第十一周Java实验作业
实验十一 集合
实验时间 2018-11-8
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API;
Vector类类似长度可变的数组,其中只能存放对象,其中的元素通过下标进行访问。
Vetor类关键属性:
capacity表示集合最多能容纳的元素个数。
capacityIncrement表示每次增加多少容量。
siize集合当前元素个数。
Vector v = new Vector (100);
Stack是Vector的子类。
Stack类描述堆栈数据结构,即LIFO 。
Stack类的关键方法:
public void push(Object item)//把栈压入栈顶
public Object pop()//移除栈顶对象并作为此函数的值返回对象
public Object peek()//查看栈顶对象而不移除它
public boolean empty()//推测堆栈是否为空
Hashtable通过键来查找元素。
Hastable用散列码(hastable)来确定键。所有对象都有有一个散列码,可以通过Object类的hastable()方法获得。
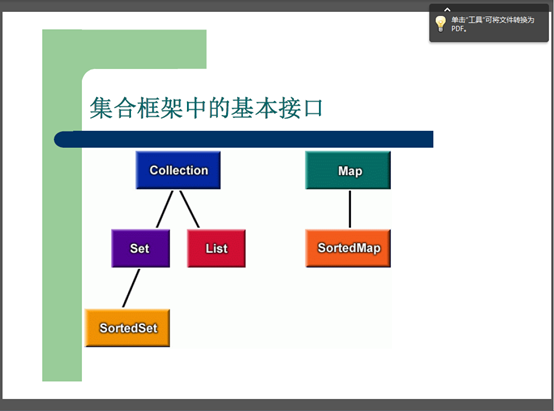
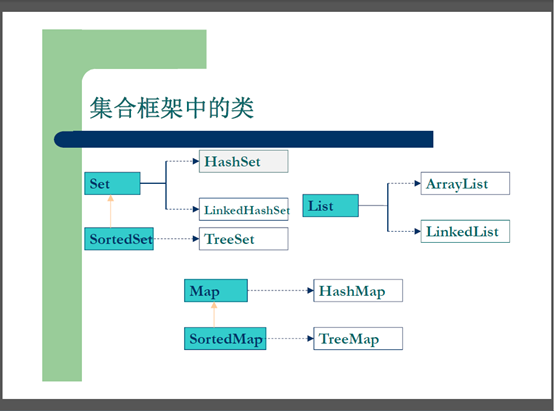
(2) 了解java集合框架体系组成;
(2) 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
ArrayList可以将其看作是能够自动增长容量的数组。
利用ArrayList类的toArray返回一个数组。
Arrays.asList()返回一个列表。
LinkedList是采用双向循环列表实现的。
(4) 了解HashSet类、TreeSet类的用途及常用API。
HashSet() 构造一个空散列表
HashSet(Collection<?extends E>elements) 构造一个散列集,并将集合中的所有元素添加到这个散列集中
HashSet(int initialCapacity) 构造一个空的具有指定容量的(桶数)的散列集。
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)构造一个具有指定容量和装填因子(一个0.0~1.0之间的数值,确定散列表填充的百分比,当大于这个百分比时,散列表进行再散列)的空散列集。
(5)了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API;
Map接口的实现类主要有HashMap,TreeMap,HashTable,Properties。
HashMap对key进行散列。
TreeMap按照key进行排序。
HashMap的速度通常都比TreeMap快,只有在需要排序功能的时候,才使用TreeMap。
(6) 结对编程(Pair programming)练习,体验程序开发中的两人合作。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第9章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 使用JDK命令运行编辑、运行以下三个示例程序,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握Vetor、Stack、Hashtable三个类的用途及常用API。
出现运行时异常,输出Dog #7 时,类型不匹配。附上两种修改方法。
示例程序1:
package 小陈;
import java.util.Vector; class Cat {
private int catNumber; Cat(int i) {
catNumber = i;
} void print() {
System.out.println("Cat #" + catNumber);
}
} class Dog {
private int dogNumber; Dog(int i) {
dogNumber = i;
} void print() {
System.out.println("Dog #" + dogNumber);
}
} public class CatsAndDogs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector cats = new Vector();
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
cats.addElement(new Cat(i));
cats.addElement(new Dog(7));
for (int i = 0; i < cats.size()-1; i++) {
System.out.println(cats.get(i).getClass());//获得类名
//if(cats.get(i).getClass() )
((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print();
}
System.out.println(cats.get(7).getClass());//获得类名
((Dog) cats.elementAt(7)).print();
}
}
/*public class CatsAndDogs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector cats = new Vector();
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
cats.addElement(new Cat(i));
cats.addElement(new Dog(7));
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
System.out.println(cats.get(i).getClass());//获得类名
//if(cats.get(i).getClass() )
((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print();
for ( i = 0; i < cats.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(cats.get(i).getClass());//获得类名
//if(cats.get(i).getClass() )
((Dog) cats.elementAt(i)).print();
}
}
System.out.println(cats.get(7).getClass());//获得类名
((Dog) cats.elementAt(7)).print();
} }*/ /*public class CatsAndDogs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vector cats = new Vector();
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
cats.addElement(new Cat(i));
cats.addElement(new Dog(7));
for (int i = 0; i < cats.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(cats.get(i).getClass());//获得类名
if(cats.elementAt(i) instanceof Cat)
{
((Cat) cats.elementAt(i)).print();
}else {
((Dog) cats.elementAt(i)).print();
}
}
}
}*/
CatsAndDogs
运行结果:

示例程序2:
package 小陈3.src;
import java.util.*;
public class Stacks {
static String[] months = { "1", "2", "3", "4" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stk = new Stack();
for (int i = 0; i < months.length; i++)
stk.push(months[i]);
System.out.println(stk);
System.out.println("element 2=" + stk.elementAt(2));
while (!stk.empty())
System.out.println(stk.pop());
}
}
Stacks
运行结果:

示例程序3:
package 小陈1;
import java.util.*; class Counter {
int i = 1;//不加任何访问权限修饰符,只允许在同一个包中进行访问。 public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(i);
}
} public class Statistics {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();//生成哈希表类对象,哈希表存储的数据是键值
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Integer r = new Integer((int) (Math.random() * 20));
//使用Math.random方法生成整型随机数r,范围是0到20
if (ht.containsKey(r))
//通过对象调用containsKey(),判断r值是否是哈希表里的键值,如果是,返回true,否则返回false
((Counter) ht.get(r)).i++;//获得哈希表里面的键值,引用Counter的属性,输出r出现的频次
else
ht.put(r, new Counter());//调用put方法向哈希表里面添加键值
}
System.out.println(ht);
}
}
Statistics
运行结果:


测试程序3:
l 使用JDK命令编辑运行ArrayListDemo和LinkedListDemo两个程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
package 小陈3;
import java.util.*; public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
ArrayList<Comparable> al = new ArrayList<Comparable>();
// Add lots of elements to the ArrayList...
al.add(new Integer(11));//添加对象元素
al.add(new Integer(12));
al.add(new Integer(13));
al.add(new String("hello"));
// First print them out using a for loop.
System.out.println("Retrieving by index:");
//System.out.println(al.size());//输出al数组的长度
for (int i = 0; i < al.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("Element " + i + " = " + al.get(i));//get方法存放索引值
}
}
}
ArrayListDemo
运行结果:

package 小陈4;
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
LinkedList l = new LinkedList();//构造一个空链表,实质为创建一个数组
l.add(new Object());//调用add方法向链表添加元素
l.add("Hello");
l.add("zhangsan");
ListIterator li = l.listIterator(0);//构造一个迭代器
while (li.hasNext())
//hasNext() 用于检查序列中是否还有元素,如果仍然有元素可以迭代,则返回true,返回迭代的下一个元素
System.out.println(li.next());//next()返回当前next()的一个对象
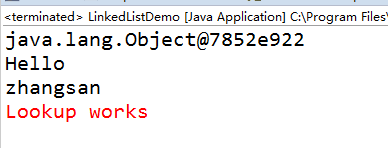
if (l.indexOf("Hello") < 0)
System.err.println("Lookup does not work");
else
System.err.println("Lookup works");
}
}
LinkListDemo.
运行结果:
l 在Elipse环境下编辑运行调试教材360页程序9-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握ArrayList、LinkList两个类的用途及常用API。
package linkedList; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates operations on linked lists.
* @version 1.11 2012-01-26
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class LinkedListTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<String> a = new LinkedList<>();//构造一个空链表,实质为创建一个String类型的数组a
a.add("Amy");//调用add方法向数组添加元素
a.add("Carl");
a.add("Erica"); List<String> b = new LinkedList<>();
b.add("Bob");
b.add("Doug");
b.add("Frances");
b.add("Gloria"); // merge the words from b into a,将a数组的内容合并到b中 ListIterator<String> aIter = a.listIterator();
//使用LinkList类的listIterator方法返回一个实现了listIterator接口的迭代器对象
Iterator<String> bIter = b.iterator(); while (bIter.hasNext())
{
if (aIter.hasNext()) aIter.next();
aIter.add(bIter.next());
} System.out.println(a); // remove every second word from b,从b数组中删除第二个单词 bIter = b.iterator();
while (bIter.hasNext())
{
bIter.next(); // skip one element
if (bIter.hasNext())
{
bIter.next(); // skip next element
bIter.remove(); // remove that element
}
} System.out.println(b); // bulk operation: remove all words in b from a a.removeAll(b); System.out.println(a);
}
}
LinkedListTest

测试程序3:
l 运行SetDemo程序,结合运行结果理解程序;
package 小陈3.src;
import java.util.*;
public class SetDemo {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
HashSet h = new HashSet(); //也可以 Set h=new HashSet()
//构造一个空散列表
h.add("One");
h.add("Two");
h.add("One"); // DUPLICATE
h.add("Three");
Iterator it = h.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
运行结果:

l 在Elipse环境下调试教材365页程序9-2,结合运行结果理解程序;了解HashSet类的用途及常用API。
package set; import java.util.*; /**
* This program uses a set to print all unique words in System.in.
* @version 1.12 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class SetTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Set<String> words = new HashSet<>(); // HashSet implements Set,利用HashSet实现Set接口
long totalTime = 0; try (Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in))
{
while (in.hasNext())
{
String word = in.next();
long callTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
words.add(word);
callTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - callTime;
totalTime += callTime;
}
} Iterator<String> iter = words.iterator();
for (int i = 1; i <= 20 && iter.hasNext(); i++)
System.out.println(iter.next());
System.out.println(". . .");
System.out.println(words.size() + " distinct words. " + totalTime + " milliseconds.");
}
}
SetTest
运行结果:

l 在Elipse环境下调试教材367页-368程序9-3、9-4,结合程序运行结果理解程序;了解TreeSet类的用途及常用API。
package treeSet; import java.util.*; /**
* This program sorts a set of item by comparing their descriptions.
* @version 1.12 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class TreeSetTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SortedSet<Item> parts = new TreeSet<>();//构造一个空树集。
parts.add(new Item("Toaster", 1234));
parts.add(new Item("Widget", 4562));
parts.add(new Item("Modem", 9912));
System.out.println(parts); NavigableSet<Item> sortByDescription = new TreeSet<>(
Comparator.comparing(Item::getDescription)); sortByDescription.addAll(parts);
System.out.println(sortByDescription);
}
}
TreeSet
package treeSet; import java.util.*; /**
* An item with a description and a part number.
*/
public class Item implements Comparable<Item>
{
private String description;
private int partNumber; /**
* Constructs an item.
*
* @param aDescription
* the item's description
* @param aPartNumber
* the item's part number
*/
public Item(String aDescription, int aPartNumber)
{
description = aDescription;
partNumber = aPartNumber;
} /**
* Gets the description of this item.
*
* @return the description
*/
public String getDescription()
{
return description;
} public String toString()
{
return "[description=" + description + ", partNumber=" + partNumber + "]";
} public boolean equals(Object otherObject)
{
if (this == otherObject) return true;
if (otherObject == null) return false;
if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false;
Item other = (Item) otherObject;
return Objects.equals(description, other.description) && partNumber == other.partNumber;
} public int hashCode()
{
return Objects.hash(description, partNumber);
} public int compareTo(Item other)
{
int diff = Integer.compare(partNumber, other.partNumber);
return diff != 0 ? diff : description.compareTo(other.description);
}
}
Item
运行结果:

测试程序4:
l 使用JDK命令运行HashMapDemo程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
package treeSet;
import java.util.*;
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
HashMap h = new HashMap();//构造一个空散列映射
// The hash maps from company name to address.
h.put("Adobe", "Mountain View, CA");//将这些元素插入到映射中
h.put("IBM", "White Plains, NY");
h.put("Sun", "Mountain View, CA");
String queryString = "Adobe";
String resultString = (String)h.get(queryString);
System.out.println("They are located in: " + resultString);
}
}
HashMapDemo
运行结果:

l 在Elipse环境下调试教材373页程序9-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
了解HashMap、TreeMap两个类的用途及常用API。
package map; import java.util.*; /**
* This program demonstrates the use of a map with key type String and value type Employee.
* @version 1.12 2015-06-21
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class MapTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Map<String, Employee> staff = new HashMap<>();//为存储的员工信息建立一个散列映射
staff.put("144-25-5464", new Employee("Amy Lee"));//a将员工信息添加到映射中
staff.put("567-24-2546", new Employee("Harry Hacker"));
staff.put("157-62-7935", new Employee("Gary Cooper"));
staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Cruz")); // print all entries System.out.println(staff); // remove an entry staff.remove("567-24-2546"); // replace an entry staff.put("456-62-5527", new Employee("Francesca Miller")); // look up a value System.out.println(staff.get("157-62-7935")); // iterate through all entries staff.forEach((k, v) ->
System.out.println("key=" + k + ", value=" + v));
}
}
MapTest
package map; /**
* A minimalist employee class for testing purposes.
*/
public class Employee
{
private String name;
private double salary; /**
* Constructs an employee with $0 salary.
* @param n the employee name
*/
public Employee(String name)
{
this.name = name;
salary = 0;
} public String toString()
{
return "[name=" + name + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
}
Employee
运行结果:

实验2:结对编程练习:
l 关于结对编程:以下图片是一个结对编程场景:两位学习伙伴坐在一起,面对着同一台显示器,使用着同一键盘,同一个鼠标,他们一起思考问题,一起分析问题,一起编写程序。
l 关于结对编程的阐述可参见以下链接:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/08/07/2130332.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pair_programming
l 对于结对编程中代码设计规范的要求参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/xinz/archive/2011/11/20/2255971.html
以下实验,就让我们来体验一下结对编程的魅力。
l 确定本次实验结对编程合作伙伴;
l 各自运行合作伙伴实验九编程练习1,结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;
l 各自运行合作伙伴实验十编程练习2,结合使用体验对所运行程序提出完善建议;
l 采用结对编程方式,与学习伙伴合作完成实验九编程练习1;
l 采用结对编程方式,与学习伙伴合作完成实验十编程练习2。
合作伙伴:王燕
合作伙伴的代码:
身份证号文件处理:
package 看到谁;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Check{
private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
studentlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("C:\\下载\\身份证号.txt");//文件读取
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String number = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String province =linescanner.nextLine();
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(name);
student.setnumber(number);
student.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
student.setage(a);
student.setprovince(province);
studentlist.add(student); }
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {//捕获异常
System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
//加入异常处理机制,维护代码的健壮性
boolean isTrue = true;
//选择所要进行的操作
while (isTrue) {
System.out.println("选择你的操作,输入正确格式的选项");
System.out.println("1.按姓名字典序输出人员信息");
System.out.println("2.输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人");
System.out.println("3.查找老乡");
System.out.println("4.查找年龄相近的人");
System.out.println("5.退出");
String m = scanner.next();
switch (m) {
case "1":
Collections.sort(studentlist);
System.out.println(studentlist.toString());
break;
case "2":
int max=0,min=100;
int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++)
{
j=studentlist.get(i).getage();
if(j>max)
{
max=j;
k1=i;
}
if(j<min)
{
min=j;
k2=i;
} }
System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1));
System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2));
break;
case "3":
System.out.println("输入省份");
String find = scanner.next();
String place=find.substring(0,3);
for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++)
{
if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place))
System.out.println("老乡"+studentlist.get(i));
}
break; case "4":
System.out.println("年龄:");
int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
int near=agenear(yourage);
int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage();
System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near));
break;
case "5":
isTrue = false;
System.out.println("退出程序!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误"); }
}
}
public static int agenear(int age) {
int j=0,min=53,value=0,k=0;
for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++)
{
value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age;
if(value<0) value=-value;
if (value<min)
{
min=value;
k=i;
}
}
return k;
} }
Check
package 看到谁;
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> { private String name;
private String number ;
private String sex ;
private int age;
private String province; public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getnumber() {
return number;
}
public void setnumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex ;
}
public void setsex(String sex ) {
this.sex =sex ;
}
public int getage() { return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
// int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
this.age= age;
} public String getprovince() {
return province;
}
public void setprovince(String province) {
this.province=province ;
} public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
}//对姓名进行字典排序 public String toString() {
return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n";
}
}
Student
简易计算器:
package 看到谁;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Caculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Caculator1 computing=new Caculator1();
PrintWriter output = null;
//使用了异常处理机制,增强代码的安全性
try {
output = new PrintWriter("Caculator.txt");
} catch (Exception e) {
}
int sum = 0;
//随机数生成,提供后续题目所用的数据
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int s = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3);
//选择所要进行的操作
switch(s)//s为随机数,可随机执行下面四种操作
{
case 1:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"/"+b+"=");
while(b==0){
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
double c = in.nextDouble();
output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c);
//修改建议:生成除法题目时,对a,b两个数进行条件判断,确保整除,还有除数不为0
if (c == (double)computing.division(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("T");
}
else {
System.out.println("F");
} break;
//
case 2:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"*"+b+"=");
int c1 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1);
if (c1 == computing.multiplication(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("T");
}
else {
System.out.println("F");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"+"+b+"=");
int c2 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2);
if (c2 == computing.addition(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("T");
}
else {
System.out.println("F");
} break ;
case 4:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"-"+b+"=");
int c3 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3);
if (c3 == computing.subtraction(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("T");
}
else {
System.out.println("F");
}
break ; } }
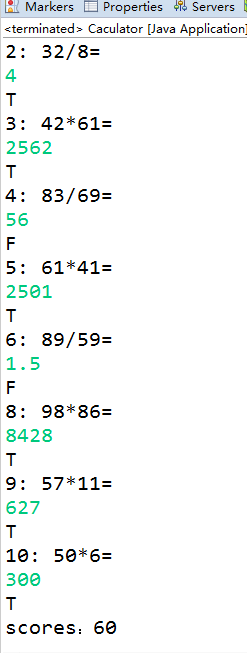
System.out.println("scores:"+sum);
output.println("scores:"+sum);
output.close(); }
}
class Caculator1
{
private int a;
private int b;
public int addition(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
public int subtraction(int a,int b)
{
if((a-b)<0)
return 0;
else
return a-b;
}
public int multiplication(int a,int b)
{
return a*b;
}
public int division(int a,int b)
{
if(b!=0)
return a/b;
else
return 0;
} }
四则运算
合作代码:
身份证号文件处理:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Identity{
private static ArrayList<Student> studentlist;
public static void main(String[] args) {
studentlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("C:/身份证号.txt");
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String number = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String province =linescanner.nextLine();
Student student = new Student();
student.setName(name);
student.setnumber(number);
student.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
student.setage(a);
student.setprovince(province);
studentlist.add(student);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件找不到");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("学生信息文件读取错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean isTrue = true;
while (isTrue) {
System.out.println("选择你的操作,输入正确格式的选项");
System.out.println("1.字典排序");
System.out.println("2.输出年龄最大和年龄最小的人");
System.out.println("3.寻找老乡");
System.out.println("4.寻找年龄相近的人");
System.out.println("0.退出");
int status = scanner.nextInt();
switch (status) {
case 1:
Collections.sort(studentlist);
System.out.println(studentlist.toString());
break;
case 2:
int max=0,min=100;
int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
for(int i=1;i<studentlist.size();i++)
{
j=studentlist.get(i).getage();
if(j>max)
{
max=j;
k1=i;
}
if(j<min)
{
min=j;
k2=i;
} }
System.out.println("年龄最大:"+studentlist.get(k1));
System.out.println("年龄最小:"+studentlist.get(k2));
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("老家?");
String find = scanner.next();
String place=find.substring(0,3);
for (int i = 0; i <studentlist.size(); i++)
{
if(studentlist.get(i).getprovince().substring(1,4).equals(place))
System.out.println("老乡"+studentlist.get(i));
}
break; case 4:
System.out.println("年龄:");
int yourage = scanner.nextInt();
int near=agenear(yourage);
int value=yourage-studentlist.get(near).getage();
System.out.println(""+studentlist.get(near));
break; case 0:
status = 0;
System.out.println("程序已退出!");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入错误");
}
}
}
public static int agenear(int age) {
int min=53,value=0,k=0;
for (int i = 0; i < studentlist.size(); i++)
{
value=studentlist.get(i).getage()-age;
if(value<0) value=-value;
if (value<min)
{
min=value;
k=i;
}
}
return k;
} }
Identity
package 看到谁;
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
private String name;
private String number ;
private String sex ;
private int age;
private String province;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getnumber() {
return number;
}
public void setnumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex ;
}
public void setsex(String sex ) {
this.sex =sex ;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age ) {
this.age=age ;
}
public String getprovince() {
return province;
}
public void setprovince(String province) {
this.province=province ;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student other) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.name.compareTo(other.getName());
}
public String toString() {
return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+number+"\t"+province+"\n";
}
}
Student
运行结果:

简易计算器:
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Caculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Caculator1 computing=new Caculator1();
PrintWriter output = null;
try {
output = new PrintWriter("Caculator.txt");
} catch (Exception e) {
}
int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
int s = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3);
switch(s)
{
case 1:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"/"+b+"=");
while(b==0){
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
}
double c = in.nextDouble();
output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c);
if (c == (double)computing.division(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("T");
}
else {
System.out.println("F");
} break; case 2:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"*"+b+"=");
int c1 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1);
if (c1 == computing.multiplication(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("T");
}
else {
System.out.println("F");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"+"+b+"=");
int c2 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2);
if (c2 == computing.addition(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("T");
}
else {
System.out.println("F");
} break ;
case 4:
System.out.println(i+": "+a+"-"+b+"=");
int c3 = in.nextInt();
output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3);
if (c3 == computing.subtraction(a, b)) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("T");
}
else {
System.out.println("F");
}
break ; } }
System.out.println("scores:"+sum);
output.println("scores:"+sum);
output.close(); }
}
class Caculator1
{
private int a;
private int b;
public int addition(int a,int b)
{
return a+b;
}
public int subtraction(int a,int b)
{
if((a-b)<0)
return 0;
else
return a-b;
}
public int multiplication(int a,int b)
{
return a*b;
}
public int division(int a,int b)
{
if(b!=0 && a%b==0)
return a/b;
else
return 0;
}
}
四则运算
运行结果:
总结:本周主要学习了集合的相关知识,课本上对代码的解释也很少,感觉这一章的代码有点读不懂,还需要继续进行学习,除此之外,本周的实验内容还有结对编程,在阅读了合作伙伴的代码之后,可以从合作伙伴身上学到很多。对
HashMap,HashSet,TreeMap,TreeSet还是不够清楚。
第十一周Java实验作业的更多相关文章
- 第十八周java实验作业
实验十八 总复习 实验时间 2018-12-30 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 综合掌握java基本程序结构: (2) 综合掌握java面向对象程序设计特点: (3) 综合掌握java GUI 程序设 ...
- 第十五周java实验作业
实验十五 GUI编程练习与应用程序部署 实验时间 2018-12-6 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 掌握Java应用程序的打包操作: Java程序的打包,程序编译完成后,程序员将.class文件压缩打 ...
- 第十七周Java实验作业
实验十七 线程同步控制 实验时间 2018-12-10 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术: 多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案:引入线程同步机制,使得另一线程使用该方法,就只 ...
- 第十六周Java实验作业
实验十六 线程技术 实验时间 2017-12-8 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 掌握线程概念: 多线程是进程执行过程中产生的多条执行线索,线程是比进程执行更小的单位. 线程不能独立存在,必须存在于进程 ...
- 第十二周java实验作业
实验十二 图形程序设计 实验时间 2018-11-14 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 掌握Java GUI中框架创建及属性设置中常用类的API: Java的集合框架实现了对各种数据结构的封装. jav ...
- 第十周Java实验作业
实验十 泛型程序设计技术 实验时间 2018-11-1 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 理解泛型概念: 泛型:也称参数化类型,就是在定义类,接口和方法时,通过类型参数只是将要处理的类型对象.(如Arra ...
- 第九周Java实验作业
实验九 异常.断言与日志 实验时间 2018-10-25 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 掌握java异常处理技术: Java的异常处理机制可以控制程序从错误产生的位置转移到能够进行错误处理的位置. Ja ...
- 第八周Java实验作业
实验六 接口的定义与使用 实验时间 2018-10-18 1.实验目的与要求 (1) 掌握接口定义方法: 声明: public interface 接口名 {...} 接口体中包含常量定义和方法定义 ...
- 第七周java实验作业
实验七 继承附加实验实验时间 2018-10-11 1.实验目的与要求 (1)进一步理解4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途: Public 该类或非该类均可访问 Private 只有该类可以访问 Pro ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu18.04安装OpenStack
Ubuntu18.04 安装Queens版本OpenStack 安装环境 系统 系统使用的是Ubuntu18,最少4核8G内存,20G硬盘空间. 工具 devstack DevStack是一系列可扩展 ...
- ES Templates push
{ "order": 0, "template": "connector-connection*", "settings" ...
- runR
Linux下使用R 运行linux下的R脚本 编写R文件 新建后缀名为R的文件 写入R程序 在脚本首行加入 1 运行R文件 这里有两种方式 大专栏 runR进入R的环境">进入R的环 ...
- JNI 问题 wrong ELF class
使用JNI发现一个问题, wrong ELF class: ELFCLASS64)主要是机器是64位的OS,默认编译的.so是64位 而java设置的默认是32位 JDK, 所以会出现这个问题.那么就 ...
- 【简单版】hexo博客搭建流程梳理
前言 本文章会为你梳理一个搭建hexo博客的流程 相关网址: Docs: https://hexo.io/docs/ Themes: https://hexo.io/themes/ 安装hexo 准备 ...
- 给你的Kubernetes集群建一个只读账户(防止高管。。。后)
给你的Kubernetes集群建一个只读账户 需求:我们知道搭完k8s集群会创建一个默认的管理员kubernetes-admin用户该用户拥有所以权限,有一天开发或测试的同学需要登录到k8s集群了解业 ...
- C语言程序设计100例之(31):全排列问题
例31 全排列问题 题目描述 输出自然数1到n所有不重复的排列,即n的全排列,要求所产生的任一数字序列中不允许出现重复的数字. 输入格式 n(1≤n≤9) 输出格式 由1-n组成的所有不重复的数字 ...
- Python安装3 —— Python3.8和2.7共存
本文内容皆为作者原创,如需转载,请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuexianqi/p/12400896.html 一:Python解释器为什么要2个版本? 众所周知,Py ...
- Ubuntu18.04LTS安装docker报错:Command 'lsb_release' not found
Ubuntu18.04LTS安装docker在执行sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/ ...
- Slog62_项目上线之ArthurSlog个人网站上线1
ArthurSlog SLog-62 Year·1 Guangzhou·China September 9th 2018 GitHub NPM Package Page ArthurSlog Page ...
