201771010113 李婷华 《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十七周总结
一.理论知识部分
Java 的线程调度采用优先级策略:优先级高的先执行,优先级低的后执行;多线程系统会自动为每个线程分配一个优先级,缺省时,继承其父类的优先级; 任务紧急的线程,其优先级较高; 同优先级的线程按“先进先出”的队列原则。
调用setPriority(int a)重置当前线程的优先级,a取值可以是前述的三个静态量。调用getPriority()获得当前线程优先级。
多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案:引入线程同步机制,使得另一线程要使用该方法,就只能等待。
在Java中解决多线程同步问题的方法有两种:J ava SE 5.0中引入ReentrantLock类。 在共享内存的类方法前加synchronized修饰符。
有关锁对象和条件对象的关键要点:锁用来保护代码片段,保证任何时刻只能有一个线程执行被保护的代码。锁管理试图进入被保护代码段的线程。锁可拥有一个或多个相关条件对象。每个条件对象管理那些已经进入被保护的代码 段但还不能运行的线程。
synchronized关键字作用: 某个类内方法用synchronized 修饰后,该方法被称为同步方法;只要某个线程正在访问同步方法,其他线程欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞,直至线程从同 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程,其他线程方可能进入同步方法。
在同步方法中使用wait()、notify 和notifyAll()方法:一个线程在使用的同步方法中时,可能根据问题的需要,必须使用wait()方法使本线程等待,暂时让出CPU的使用权,并允许其它线程使用这个同步方法。线程如果用完同步方法,应当执行notifyAll()方 法通知所有由于使用这个同步方法而处于等待的线程结束等待。
二.实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术;
(2) 线程综合编程练习
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
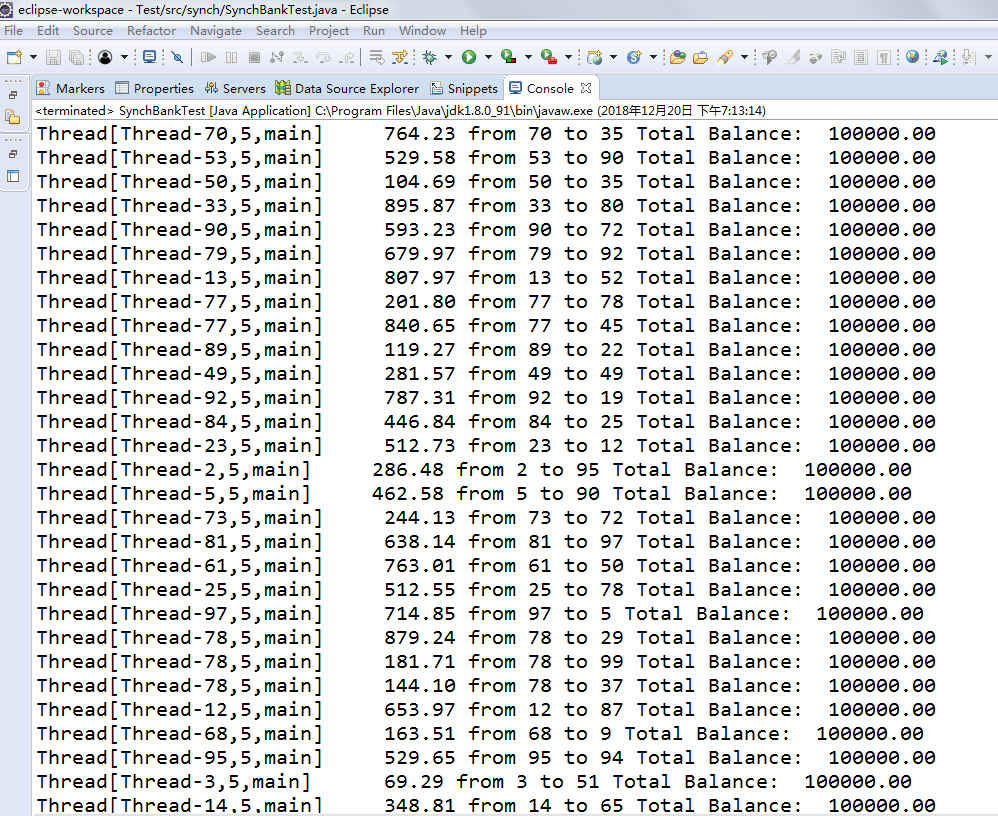
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材651页程序14-7,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握利用锁对象和条件对象实现的多线程同步技术。
package synch; /**
* This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure.
* @version 1.31 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SynchBankTest
{
public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100;
public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000;
public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 10; public static void main(String[] args)
{
Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE);
for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++)
{
int fromAccount = i;
Runnable r = () -> {
try
{
while (true)
{
int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random());
double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random();
bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount);
Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));//随机生成时间,使正在执行的线程休眠
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();//开始线程
}
}
}
SynchBankTest
package synch; import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.*; /**
* A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses locks for serializing access.
* @version 1.30 2004-08-01
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Bank
{
private final double[] accounts;
private Lock bankLock;
private Condition sufficientFunds; /**
* Constructs the bank.
* @param n the number of accounts
* @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account
*/
public Bank(int n, double initialBalance)
{
accounts = new double[n];
Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance);
bankLock = new ReentrantLock();
sufficientFunds = bankLock.newCondition();
} /**
* Transfers money from one account to another.
* @param from the account to transfer from
* @param to the account to transfer to
* @param amount the amount to transfer
*/
public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException
{
bankLock.lock();//使用锁对象,获取锁
try
{
while (accounts[from] < amount)
sufficientFunds.await();
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());
accounts[from] -= amount;
System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to);
accounts[to] += amount;
System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance());
sufficientFunds.signalAll();//唤醒所有线程
}
finally
{
bankLock.unlock();//释放锁
}
} /**
* Gets the sum of all account balances.
* @return the total balance
*/
public double getTotalBalance()
{
bankLock.lock();
try
{
double sum = 0; for (double a : accounts)
sum += a; return sum;
}
finally
{
bankLock.unlock();
}
} /**
* Gets the number of accounts in the bank.
* @return the number of accounts
*/
public int size()
{
return accounts.length;
}
}
Bank
测试程序2:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材655页程序14-8,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握synchronized在多线程同步中的应用。
package synch2; import java.util.*; /**
* A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses synchronization primitives.
* @version 1.30 2004-08-01
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Bank
{
private final double[] accounts; /**
* Constructs the bank.
* @param n the number of accounts
* @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account
*/
public Bank(int n, double initialBalance)
{
accounts = new double[n];
Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance);
} /**
* Transfers money from one account to another.
* @param from the account to transfer from
* @param to the account to transfer to
* @param amount the amount to transfer
*/
//使用synchronized修饰符
public synchronized void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException
{
while (accounts[from] < amount)
wait();//来自Object类
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());
accounts[from] -= amount;
System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to);
accounts[to] += amount;
System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance());
notifyAll();//解除所有线程的阻塞状态
} /**
* Gets the sum of all account balances.
* @return the total balance
*/
public synchronized double getTotalBalance()
{
double sum = 0; for (double a : accounts)
sum += a; return sum;
} /**
* Gets the number of accounts in the bank.
* @return the number of accounts
*/
public int size()
{
return accounts.length;
}
}
Bank
package synch2; /**
* This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure,
* using synchronized methods.
* @version 1.31 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SynchBankTest2
{
public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100;
public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000;
public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000;
public static final int DELAY = 10; public static void main(String[] args)
{
Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE);
for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++)
{
int fromAccount = i;
Runnable r = () -> {
try
{
while (true)
{
int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random());
double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random();
bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount);
Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
};
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
}
}
}
SynchBankTest2

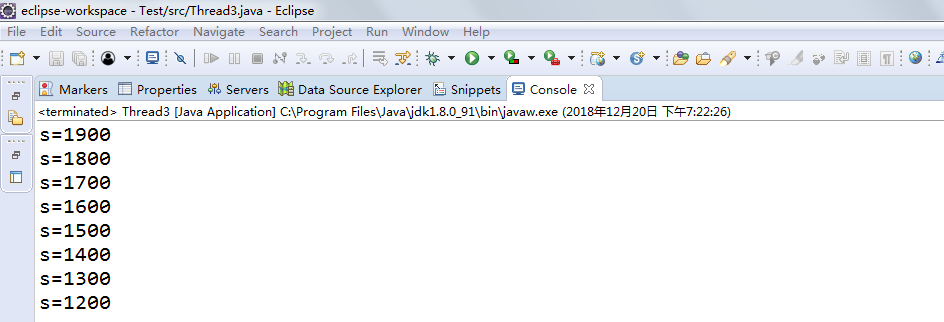
测试程序3:
l 在Elipse环境下运行以下程序,结合程序运行结果分析程序存在问题;
l 尝试解决程序中存在问题。
|
class Cbank { private static int s=2000; public static void sub(int m) { int temp=s; temp=temp-m; try { Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } s=temp; System.out.println("s="+s); } } class Customer extends Thread { public void run() { for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) Cbank.sub(100); } } public class Thread3 { public static void main(String args[]) { Customer customer1 = new Customer(); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer1.start(); customer2.start(); } } |
class Cbank
{
private static int s=2000;
public static synchronized void sub(int m)
{ int temp=s;
temp=temp-m;
try {
Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random()));
}
catch (InterruptedException e) { }
s=temp;
System.out.println("s="+s);
}
} class Customer extends Thread
{
public void run()
{
for( int i=1; i<=4; i++)
Cbank.sub(100);
}
}
public class Thread3
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Customer customer1 = new Customer();
Customer customer2 = new Customer();
customer1.start();
customer2.start();
}
}
Cbank
实验2 编程练习
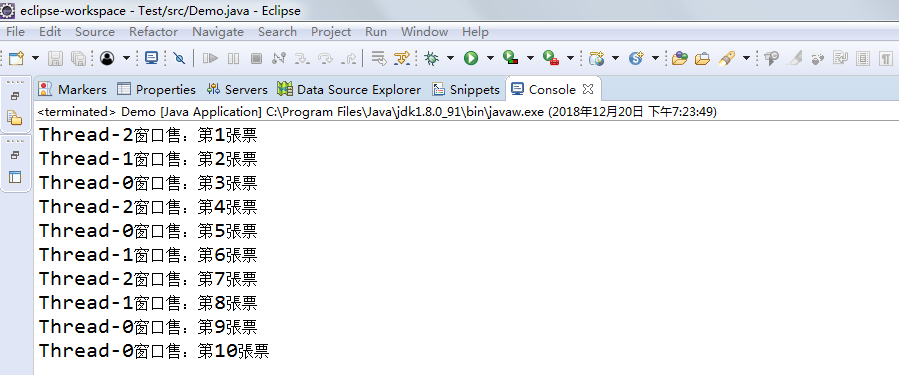
利用多线程及同步方法,编写一个程序模拟火车票售票系统,共3个窗口,卖10张票,程序输出结果类似(程序输出不唯一,可以是其他类似结果)。
Thread-0窗口售:第1张票
Thread-0窗口售:第2张票
Thread-1窗口售:第3张票
Thread-2窗口售:第4张票
Thread-2窗口售:第5张票
Thread-1窗口售:第6张票
Thread-0窗口售:第7张票
Thread-2窗口售:第8张票
Thread-1窗口售:第9张票
Thread-0窗口售:第10张票
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Myrhread myrhread = new Myrhread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(myrhread);
Thread t2 = new Thread(myrhread);
Thread t3 = new Thread(myrhread);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
class Myrhread implements Runnable {
int t = 1;
boolean flag = true;
public void run() {
while (flag) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (this) {
if (t <= 10) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "窗口售:第" + t + "張票");
t++;
}
if (t > 10) {
flag = false;
}
}
}
}
}
Demo
3.实验总结:
本周的实验容量很少,实验也相对来说简单,完成的还算顺利。学长也教了我们常用的一些快捷键,本周的收获还是很大的。
201771010113 李婷华 《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第十七周总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201771010113 李婷华 《面向java对象程序设计(Java)》第四章学习总结
一. 理论知识部分 第四章 对象与类 本章主要讲述面向对象程序设计.如何创建标准Java类库中的类对象.如何编写自己的类. 1.面向对象程序设计的几个主要概念: 抽象数据类型.类和对象.封装.类层次( ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 面向对象程序设计--Java语言第二周编程题:有秒计时的数字时钟
有秒计时的数字时钟 题目内容: 这一周的编程题是需要你在课程所给的时钟程序的基础上修改而成.但是我们并不直接给你时钟程序的代码,请根据视频自己输入时钟程序的Display和Clock类的代码,然后来做 ...
随机推荐
- 基于mui的H5套壳APP开发web框架分享
前言 创建一个main主页面,只有主页面有头部.尾部,中间内容嵌入iframe内容子页面,如果在当前页面进行跳转操作,也是在iframe中进行跳转,而如果点击尾部按钮切换模块.页面,那就切换ifram ...
- 怎么入门python?不懂你别瞎尝试,看看大佬怎么说
学习任何一门语言都是从入门,通过不间断练习达到熟练水准.虽然万事开头难,但好的开始是成功的一半,今天这篇文章就来谈谈怎么入门python? 在开始学习python之前,你需要确定好学习计划和方式 比如 ...
- Gallery实现图片拖动切换
Gallery中文意思为画廊,通过Gallery能够实现用手指在屏幕上滑动实现图片的拖动.效果如下: 上面,为了学习了解,只用了android默认的Icon图片. 主程序中创建了一个继承自BaseAd ...
- Thinking in Java,Fourth Edition(Java 编程思想,第四版)学习笔记(九)之Interfaces
Interfaces and abstract classes provide more structured way to separate interface from implementatio ...
- Spring Boot 集成 Spring Security 入门案例教程
前言 本文作为入门级的DEMO,完全按照官网实例演示: 项目目录结构 Maven 依赖 <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot&l ...
- week homework: 大家来找茬
上周课程主题为用户体验,每位同学也根据自己使用APP的体验,例举出一些手机或电脑客户端软件的bug或用户体验非常不好的地方: Tianfu: GitHub.com:界面不够直观,有许多功能不知道入口在 ...
- stand up meeting 11/20/2015
3组员 今日工作 工作耗时/h 明日计划 计划耗时/h 冯晓云 将输出string里的翻译合理取分为动名词等各种词性,按约定格式返回,按热度排列,但每一个词性下的解释仍然是由“$$”分词:对于查询词为 ...
- 数据结构之栈—强大的四则复杂运算计算器(超过windows自带的科学计算器)【中缀转后缀表达式】
比windows自带计算器还强的四则复杂运算计算器! 实测随机打出两组复杂算式:-7.5 * 6 / ( -2 + ( -6.5 - -5.22 ) )与7.5+-3*8/(7+2) windows ...
- 设计模式-原型模式(Prototype)【重点:浅复制与深复制】
讲故事 最近重温了一下星爷的<唐伯虎点秋香>,依然让我捧腹不已,幻想着要是我也能有一名秋香如此的侍女,夫复何求呀,带着这个美好的幻想沉沉睡去... 突然想到,我是一名程序猿呀,想要什么对象 ...
- js 异或加密
// 按位异或 加密 var posNo = 'C0041710190002' // 特殊字符不进行 与或 加密 (因为A,a,Z,z,转换后会变成符号,不方面用户输入 ...
