[LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫 II
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball's start position, the destination and the maze, find the shortest distance for the ball to stop at the destination. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the destination (included). If the ball cannot stop at the destination, return -1.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1
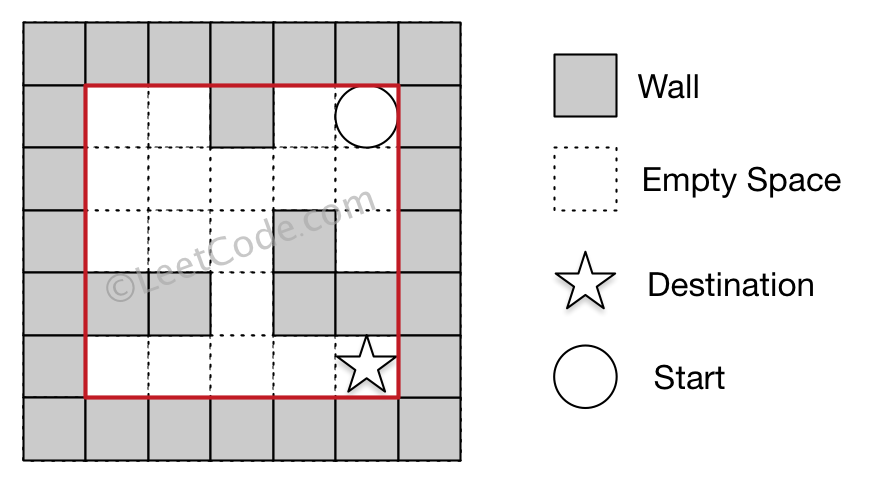
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4) Output: 12
Explanation: One shortest way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.
The total distance is 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.
Example 2
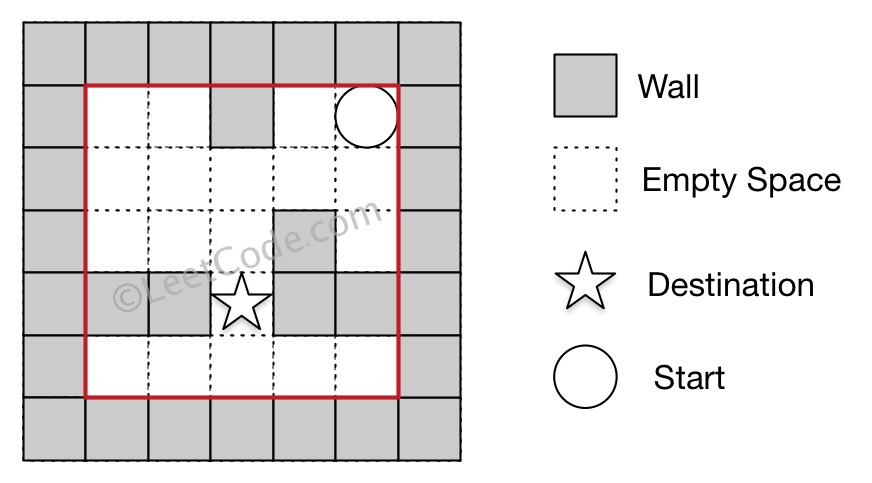
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (3, 2) Output: -1
Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination.
Note:
- There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
- Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won't exceed 100.
490. The Maze 的拓展,490题只判断能否到达终点,而这道题让求出到达终点的最少步数。
要求最短的路径,普通的遍历dfs和bfs都是可以做的,但是求最短路径的话还是用Dijksra。这里相当于每个点有至多4条edge相连,每条edge的weight就是到墙之前的长度。
Java:
public class Solution {
public int shortestDistance(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
// base case
if(Arrays.equals(start, destination)) return 0;
m = maze.length; n = maze[0].length;
return shortestPath(maze, start, destination);
}
int m, n;
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
private int shortestPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
// get the vertice has the minimum distance to start
PriorityQueue<Node> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a.distance - b.distance);
minHeap.offer(new Node(start[0], start[1], 0));
// map that contains information of node: distance to start point
int[][] visited = new int[m][n];
for(int[] arr : visited) Arrays.fill(arr, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
while(!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = minHeap.poll();
// find the shortest path
if(cur.x == destination[0] && cur.y == destination[1]) return cur.distance;
for(int[] dir : dirs) {
int nx = cur.x, ny = cur.y;
while(isInMaze(nx + dir[0], ny + dir[1]) && maze[nx + dir[0]][ny + dir[1]] != 1) {
nx += dir[0]; ny += dir[1];
}
int distance = cur.distance + Math.abs(nx - cur.x) + Math.abs(ny - cur.y);
if(visited[nx][ny] > distance) {
minHeap.offer(new Node(nx, ny, distance));
visited[nx][ny] = distance;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
private boolean isInMaze(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n;
}
class Node {
int x;
int y;
// distance to start point
int distance;
Node(int x, int y, int distance) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
}
Python:
class Solution(object):
def findShortestWay(self, maze, ball, hole):
"""
:type maze: List[List[int]]
:type ball: List[int]
:type hole: List[int]
:rtype: str
"""
ball, hole = tuple(ball), tuple(hole)
dmap = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(int))
w, h = len(maze), len(maze[0])
for dir in 'dlru': dmap[hole][dir] = hole
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['u'] = dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] if x > 0 and dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['l'] = dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] if y > 0 and dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] else (x, y)
for x in range(w - 1, -1, -1):
for y in range(h - 1, -1, -1):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['d'] = dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] if x < w - 1 and dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['r'] = dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] if y < h - 1 and dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] else (x, y)
bmap = {ball : (0, '')}
distance = lambda pa, pb: abs(pa[0] - pb[0]) + abs(pa[1] - pb[1])
queue = collections.deque([(ball, 0, '')])
while queue:
front, dist, path = queue.popleft()
for dir in 'dlru':
if dir not in dmap[front]: continue
np = dmap[front][dir]
ndist = dist + distance(front, np)
npath = path + dir
if np not in bmap or (ndist, npath) < bmap[np]:
bmap[np] = (ndist, npath)
queue.append((np, ndist, npath))
return bmap[hole][1] if hole in bmap else 'impossible'
Python: Dijkstra算法
class Solution(object):
def findShortestWay(self, maze, ball, hole):
"""
:type maze: List[List[int]]
:type ball: List[int]
:type hole: List[int]
:rtype: str
"""
ball, hole = tuple(ball), tuple(hole)
dmap = collections.defaultdict(lambda: collections.defaultdict(int))
w, h = len(maze), len(maze[0])
for dir in 'dlru': dmap[hole][dir] = hole
for x in range(w):
for y in range(h):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['u'] = dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] if x > 0 and dmap[(x - 1, y)]['u'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['l'] = dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] if y > 0 and dmap[(x, y - 1)]['l'] else (x, y)
for x in range(w - 1, -1, -1):
for y in range(h - 1, -1, -1):
if maze[x][y] or (x, y) == hole: continue
dmap[(x, y)]['d'] = dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] if x < w - 1 and dmap[(x + 1, y)]['d'] else (x, y)
dmap[(x, y)]['r'] = dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] if y < h - 1 and dmap[(x, y + 1)]['r'] else (x, y)
bmap = {ball : (0, '', ball)}
vset = set()
distance = lambda pa, pb: abs(pa[0] - pb[0]) + abs(pa[1] - pb[1])
while bmap:
dist, path, p = min(bmap.values())
if p == hole: return path
del bmap[p]
vset.add(p)
for dir in 'dlru':
if dir not in dmap[p]: continue
np = dmap[p][dir]
ndist = dist + distance(p, np)
npath = path + dir
if np not in vset and (np not in bmap or (ndist, npath, np) < bmap[np]):
bmap[np] = (ndist, npath, np)
return 'impossible'
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dists(m, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));
vector<vector<int>> dirs{{0,-1},{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0}};
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({start[0], start[1]});
dists[start[0]][start[1]] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto d : dirs) {
int x = t.first, y = t.second, dist = dists[t.first][t.second];
while (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && maze[x][y] == 0) {
x += d[0];
y += d[1];
++dist;
}
x -= d[0];
y -= d[1];
--dist;
if (dists[x][y] > dist) {
dists[x][y] = dist;
if (x != destination[0] || y != destination[1]) q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
int res = dists[destination[0]][destination[1]];
return (res == INT_MAX) ? -1 : res;
}
};
C++: DFS
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> dirs{{0,-1},{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0}};
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dists(m, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));
dists[start[0]][start[1]] = 0;
helper(maze, start[0], start[1], destination, dists);
int res = dists[destination[0]][destination[1]];
return (res == INT_MAX) ? -1 : res;
}
void helper(vector<vector<int>>& maze, int i, int j, vector<int>& destination, vector<vector<int>>& dists) {
if (i == destination[0] && j == destination[1]) return;
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[0].size();
for (auto d : dirs) {
int x = i, y = j, dist = dists[x][y];
while (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && maze[x][y] == 0) {
x += d[0];
y += d[1];
++dist;
}
x -= d[0];
y -= d[1];
--dist;
if (dists[x][y] > dist) {
dists[x][y] = dist;
helper(maze, x, y, destination, dists);
}
}
}
};
类似题目:
[LeetCode] 499. The Maze III 迷宫 III
All LeetCode Questions List 题目汇总
[LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫 II的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 499. The Maze III 迷宫 III
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- [LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫之二
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- LeetCode 505. The Maze II
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze-ii/ 题目: There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces a ...
- 老鼠走迷宫II
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/holymaple/article/details/8636234 由于迷宫的设计,老鼠走迷宫的入口至出口路径可能不止一条,如何求出所有的路径呢? 解法 ...
- (╭ ̄3 ̄)╭ 小希的迷宫II
(╭ ̄3 ̄)╭ 小希的迷宫II TimeLimit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) MenoryLimit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) 64-b ...
- [LeetCode] 95. Unique Binary Search Trees II(给定一个数字n,返回所有二叉搜索树) ☆☆☆
Unique Binary Search Trees II leetcode java [LeetCode]Unique Binary Search Trees II 异构二叉查找树II Unique ...
- 【python】Leetcode每日一题-反转链表 II
[python]Leetcode每日一题-反转链表 II [题目描述] 给你单链表的头节点 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right .请你反转从位置 ...
- 【LeetCode】522. Longest Uncommon Subsequence II 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]522. Longest Uncommon Subsequence II 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): LeetCode 作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemin ...
- 3299: [USACO2011 Open]Corn Maze玉米迷宫
3299: [USACO2011 Open]Corn Maze玉米迷宫 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 137 Solved: 59[ ...
随机推荐
- AD-logon workstation
默认AD登录到限制为64个 原因 发生此问题的原因是User-Workstations属性的Range-Upper值为1,024个字符.使用Active Directory用户和计算机输入NetBIO ...
- Apache虚拟主机&伪静态配置
Apache基本操作 安装:yum install httpd 启动:systemctl start httpd 查看进程:ps -ef | grep httpd 查看端口:sudo netstat ...
- 《CoderXiaoban》第九次团队作业:Beta冲刺与验收准备
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 任课教师博客主页链接 这个作业的要求在哪里 实验十三 团队作业9:BETA冲刺与团队项目验收 团队名称 Coderxiaoban团队 作业学习目标 (1)掌握软件黑盒 ...
- 【CLAA系列】CLAA 通讯过程
名词: MSP:中兴服务器 CS:客户服务器,也就是我们的服务器 GW:网关,这里默认是中兴的网关 Chip:芯片,这里特指包含了Lora标准通讯模块,且针对CLAA做过特殊优化的芯片. Lora:L ...
- go 学习 (四):接口 & 方法
接口声明 // 接口声明 语法:接口是一个 函数签名 的集合,函数签名(函数的声明,不包括实现) type interfaceName interface { method1(param param ...
- 数论--扩展欧几里得exgcd
算法思想 我们想求得一组\(x,y\)使得 \(ax+by = \gcd(a,b)\) 根据 \(\gcd(a,b) = \gcd(b,a\bmod b)\) 如果我们现在有\(x',y'\) 使得 ...
- redis 设置为只读模式
数据库的只读模式,对于在系统出现重大故障,但是又不影响用户的查询操作还是很重要的 对于redis 设置只读模式需要分不同的场景 master-slave cluster single master-s ...
- 回文数 js 解法
判断一个整数是否是回文数.回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数. 示例 1: 输入: 121 输出: true 示例 2: 输入: -121 输出: false 解释: 从左向 ...
- Time of Trial
Time of Trial(思维) 题目大意:一个人想逃,一个人要阻止那个人逃跑 ,阻止者念每一个符咒的时间为b[i],逃跑者念每一个符咒的时间为a[i],逃跑者如果念完了第i个符咒,阻止者还没有念完 ...
- mysql count() 函数,对结果统计计数
mysql> ; +----------+------------+-----+---------------------+ | name_new | transactor | pid | or ...
