TensorFlow(十):卷积神经网络实现手写数字识别以及可视化
上代码:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True) #每个批次的大小
batch_size = 100
#计算一共有多少个批次
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size #参数概要
def variable_summaries(var):
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean)#平均值
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev)#标准差
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var))#最大值
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var))#最小值
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var)#直方图 #初始化权值
def weight_variable(shape,name):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1)#生成一个截断的正态分布
return tf.Variable(initial,name=name) #初始化偏置
def bias_variable(shape,name):
initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial,name=name) #卷积层
def conv2d(x,W):
#x input tensor of shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]`
#W filter / kernel tensor of shape [filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]
#`strides[0] = strides[3] = 1`. strides[1]代表x方向的步长,strides[2]代表y方向的步长
#padding: A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,W,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') #池化层
def max_pool_2x2(x):
#ksize [1,x,y,1]
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME') #命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
#定义两个placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope('x_image'):
#改变x的格式转为4D的向量[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]`
x_image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1],name='x_image') with tf.name_scope('Conv1'):
#初始化第一个卷积层的权值和偏置
with tf.name_scope('W_conv1'):
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32],name='W_conv1')#5*5的采样窗口,32个卷积核从1个平面抽取特征
with tf.name_scope('b_conv1'):
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32],name='b_conv1')#每一个卷积核一个偏置值 #把x_image和权值向量进行卷积,再加上偏置值,然后应用于relu激活函数
with tf.name_scope('conv2d_1'):
conv2d_1 = conv2d(x_image,W_conv1) + b_conv1
with tf.name_scope('relu'):
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d_1)
with tf.name_scope('h_pool1'):
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)#进行max-pooling with tf.name_scope('Conv2'):
#初始化第二个卷积层的权值和偏置
with tf.name_scope('W_conv2'):
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64],name='W_conv2')#5*5的采样窗口,64个卷积核从32个平面抽取特征
with tf.name_scope('b_conv2'):
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64],name='b_conv2')#每一个卷积核一个偏置值 #把h_pool1和权值向量进行卷积,再加上偏置值,然后应用于relu激活函数
with tf.name_scope('conv2d_2'):
conv2d_2 = conv2d(h_pool1,W_conv2) + b_conv2
with tf.name_scope('relu'):
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d_2)
with tf.name_scope('h_pool2'):
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)#进行max-pooling #28*28的图片第一次卷积后还是28*28,第一次池化后变为14*14
#第二次卷积后为14*14,第二次池化后变为了7*7
#进过上面操作后得到64张7*7的平面 with tf.name_scope('fc1'):
#初始化第一个全连接层的权值
with tf.name_scope('W_fc1'):
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024],name='W_fc1')#上一场有7*7*64个神经元,全连接层有1024个神经元
with tf.name_scope('b_fc1'):
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024],name='b_fc1')#1024个节点 #把池化层2的输出扁平化为1维
with tf.name_scope('h_pool2_flat'):
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2,[-1,7*7*64],name='h_pool2_flat')
#求第一个全连接层的输出
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b1'):
wx_plus_b1 = tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat,W_fc1) + b_fc1
with tf.name_scope('relu'):
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(wx_plus_b1) #keep_prob用来表示神经元的输出概率
with tf.name_scope('keep_prob'):
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name='keep_prob')
with tf.name_scope('h_fc1_drop'):
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1,keep_prob,name='h_fc1_drop') with tf.name_scope('fc2'):
#初始化第二个全连接层
with tf.name_scope('W_fc2'):
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10],name='W_fc2')
with tf.name_scope('b_fc2'):
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10],name='b_fc2')
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b2'):
wx_plus_b2 = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,W_fc2) + b_fc2
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
#计算输出
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b2) #交叉熵代价函数
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'):
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(labels=y,logits=prediction),name='cross_entropy')
tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy',cross_entropy) #使用AdamOptimizer进行优化
with tf.name_scope('train'):
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) #求准确率
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
#结果存放在一个布尔列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction,1),tf.argmax(y,1))#argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
#求准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy',accuracy) #合并所有的summary
merged = tf.summary.merge_all() with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/train',sess.graph)
test_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/test',sess.graph)
for i in range(1001):
#训练模型
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:0.5})
#记录训练集计算的参数
summary = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:1.0})
train_writer.add_summary(summary,i)
#记录测试集计算的参数
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.test.next_batch(batch_size)
summary = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:1.0})
test_writer.add_summary(summary,i) if i%100==0:
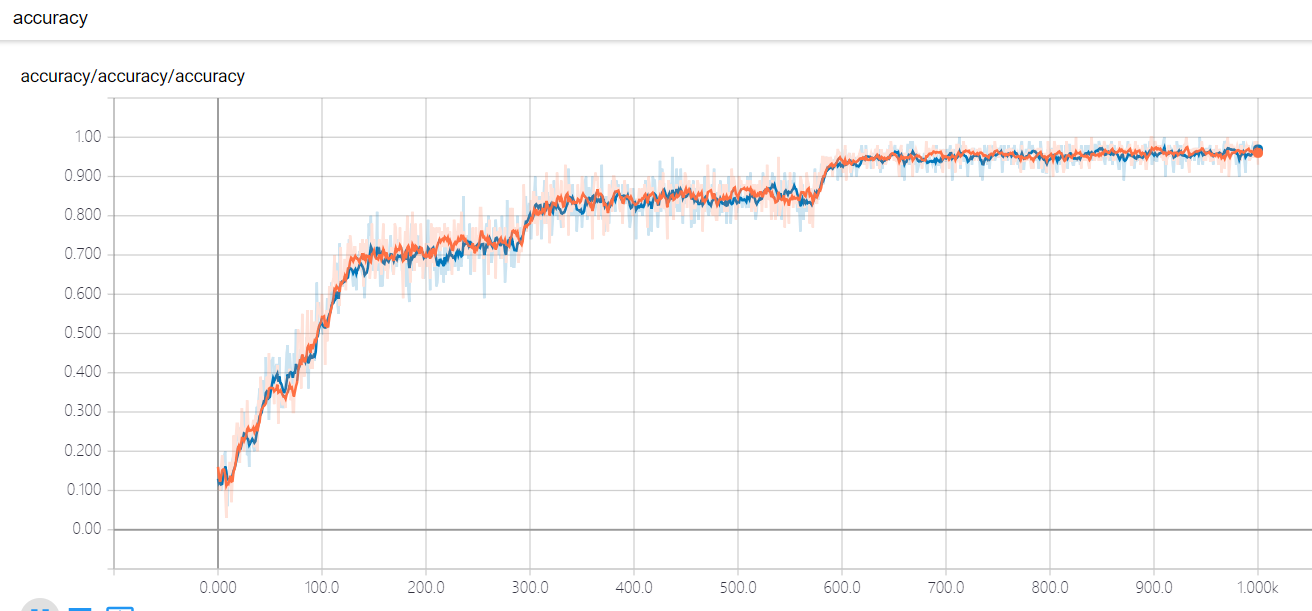
test_acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0})
train_acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.train.images[:10000],y:mnist.train.labels[:10000],keep_prob:1.0})
print ("Iter " + str(i) + ", Testing Accuracy= " + str(test_acc) + ", Training Accuracy= " + str(train_acc))
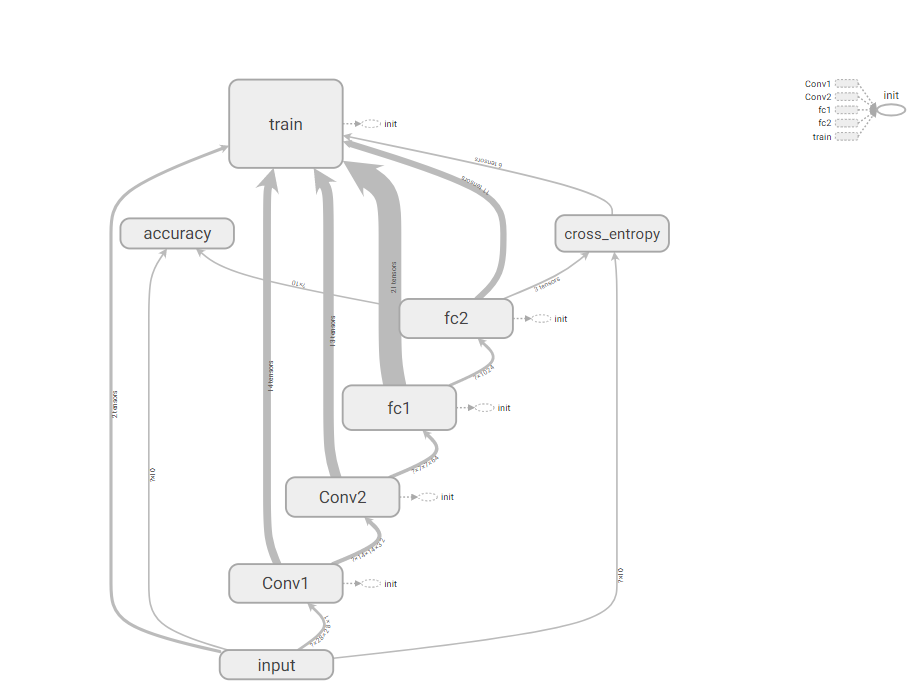
打开cmd,进入当前文件夹,执行tensorboard --logdir='C:\Users\FELIX\Desktop\tensor学习\logs'
就可以进入tensorboard可视化界面了。
TensorFlow(十):卷积神经网络实现手写数字识别以及可视化的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow卷积神经网络实现手写数字识别以及可视化
边学习边笔记 https://www.cnblogs.com/felixwang2/p/9190602.html # https://www.cnblogs.com/felixwang2/p/9190 ...
- 第二节,TensorFlow 使用前馈神经网络实现手写数字识别
一 感知器 感知器学习笔记:https://blog.csdn.net/liyuanbhu/article/details/51622695 感知器(Perceptron)是二分类的线性分类模型,其输 ...
- 卷积神经网络CNN 手写数字识别
1. 知识点准备 在了解 CNN 网络神经之前有两个概念要理解,第一是二维图像上卷积的概念,第二是 pooling 的概念. a. 卷积 关于卷积的概念和细节可以参考这里,卷积运算有两个非常重要特性, ...
- 基于卷积神经网络的手写数字识别分类(Tensorflow)
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_dat ...
- 莫烦pytorch学习笔记(八)——卷积神经网络(手写数字识别实现)
莫烦视频网址 这个代码实现了预测和可视化 import os # third-party library import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch ...
- BP神经网络的手写数字识别
BP神经网络的手写数字识别 ANN 人工神经网络算法在实践中往往给人难以琢磨的印象,有句老话叫“出来混总是要还的”,大概是由于具有很强的非线性模拟和处理能力,因此作为代价上帝让它“黑盒”化了.作为一种 ...
- 利用c++编写bp神经网络实现手写数字识别详解
利用c++编写bp神经网络实现手写数字识别 写在前面 从大一入学开始,本菜菜就一直想学习一下神经网络算法,但由于时间和资源所限,一直未展开比较透彻的学习.大二下人工智能课的修习,给了我一个学习的契机. ...
- TensorFlow.NET机器学习入门【5】采用神经网络实现手写数字识别(MNIST)
从这篇文章开始,终于要干点正儿八经的工作了,前面都是准备工作.这次我们要解决机器学习的经典问题,MNIST手写数字识别. 首先介绍一下数据集.请首先解压:TF_Net\Asset\mnist_png. ...
- 用Keras搭建神经网络 简单模版(三)—— CNN 卷积神经网络(手写数字图片识别)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np np.random.seed(1337) #for reproducibility再现性 from keras.d ...
随机推荐
- ALV报表——选择屏幕选项卡
ALV选择屏幕选项卡 运行效果: 代码: *&--------------------------------------------------------------------* *&a ...
- PB笔记之导入、导出组件
导入组件 导出组件
- 在论坛中出现的比较难的sql问题:46(日期条件出现的奇怪问题)
原文:在论坛中出现的比较难的sql问题:46(日期条件出现的奇怪问题) 最近,在论坛中,遇到了不少比较难的sql问题,虽然自己都能解决,但发现过几天后,就记不起来了,也忘记解决的方法了. 所以,觉得有 ...
- 线程三(Mutex)
C# 中 Mutex 类也是用于线程同步操作的类,例如,当多个线程同时访问一个资源时保证一次只能有一个线程访问资源. 在 Mutex 类中,WaitOne() 方法用于等待资源被释放, Release ...
- Dijkstra+Heap模板
普通Dijkstra: void DijkstraPath(int v0,int vis[],int dist[],int path[]) { int onePath[maxn]; int d; in ...
- MySQL 数据库的安装与卸载
一.安装 (1)打开下载的 mysql 安装文件双击解压缩,运行“mysql-5.5.40-win32.msi” (2)选择安装类型, 有“Typical(默认) ”. “Complete(完全) ” ...
- Fortify漏洞之Access Control: Database(数据越权)
继续对Fortify的漏洞进行总结,本篇主要针对 Access Control: Database(数据越权)的漏洞进行总结,如下: 1.Access Control: Database(数据越权) ...
- 删除MRP单据
select *into newtable from a_mplist 把a_mplist的表中的数据复制到newtable表中结构也是一样的 insert into newtable select ...
- 七、玩转select条件查询
前言: 电商中:我们想查看某个用户所有的订单,或者想查看某个用户在某个时间段内所有的订单,此时我们需要对订单表数据进行筛选,按照用户.时间进行过滤,得到我们期望的结果. 此时我们需要使用条件查询来对指 ...
- cdh的web管理界面503
503 Service Unavailable No server is available to handle this request. 重启 agent 以及 server
