最高温度最小的路径,如果有多条,输出长度最短的路径: 思路:用最小费用(最短路径)最大流(最小温度)也能搞吧,但因 ...
- hdu 2413(最大匹配+二分)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2413 思路:由于要求最少的时间,可以考虑二分,然后就是满足在limit时间下,如果地球战舰数目比外星战 ...
- HDU 5884 Sort (二分)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5884 nn个有序序列的归并排序.每次可以选择不超过kk个序列进行合并,合并代价为这些序列的长度和.总的 ...
- hdu 1281棋盘游戏(二分匹配)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1281 Problem Description 小希和Gardon在玩一个游戏:对一个N*M的棋盘, ...
- HDU 1025 DP + 二分
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1025 求最长递增子序列,O(n^2)的复杂度超时,需要优化为O(n*logn) f[i]存储长度为i的最小 ...
- hdu 2289 要二分的杯子
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2289 大意是 一个Cup,圆台形,给你它的顶部圆的半径,底部圆的半径,杯子的高度,和此时里面装的水的体 ...
- HDU 1025 LIS二分优化
题目链接: acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1025 Constructing Roads In JGShining's Kingdom Time Limit: ...
- HDU 5200 Trees 二分
题目链接: hdu:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5200 bc(中文):http://bestcoder.hdu.edu.cn/contests ...
随机推荐
- VS2010 远程调试
1.在客户端电脑建一个账户,账户名和密码和调试端的账户密码一样 2.在客户端电脑进入 管理工具-本地安全策略-本地策略-安全选项 网络访问:本地账户的共享和安全模式”,改为“经典-本地用户以自己的身份 ...
- [翻译]比较ADO.NET中的不同数据访问技术(Performance Comparison:Data Access Techniques)
Performance Comparison: Data Access Techniques Priya DhawanMicrosoft Developer Network January 2002 ...
- ref和out的使用与区别
out的使用 ————————————————————————————————————————————————— class Program { static void Main( ...
- gitignore无效最简单解决办法
git rm --cached 文件或者文件夹 git commit 提交 git push 提交
- iOS开发-核心动画随笔
核心动画可以让View旋转,缩放,平移(主要是操作View的layer(层)属性)但是核心动画改变的位置不是真实的位置,一切都是假象所以有时候要用到其他动画,如UIView本来封装的动画,还有定时器 ...
- hdu4291之矩阵快速幂
A Short problem Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-2 INITIALIZATION and DATA TRANSFER
http://ecad.tu-sofia.bg/et/2005/pdf/Paper097-P_Dzhelekarski1.pdf INITIALIZATION Prior to any diagnos ...
- js查看浏览器类型和版本
var Sys = {}; var ua = navigator.userAgent.toLowerCase(); var s; var scan; (s = ua.match(/msie ([\d. ...
- 14的路 MySQL的btree索引和hash索引的区别
http://www.cnblogs.com/vicenteforever/articles/1789613.html ash 索引结构的特殊性,其检索效率非常高,索引的检索可以一次定位,不像B-Tr ...
- Java学习笔记之==与equals
一.问题引入 Java测试两个变量是否相等有两种方式:==运算符和equals方法. 但是这二者完全一样吗?考虑下面程序: public class TestEqual { public static ...
