深度学习中batch normalization
目录
Batch Normalization笔记
我们将会用MNIST数据集来演示这个batch normalization的使用, 以及他所带来的效果:
引包
import tensorflow as tf
import os
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from tensorflow.contrib.layers import flatten
import numpy as np
import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim
构建模型:
def model1(input, is_training, keep_prob):
input = tf.reshape(input, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
batch_norm_params = {
'decay': 0.95,
'updates_collections': None
}
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm, slim.dropout], is_training=is_training):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected],
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1),
normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm, normalizer_params=batch_norm_params,
activation_fn=tf.nn.crelu):
conv1 = slim.conv2d(input, 16, 5, scope='conv1')
pool1 = slim.max_pool2d(conv1, 2, scope='pool1')
conv2 = slim.conv2d(pool1, 32, 5, scope='conv2')
pool2 = slim.max_pool2d(conv2, 2, scope='pool2')
flatten = slim.flatten(pool2)
fc = slim.fully_connected(flatten, 1024, scope='fc1')
print(fc.get_shape())
drop = slim.dropout(fc, keep_prob=keep_prob)
logits = slim.fully_connected(drop, 10, activation_fn=None, scope='logits')
return logits
def model2(input, is_training, keep_prob):
input = tf.reshape(input, shape=[-1, 28, 28, 1])
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected],
weights_initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1),
normalizer_fn=None, activation_fn=tf.nn.crelu):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.dropout], is_training=is_training):
conv1 = slim.conv2d(input, 16, 5, scope='conv1')
pool1 = slim.max_pool2d(conv1, 2, scope='pool1')
conv2 = slim.conv2d(pool1, 32, 5, scope='conv2')
pool2 = slim.max_pool2d(conv2, 2, scope='pool2')
flatten = slim.flatten(pool2)
fc = slim.fully_connected(flatten, 1024, scope='fc1')
print(fc.get_shape())
drop = slim.dropout(fc, keep_prob=keep_prob)
logits = slim.fully_connected(drop, 10, activation_fn=None, scope='logits')
return logits
构建训练函数
def train(model, model_path, train_log_path, test_log_path):
# 计算图
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
X = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 28 * 28])
Y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])
is_training = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool)
logit = model(X, is_training, 0.7)
loss =tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logit, labels=Y))
accuray = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(logit, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1)), tf.float32))
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(0.1, global_step, 1000, 0.95, staircase=True)
optimizer = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)
update = slim.learning.create_train_op(loss, optimizer, global_step)
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("tmp", one_hot=True)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
tf.summary.scalar("loss", loss)
tf.summary.scalar("accuracy", accuray)
merged_summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
train_summary_writter = tf.summary.FileWriter(train_log_path, graph=tf.get_default_graph())
test_summary_writter = tf.summary.FileWriter(test_log_path, graph=tf.get_default_graph())
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
iter_num = 10000
batch_size = 1024
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = '2' # 选择cuda的设备
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.2) # gpu显存使用
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)) as sess:
sess.run(init)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.dirname(model_path)):
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(model_path))
else:
try:
saver.restore(sess, model_path)
except:
pass
for i in range(iter_num):
x, y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(update, feed_dict={X:x, Y:y, is_training:True})
if i % 100 == 0:
x_test, y_test = mnist.test.next_batch(batch_size)
print("train:", sess.run(accuray, feed_dict={X: x, Y: y, is_training:False}))
print("test:", sess.run(accuray, feed_dict={X: x_test, Y: y_test, is_training:False}))
saver.save(sess, model_path)
g, summary = sess.run([global_step, merged_summary_op], feed_dict={X: x, Y: y, is_training:False})
train_summary_writter.add_summary(summary, g)
train_summary_writter.flush()
g, summary = sess.run([global_step, merged_summary_op], feed_dict={X: x_test, Y: y_test, is_training:False})
test_summary_writter.add_summary(summary, g)
test_summary_writter.flush()
train_summary_writter.close()
test_summary_writter.close()
下面我们来进行计算:
train(model1, "model1/model", "model1_train_log", "model1_test_log")
train(model2, "model2/model", "model2_train_log", "model2_test_log")
结论
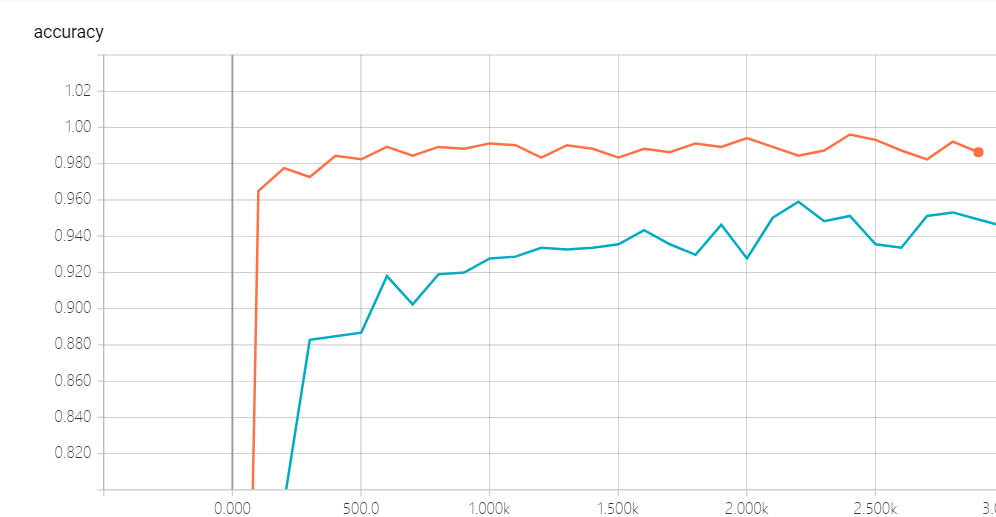
我们发现, 加了batch norm的似乎收敛的更快一些, 这个我们可以从对比上可以很清楚的看到, 所以这个bn是我们一个很好的技术, 前提是你选的参数比较适合.
以下是两个注意点:
The keys to use batch normalization in slim are:
Set proper decay rate for BN layer. Because a BN layer uses EMA (exponential moving average) to approximate the population mean/variance, it takes sometime to warm up, i.e. to get the EMA close to real population mean/variance. The default decay rate is 0.999, which is kind of high for our little cute MNIST dataset and needs ~1000 steps to get a good estimation. In my code, decay is set to 0.95, then it learns the population statistics very quickly. However, a large value of decay does have it own advantage: it gathers information from more mini-batches thus is more stable.
Use slim.learning.create_train_op to create train op instead of tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) or something else!.
深度学习中batch normalization的更多相关文章
- 深度学习中 Batch Normalization
深度学习中 Batch Normalization为什么效果好?(知乎) https://www.zhihu.com/question/38102762
- 深度学习中 Batch Normalization为什么效果好
看mnist数据集上其他人的CNN模型时了解到了Batch Normalization 这种操作.效果还不错,至少对于训练速度提升了很多. batch normalization的做法是把数据转换为0 ...
- zz详解深度学习中的Normalization,BN/LN/WN
详解深度学习中的Normalization,BN/LN/WN 讲得是相当之透彻清晰了 深度神经网络模型训练之难众所周知,其中一个重要的现象就是 Internal Covariate Shift. Ba ...
- 深度学习中的Normalization模型
Batch Normalization(简称 BN)自从提出之后,因为效果特别好,很快被作为深度学习的标准工具应用在了各种场合.BN 大法虽然好,但是也存在一些局限和问题,诸如当 BatchSize ...
- [优化]深度学习中的 Normalization 模型
来源:https://www.chainnews.com/articles/504060702149.htm 机器之心专栏 作者:张俊林 Batch Normalization (简称 BN)自从提出 ...
- 深度学习之Batch Normalization
在机器学习领域中,有一个重要的假设:独立同分布假设,也就是假设训练数据和测试数据是满足相同分布的,否则在训练集上学习到的模型在测试集上的表现会比较差.而在深层神经网络的训练中,当中间神经层的前一层参数 ...
- 深度学习中优化【Normalization】
深度学习中优化操作: dropout l1, l2正则化 momentum normalization 1.为什么Normalization? 深度神经网络模型的训练为什么会很困难?其中一个重 ...
- 深度学习中的batch、epoch、iteration的含义
深度学习的优化算法,说白了就是梯度下降.每次的参数更新有两种方式. 第一种,遍历全部数据集算一次损失函数,然后算函数对各个参数的梯度,更新梯度.这种方法每更新一次参数都要把数据集里的所有样本都看一遍, ...
- 深度学习中 --- 解决过拟合问题(dropout, batchnormalization)
过拟合,在Tom M.Mitchell的<Machine Learning>中是如何定义的:给定一个假设空间H,一个假设h属于H,如果存在其他的假设h’属于H,使得在训练样例上h的错误率比 ...
随机推荐
- Log4j源码解析--Layout类解析
本文转载上善若水的博客,原文出处:http://www.blogjava.net/DLevin/archive/2012/07/04/382131.html.感谢作者的分享. Layout负责将Log ...
- sed 变量替换和Linux的特殊符号大全
1 sed支持两种方式的变量替换,建议使用下面的第二种,比较简单 这样就可以给变量a赋值很多特殊字符了,比如 赋值a='!@#¥%……' sed -n 's/echo/'"$a"' ...
- linux 中 ping的回传值
今天在学习鸟哥私房菜的过程中,不明白ping的回传值是怎么设置的,后来网上找的结果了,特此记录一下 1 题目大意是指,ping一个网段的机器,如果可以通,就显示UP,如果不通就显示Down,其中一 ...
- junit源码解析总结
前面的博客我们也已经整理到了,我们使用junit38,在写测试类的时候我们的测试类必须继承TestCase.这个所有测试类的父类在junit.framework包下面. 前面我们的整理都是说直接在ID ...
- ios 判断屏幕显示是@2x还是@3x来调用字体大小
传统font大小适配可能会根据屏幕宽度与iphone5或iphone6宽度的一个比例来适配.但如果有这样一个需求,在显示@2x图片的手机上显示一种字体,在显示@3x图片的手机上显示另一个固定大小的字体 ...
- PHP中利用PHPMailer配合QQ邮箱实现发邮件
PHPMailer的介绍: 优点: 可运行在任何平台之上 支持SMTP验证 发送邮时指定多个收件人,抄送地址,暗送地址和回复地址:注:添加抄送.暗送仅win平台下smtp方式支持 支持多种邮件编码包括 ...
- Redis Crackit漏洞防护
Redis Crackit漏洞利用和防护 注意:本文只是阐述该漏洞的利用方式和如何预防.根据职业道德和<中华人民共和国计算机信息系统安全保护条例>,如果发现的别人的漏洞,千万不要轻易入侵, ...
- DRBD的主备安装配置
drbd软件包链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1eUcXVyU 密码:00ul 1.使用的资源:1.1 系统centos6.9 mini1.2 两台节点主机node1.node2 ...
- centos 6.3安装ssh
centos 6.3安装ssh 安装ssh服务器端软件 yum install openssh-server 安装ssh客户端软件 yum install openssh-clients ...
- xBIM IFC 输出 Excel 报表
目录 xBIM 应用与学习 (一) xBIM 应用与学习 (二) xBIM 基本的模型操作 xBIM 日志操作 XBIM 3D 墙壁案例 xBIM 格式之间转换 xBIM 使用Linq 来优化查询 x ...
