RNN和LSTM
一、RNN
全称为Recurrent Neural Network,意为循环神经网络,用于处理序列数据。
序列数据是指在不同时间点上收集到的数据,反映了某一事物、现象等随时间的变化状态或程度。即数据之间有联系。
RNN的特点:1,,层间神经元也有连接(主要为隐层);2,共享参数
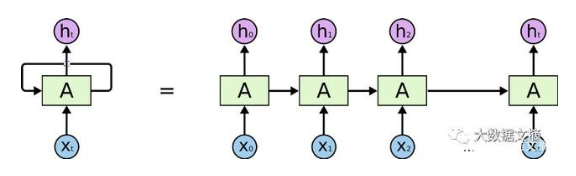
其结构如上图所示,数据为顺序处理,在处理长序列数据时,极易导致梯度消失问题。
二、LSTM
LSTM为长短期记忆,是一种变种的RNN,在RNN的基础上引入了细胞状态,根据细胞状态可决定哪些状态应该保留下来,哪些状态应该被遗忘。
LSTM可一定程度上解决梯度消失问题。
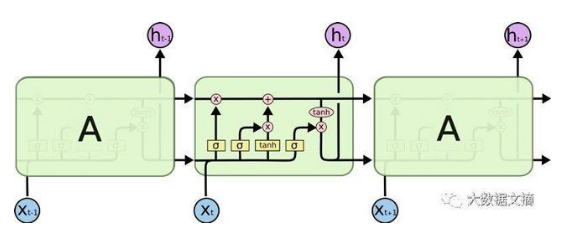
由上图可知,在RNN的基础上,增加了一路输入和输出,增加的这一路就是细胞状态。
由上一时刻的输出和当前时刻的输入,经过sigmod函数之后,趋近于0被遗忘的多,趋近于1被遗忘的少。
由上一时刻的输出和当前时刻的输入,经过sigmod函数之后,决定哪些内容应该被记住,被记住的内容并不是上一时刻的输出和当前时刻的输入,而是需要经过tanh函数。
程序:应用LSTM训练mnist数据集
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.transforms as transforms # torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible # Hyper Parameters
EPOCH = 1 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 64
LR = 0.01 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False #已下载好数据集,就设置为False,否则为TRUE
TIME_STEP=28 #可理解为输入图像维度
INPUT_SIZE=28 # Mnist digits dataset
if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True train_data = dsets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST,
) # plot one example
# print(train_data.train_data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)
# print(train_data.train_labels.size()) # (60000)
# plt.imshow(train_data.train_data[0].numpy(), cmap='gray')
# plt.title('%i' % train_data.train_labels[0])
# plt.show() # Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True) # pick 2000 samples to speed up testing
test_data = dsets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False,transform=transforms.ToTensor())
test_x = test_data.test_data.type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000]/255. # shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1)
test_y = test_data.test_labels.numpy()[:2000] class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(
input_size=INPUT_SIZE,
hidden_size=64,
num_layers=1,
batch_first=True
) self.out=nn.Linear(64,10)
def forward(self,x):
r_out,(h_n,h_c)=self.rnn(x,None)
out=self.out(r_out[:,-1,:]) #数据格式为[batch,time_step,input],因此输出参考的是最后时刻的数据
return out rnn=RNN()
print(rnn) # net architecture optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # the target label is not one-hotted for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader): # gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader
b_x=Variable(x.view(-1,28,28))
b_y=Variable(y)
output = rnn(b_x) # cnn output
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients if step % 50 == 0:
test_output = rnn(test_x)
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy().squeeze()
accuracy =float((pred_y==test_y).astype(int).sum())/float(test_y.size)
print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss: %.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), '| test accuracy: %.2f' % accuracy) # print 10 predictions from test data
test_output = rnn(test_x[:10].view(-1,28,28))
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy().squeeze()
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y[:10], 'real number')
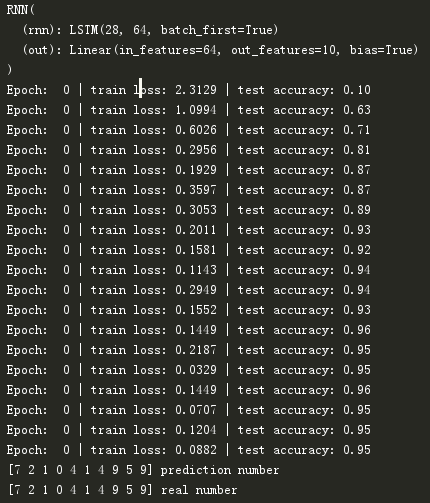
运行结果为:
RNN和LSTM的更多相关文章
- RNN and LSTM saliency Predection Scene Label
http://handong1587.github.io/deep_learning/2015/10/09/rnn-and-lstm.html //RNN and LSTM http://hando ...
- RNN 与 LSTM 的应用
之前已经介绍过关于 Recurrent Neural Nnetwork 与 Long Short-Trem Memory 的网络结构与参数求解算法( 递归神经网络(Recurrent Neural N ...
- Naive RNN vs LSTM vs GRU
0 Recurrent Neural Network 1 Naive RNN 2 LSTM peephole Naive RNN vs LSTM 记忆更新部分的操作,Naive RNN为乘法,LSTM ...
- TensorFlow之RNN:堆叠RNN、LSTM、GRU及双向LSTM
RNN(Recurrent Neural Networks,循环神经网络)是一种具有短期记忆能力的神经网络模型,可以处理任意长度的序列,在自然语言处理中的应用非常广泛,比如机器翻译.文本生成.问答系统 ...
- 浅谈RNN、LSTM + Kreas实现及应用
本文主要针对RNN与LSTM的结构及其原理进行详细的介绍,了解什么是RNN,RNN的1对N.N对1的结构,什么是LSTM,以及LSTM中的三门(input.ouput.forget),后续将利用深度学 ...
- 3. RNN神经网络-LSTM模型结构
1. RNN神经网络模型原理 2. RNN神经网络模型的不同结构 3. RNN神经网络-LSTM模型结构 1. 前言 之前我们对RNN模型做了总结.由于RNN也有梯度消失的问题,因此很难处理长序列的数 ...
- RNN以及LSTM的介绍和公式梳理
前言 好久没用正儿八经地写博客了,csdn居然也有了markdown的编辑器了,最近花了不少时间看RNN以及LSTM的论文,在组内『夜校』分享过了,再在这里总结一下发出来吧,按照我讲解的思路,理解RN ...
- 深度学习:浅谈RNN、LSTM+Kreas实现与应用
主要针对RNN与LSTM的结构及其原理进行详细的介绍,了解什么是RNN,RNN的1对N.N对1的结构,什么是LSTM,以及LSTM中的三门(input.ouput.forget),后续将利用深度学习框 ...
- 利用RNN(lstm)生成文本【转】
本文转载自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/1a4f7f5b05ae 致谢以及参考 最近在做序列化标注项目,试着理解rnn的设计结构以及tensorflow中的具体实现方法.在知乎 ...
随机推荐
- C: printf参数执行顺序与前置后置自增自减的影响
起源: 今天在了解副作用side-effect的过程中,看到了下面的网页,把我带到了由printf引起的一系列问题,纠结了一整天,勉强弄懂. 第一个代码没什么好解释的.而第二个printf(" ...
- C# WinForm 技巧十: winfrom 全屏自适应屏幕分辨率
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(); rect = Screen.GetWorkingArea(this); this.Width = rect.Width;//屏幕宽 ...
- PyCharm中Django项目主urls导入应用中views的红线问题
PyCharm中Django项目主urls导入应用中views的红线问题 使用PyCharm学习Django框架,从项目的主urls中导入app中的views的时候,导入的包中下面有红线报错,但是却能 ...
- 【问题解决方案】ImportError: No module named 'pygal'
<Python编程:从入门到实践>一书,第二个项目-可视化,第四节用到pygal 安装部分用 'python -m pip install pygal==1.7' 安装,但使用时仍然报错 ...
- python学习之时间处理
主要学习datetime,time,时区 待更新...
- centos关机与重启命令
Linux centos重启命令: 1.reboot 普通重启 2.shutdown -r now 立刻重启(root用户使用) 3.shutdown -r 10 过10分钟自动重启(root用户 ...
- Linux(Ubuntu)使用日记------markdown文档转化为word文档
Linux(Ubuntu)使用日记------markdown文档转化为word文档
- Java代理模式之Cglib代理
Cglib代理,也叫做子类代理.在内存中构建一个子类对象从而实现对目标对象功能的扩展. CGLIB包的底层是通过使用一个小而快的字节码处理框架ASM,来转换字节码并生成新的类.不鼓励直接使用ASM,因 ...
- pc端手機端自適應佈局方案
https://blog.csdn.net/chose_DoIt/article/details/80424341 https://blog.csdn.net/cxz792116/article/de ...
- C#中声明、调用和配置事件的演示源码
下面的内容是关于C#中声明.调用和配置事件的演示的内容,应该能对大伙有些好处. using System;namespace MyCollections { using System.Collecti ...
