SpringBoot(二) - 核心配置文件
1、application.properties 和 application.yml 配置文件格式区别
1.1 文件格式
application.properties
# 端口号
server.port=8096
application.yml
# 服务端口
server:
port: 8096
1.2 区别
- properties的优先级高于yml,同等配置,高优先级会覆盖低优先级,不同的配置时互补配置(增补,不管哪个配置文件中有,都可以生效);
- properties的核心语法是:通过 . 作为层级分隔符,配置值是用 = ,比如 server.port=9096
yml的核心语法是:通过层级+缩进的方式,同一给等级,缩进是相同的,配置使用key: value方式- server:
port: 8096 #注意值前面必须有空格
- server:
- 小结:yml格式配置,可以简化配置内容,层次清晰,更适合作为核心配置文件;
2、自定义配置
2.1 配置信息 yml 语法
注意:值前面必须有空格;
2.1.1 基本类型数据
user:
userId: kh96
user-Name: gala # 支持松散绑定
user_age: 17
adult: true # 是否成年
salary: 9696.0
userTel: 13501020304
birthday: 2002/10/11 10:10:10
email: kh96@163.com
2.1.2 数组,List,Set
user:
hobbies: # 爱好 list集合
- springboot
- linux
- mysql
- ssm
- jvaweb
- springvloud
#行内写法
#hobbies:[springboot,linux,mysql,ssm,jvaweb,springvloud]
2.1.3 Map
user:
carMap: # 爱车 map 集合
bnm: 宝马325
audi: 奥迪A41
benz: 奔驰C200
#行内写法
#carMap:{bnm: 宝马325;audi: 奥迪A41;benz: 奔驰C200}
2.1.4 实体参数
user:
userRole:
role-id: R96 ${random.uuid} #${}可以去一些内置的自定义参数
role_name: root
2.1.5 值的写法
2.1.5.1 单引号:
会转义特殊字符。
user:
msg: '你好!\n小可爱!'
输出:
你好!\n小可爱!
2.1.5.2 双引号:
不会转义字符里的特殊字符,特殊字符仍然是本身的意思
user:
msg: "你好!\n小可爱!"
输出:
你好!
小可爱!
2.2 获取 配置信息
2.2.1 批量自动读取
使用注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "xxx") ,必须配合@Component 注解获取在核心启动类上使用 @EnableConfigurationProperties(配置属性读取类.class)使用;
特点:支持松散绑定(可以自动识别驼峰,-,_),支持复杂类型绑定(实体,集合-list,set,array,map等),支持数据格式校验;
@Component + @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
或
@Component
+
@EnableConfigurationProperties(UserProperties.class) //写在主启动类上
2.2.1.1 UserProperties
@Data
@Component //第一个写法,使用普通组件
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user") //不能单独使用,必须配合@EnableConfigurationProperties 或指定为spring容器中的普通组件
public class UserProperties {
//用户编号
private String userId;
//用户名
private String userName;
//用户年龄
private Integer userAge;
//是否成年
private boolean adult;
//工资
private double salary;
//联系方式
private String userTel;
//生日
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8") //springMVC将将数据转成json格式,时间格式规则
private Date birthday;
//用户角色
private UserRole userRole; //实体参数
//爱好
private List<String> hobbies;
//爱车
private Map<String,String> carMap;
//邮箱
@Email //邮箱格式校验
private String email;
}
2.2.1.1.2 运行结果:
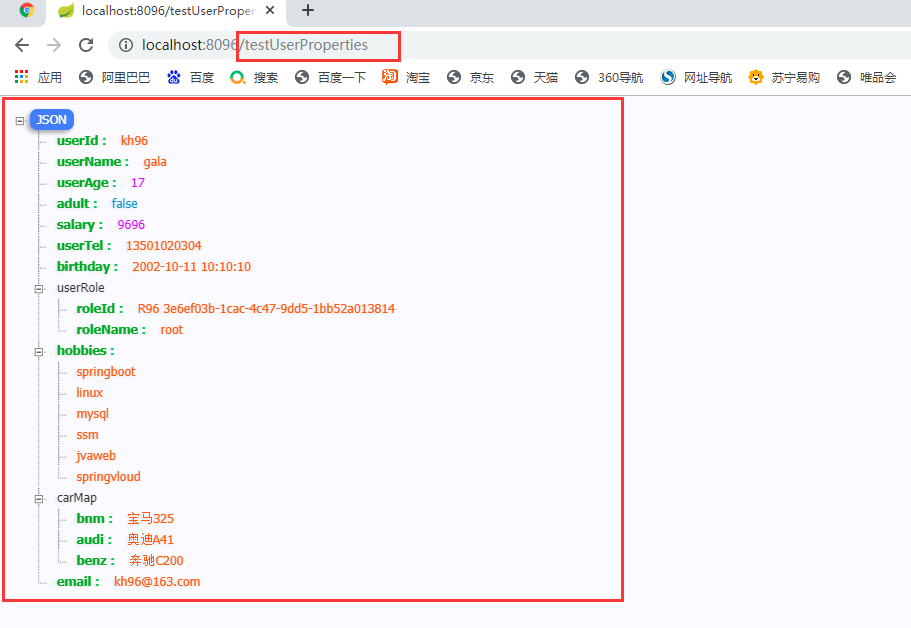
2.2.2 单个手动读取
用法:使用注解@Value("${xxx.xxx}");
特点:写法灵活,可以指定默认值等,但是不支持松散绑定,单个读取的配置要求指定的读取属性key必须和自定义配置一直,否者报错;
@Component + @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
2.2.2.1 UserProperties
@Data
@Component
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:user.properties")
//@EnableConfigurationProperties(UserProperties.class) //第二种方式,核心启动类上,增加指定开启自动配置读取,但是一般不怎么使用,且容易忘记
public class UserProperties {
//用户编号
@Value("${user.userId}")
private String userId;
//用户名
@Value("${user.user-Name}")
private String userName;
//昵称
@Value("#{userValues.userName}") //获取的是容器中已有的实体的值
//@Value("#{'xiaoming'}") //可以赋默认值
private String niceName;
//用户年龄
@Value("${user.user_age}")
// @Value("16") //直接赋值
private Integer userAge;
//是否成年
@Value("#{(${user.user_age}>17)?true:false}") //spel 表达式
private boolean adult;
//工资
@Value("#{${user.salary}*10}") //#{} 和 ${}套用
private double salary;
//联系方式
@Value("${user.userTel}")
private String userTel;
//生日
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8") //springMVC将将数据转成json格式,时间格式规则
@Value("${user.birthday}")
private Date birthday;
//用户角色
//@Value("${user.userRole}") //不可以单个手动获取石参数
private UserRole userRole; //实体参数
//爱好
//@Value("${user.hobbies}") //不可以单个手动获取复杂参数
private List<String> hobbies;
//爱车
//@Value("${user.carMap}")
private Map<String,String> carMap;
//邮箱
@Email //邮箱格式校验
@Value("${user.email:abc@kgc.com}") //添加默认值,配置信息没有就使用默认值
private String email;
}
2.2.2.2运行结果:
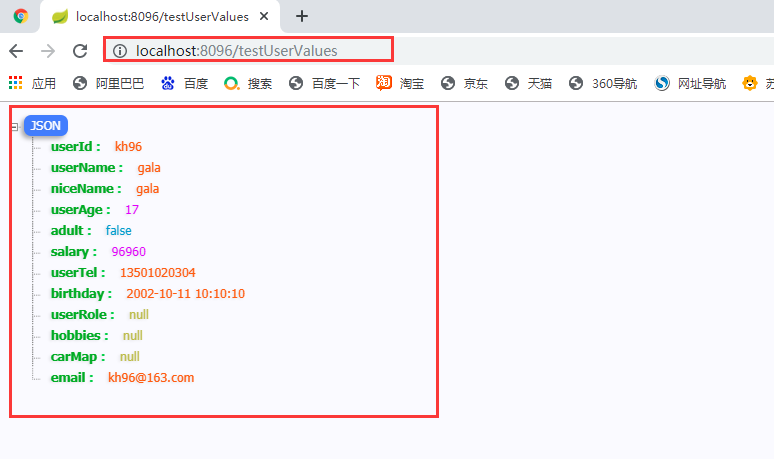
2.2.3 ${} 和 #{} 的区别
- ${}:用于读取核心配置文件中的自定义配置,也可以给属性指定默认值 (${xxx.xx:default值});
- #{}:不可以读取核心配置文件中的自定义配置,可以给属性发指定默认值#{default值} (可以使用表达式),还可以读取容器中已用实体的属性值;
- 两种读取自定义配置的方式,是可以混用的,但是实际开发中,尽量使用其中一种,,一般都是少量配置,单个读取,多个读取,使用批量读取;
3、自定义配置文件并获取配置信息
3.1xxx.properties
3.1.1 student.properties
student.studentId=19130010
student.studentName=huayu
student.studentClass=计算机科学与技术(2)
student.graduationSchool=金陵科技学院
student.graduationTime=2023/7/1 12:12:12
student.nativePlace=南京
student.hasGirFriends=true
3.1.2 StudentProperties.java
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
public class StudentProperties {
// 学号
private String studentId;
// 姓名
private String studentName;
// 班级
private String studentClass;
// 毕业院校
private String graduationSchool;
// 毕业时间
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
private Date graduationTime;
// 籍贯
private String nativePlace;
// 有没有女朋友
private boolean hasGirFriends;
}
3.1.3 StudentValues.java
@Data
@Component //第一个写法,使用普通组件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:student.properties")//单个从student.properties 中获取参数
public class StudentValues {
// 学号
@Value("${student.studentId}")
private String studentId;
// 姓名
@Value("${student.studentName}")
private String studentName;
// 班级
@Value("${student.studentClass}")
private String studentClass;
// 毕业院校
@Value("${student.graduationSchool}")
private String graduationSchool;
// 毕业时间
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
@Value("${student.graduationTime}")
private Date graduationTime;
// 籍贯
@Value("${student.nativePlace}")
private String nativePlace;
// 有没有女朋友
@Value("${student.hasGirFriends}")
private boolean hasGirFriends;
}
3.2 xxx.yml
3.2.1 student.yml
student:
studentId: 19130010
studentName: huayu
studentClass: 计算机科学与技术(2)
graduationSchool: 金陵科技学院
graduationTime: 2023/7/1 12:12:12
nativePlace: 南京
hasGirFriends: true
3.2.2 StudentProperties.java
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:student.yml",encoding = "utf-8",factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class) //从自定义的 student.yml 中获取
public class StudentProperties {
......
}
3.2.3 StudentValues.java
@Data
@Component
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:my.yml", factory = YamlPropertySourceFactory.class) //从自定义的 student.yml 中获取
public class StudentValues {
......
}
3.2.4 YamlPropertySourceFactory.java yml配置映射类
@PropertySource读取不能直接自定义yaml配置文件,需要自定义一个继承 PropertySourceFactory 的 YamlPropertySourceFactory 编写配置映射类
public class YamlPropertySourceFactory implements PropertySourceFactory {
@Override
public PropertySource<?> createPropertySource(String name, EncodedResource encodedResource) {
Resource resource = encodedResource.getResource();
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean factory = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
factory.setResources(resource);
Properties props = factory.getObject();
return new PropertiesPropertySource(resource.getFilename(), props);
}
}
3.3 测试
3.3.1 testStudentProperties
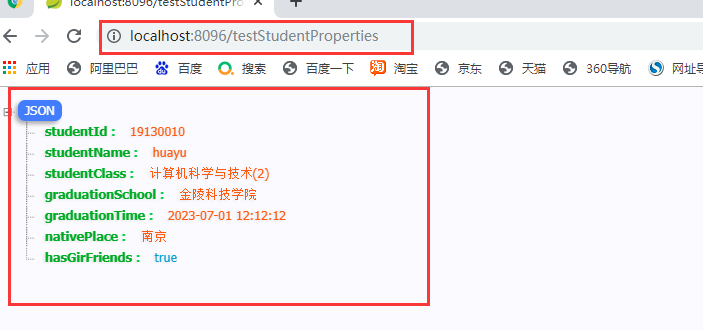
3.3.2 testStudentValues

4、*@Configuration配置类的用法,可以实现自定义组件加入容器
4.1 实体
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserRole {
//角色
private String roleId;
//角色名称
private String roleName;
}
4.2 UserRoleConfig 配置类
@Configuration //凡是被此注解修饰的类,就是一个配置类,在项目启动是,自动加载,功能跟spring的核心配置文件xml文件是同等的
public class UserRoleConfig {
//手动添加自定义对象,放入容器中以前spring框架,通过xml配置文件,添加<bean id="xx" class="xx">...</bran>
@Bean //标注的方法,会自动将当前方法返回的实例对象放入容器中,默认的bean的id值就是方法名
public UserRole userRole1(){
return UserRole.builder()
.roleId("R001")
.roleName("admin")
.build();
}
@Bean
public UserRole userRole2(){
return UserRole.builder()
.roleId("R002")
.roleName("admin")
.build();
}
}
4.3 测试类
@RestController
public class SpringBootConfigController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userRole2")
UserRole userRole;
//可以实现自定义实体加入容器
@GetMapping("/testUserRole")
public UserRole testUserRole(){
return userRole;
}
}
运行结果:

5、激活环境
5.1 多套环境配置文件
激活环境 (实际开发中,主要有三个环境:开发环境,测试环境,生产环境(线上环境),还有一个环境,灰度环境,也是线上环境,叫预上限环境);
好处:可以隔离不同环境的不同配置,需要使用哪个环境,就直接切换核心配置文件;
application-devp.properties
application-prod.properties
application-test.properties
5.2 激活环境
active: test # 指定当前的profiles值,环境是什么是通过核心配置文件名中,application-${profiles},profiles写的是什么就是什么环境;
spring:
profiles:
active: test #激活测试环境
6、核心配置文件加载位置
优先级从高到底依次为:
项目根路径下的config目录
项目根路径下
类路径(resource)下的
类路径(resource)下
注意:模块项目的 项目根路径 是 父项目的根路径;

7、邮件发送 和 短信测试发送
7.1 邮件发送
7.1.1 依赖
<!-- spring-boot-starter-mail start -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-boot-starter-mail end -->
7.1.2 邮件配置信息
7.1.3 类里面写配置信息
配置信息直接写在 对象里面;
@GetMapping("/sendEmail")
public String sendEmail(@RequestParam(value = "setToEmail",required = false) String setToEmail){
System.out.println("--------------[mail/mailSend] start------------------");
try {
MimeMessage message=javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();
MimeMessageHelper helper=new MimeMessageHelper(message,true);
helper.setFrom("2663092414@qq.com","2663092414");
helper.setTo(setToEmail);
helper.setSubject("KH-96-王松—核心配置文件读取");
helper.setText("正在使用SpringBoot读取自定义核心配置,发送邮件成功!<br/>"+studentProperties.toString(),true);
javaMailSender.send(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("邮件发送失败"+ e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("--------------[mail/mailSend] end------------------");
return studentProperties.toString();
}
//实例化javaMailSender 并写入配置信息
private static JavaMailSenderImpl javaMailSender;
static {
javaMailSender = new JavaMailSenderImpl();
javaMailSender.setHost("smtp.qq.com");//链接服务器
//javaMailSender.setPort(25);//默认使用25端口发送
javaMailSender.setUsername("2663092414@qq.com");//账号
javaMailSender.setPassword("dwxlbkrmdyagebhe");//授权码
javaMailSender.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
Properties properties = new Properties();
//properties.setProperty("mail.debug", "true");//启用调试
//properties.setProperty("mail.smtp.timeout", "1000");//设置链接超时
//设置通过ssl协议使用465端口发送、使用默认端口(25)时下面三行不需要
properties.setProperty("mail.smtp.auth", "true");//开启认证
properties.setProperty("mail.smtp.socketFactory.port", "465");//设置ssl端口
properties.setProperty("mail.smtp.socketFactory.class", "javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory");
javaMailSender.setJavaMailProperties(properties);
}
7.1.4 application.yaml中写配置信息
7.1.4.1 application.yaml
spring:
mail:
default-encoding: UTF-8
host: smtp.qq.com
port: 587
username: xxxxxx@qq.com
password: 授权码
7.1.4.2 请求方法
@GetMapping("/sendEmail2")
public String sendEmail2(@RequestParam(value = "setToEmail",required = false) String setToEmail){
SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage();
mailMessage.setFrom("xxxxxx@qq.com"); //发送邮箱
mailMessage.setTo("xxxxxx@qq.com"); //目标邮箱
mailMessage.setText("你好 hello world");
mailMessage.setSubject("测试 Springboot 邮箱服务");
mailSender.send(mailMessage);
return "====完成发送!====";
}
7.2 短信测试发送
7.2.1 依赖
<!-- SMS star -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>dysmsapi20170525</artifactId>
<version>2.0.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>tea</artifactId>
<version>1.1.14</version>
</dependency>
<!-- SMS end -->
7.2.2 代码
其中:accessKeyId ,accessKeySecret 填写自己的用户 AccessKey,最好用子用户 AccessKey;
public class Sample {
/**
* 使用AK&SK初始化账号Client
*
* @param accessKeyId
* @param accessKeySecret
* @return Client
* @throws Exception
*/
public static com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.Client createClient(String accessKeyId, String accessKeySecret) throws Exception {
com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config config = new com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config()
// 您的 AccessKey ID
.setAccessKeyId(accessKeyId)
// 您的 AccessKey Secret
.setAccessKeySecret(accessKeySecret);
// 访问的域名
config.endpoint = "dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com";
return new com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.Client(config);
}
public static void main(String[] args_) throws Exception {
java.util.List<String> args = java.util.Arrays.asList(args_);
com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.Client client = Sample.createClient("accessKeyId", "accessKeySecret"); //accessKeyId ,accessKeySecret 填写自己的用户信息
com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.models.SendSmsRequest sendSmsRequest = new com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.models.SendSmsRequest()
.setSignName("阿里云短信测试")
.setTemplateCode("SMS_154950909")
.setPhoneNumbers("发送短信的手机号")
.setTemplateParam("{\"code\":\"131313\"}");
com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions runtime = new com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions();
try {
// 复制代码运行请自行打印 API 的返回值
SendSmsResponse sendSmsResponse = client.sendSmsWithOptions(sendSmsRequest, runtime);
} catch (TeaException error) {
// 如有需要,请打印 error
String errerMsg = Common.assertAsString(error.message);
} catch (Exception _error) {
TeaException error = new TeaException(_error.getMessage(), _error);
// 如有需要,请打印 error
String errorMsg = Common.assertAsString(error.message);
}
}
}
SpringBoot(二) - 核心配置文件的更多相关文章
- springboot的核心配置文件
一.springboot主要配置文件种类 1.bootstrap (.yml或.properties) 2.application(.yml或.properties) 二.bootstrap与appl ...
- springboot(二十)-配置文件 bootstrap和application区别
用过 Spring Boot 的都知道在 Spring Boot 中有以下两种配置文件 bootstrap (.yml 或者 .properties) application (.yml 或者 .pr ...
- SpringBoot(二) SpringBoot核心配置文件application.yml/properties
我们都知道在Spring中有着application.xml文件对Spring进行相关配置,通过web.xml中的contextConfigLocation指定application.xml文件所在位 ...
- SpringBoot学习<二>——SpringBoot的默认配置文件application和多环境配置
一.SpringBoot的默认文件appliction 上一篇文章已经说明,springboot启动会内嵌tomcat,端口也是默认的8080,如果我们想要改变端口如果做呢? 在springboot项 ...
- MyBatis学习总结(二)——MyBatis核心配置文件与输入输出映射
在上一章中我们学习了<MyBatis学习总结(一)——ORM概要与MyBatis快速起步>,这一章主要是介绍MyBatis核心配置文件.使用接口+XML实现完整数据访问.输入参数映射与输出 ...
- Springboot学习:核心配置文件
核心配置文件介绍 SpringBoot使用一个全局配置文件,配置文件名是固定的 application.properties application.yml 配置文件的作用:修改SpringBoot自 ...
- 【Nginx(二)】Nginx目录结构和常用的命令以及核心配置文件
Nginx的目录结构: 默认的安装路径 : /usr/local/nginx 安装完成后,Nginx的目录结构如下: conf: #所有配置文件的目录 nginx.conf #默认的主要配置文件 ...
- Springboot读取自定义配置文件的几种方法
一.读取核心配置文件 核心配置文件是指在resources根目录下的application.properties或application.yml配置文件,读取这两个配置文件的方法有两种,都比较简单. ...
- Springboot 日志、配置文件、接口数据如何脱敏?老鸟们都是这样玩的!
一.前言 核心隐私数据无论对于企业还是用户来说尤其重要,因此要想办法杜绝各种隐私数据的泄漏.下面陈某带大家从以下三个方面讲解一下隐私数据如何脱敏,也是日常开发中需要注意的: 配置文件数据脱敏 接口返回 ...
随机推荐
- [极客大挑战 2019]BabySQL-1|SQL注入
1.打开题目之后,查看源代码信息,发现check.php文件,结果如下: 2.那就只能尝试登录,经测试当输入or.by.select.from.and.where等关键字时会被过滤且会被过滤为空(过滤 ...
- gitlab root密码重置
版本:Gitlab Ruby Gem 4.16.1 root密码在gitlab第一次运行的时候,如果你没有配置root用户的密码文件,它就会生成一个随机密码,并保存在固定的文件中,然后输出在屏幕上.但 ...
- MyBatis-知识点详解
Mybatis 中$与#的区别 1 #是将传入的值当做字符串的形式,eg:select id,name,age from student where id =#{id},当前端把id值1,传入到后台的 ...
- 一文带你掌握Spring Web异常处理方式
一.前言 大家好,我是 去哪里吃鱼 ,也叫小张. 最近从单位离职了,离开了五年多来朝朝夕夕皆灯火辉煌的某网,激情也好悲凉也罢,觥筹场上屡屡物是人非,调转过事业部以为能换种情绪,岂料和下了周五的班的前同 ...
- 基础2:js创建对象的多种方式
js创建对象的多种方式 1. 工厂模式 function createPerson(name) { var o = new Object() 0.name = name return o } var ...
- springBoot项目实现发送邮件功能
需要的依赖: <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId> ...
- Hadoop集群搭建的详细过程
Hadoop集群搭建 一.准备 三台虚拟机:master01,node1,node2 时间同步 1.date命令查看三台虚拟机时间是否一致 2.不一致时间同步:ntpdate ntp.aliyun.c ...
- Linus命令
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44191814/article/details/120091363 vim编辑器 ## Vim基本模式 [对文件进行操作]vim 文 ...
- Java开发学习(二十八)----拦截器(Interceptor)详细解析
一.拦截器概念 讲解拦截器的概念之前,我们先看一张图: (1)浏览器发送一个请求会先到Tomcat的web服务器 (2)Tomcat服务器接收到请求以后,会去判断请求的是静态资源还是动态资源 (3)如 ...
- format添加未知个参数方法
一个python巧妙技巧,分享给大家 我的需求是将一个dict的键都format输出,用到了*对字典解包 data = {a: 1, b: 2...} msg = f"{'{} '*len( ...
